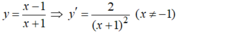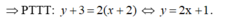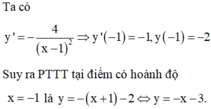Viết phương trình tiếp tuyến của đồ thị hàm số tại điểm M(1;0).
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a, Hệ số góc của tiếp tuyến của đồ thị là:
\(y'\left(2\right)=-4\cdot2+1=-7\)
b, Phương trình tiếp tuyến của đồ thị (C) tại điểm M(2;-6) là:
\(y=y'\left(2\right)\cdot\left(x-2\right)-6=-7\left(x-2\right)-6=-7x+8\)

Đặt \(y=f(x)=x^3+2x^2+x-1 \)
\(f'(x)=3x^2+4x+1\)
Phương trình tiếp tuyến của đồ thị hàm số y tại M là:
\(y=f'(x_m)(x-x_m)+f(x_m)=f'(1)(x-1)+f(1)=8(x-1)+3=8x-5 \)

Ta có: \(y'=3x^2+6x\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y'\left(1\right)=9\\y\left(1\right)=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình tiếp tuyến là: \(y=9\left(x-1\right)+3=9x-6\)

Gọi \(M\left(x_0;y_0\right)\) là tiếp điểm
Ta có: y' \(=\dfrac{-3}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
k=f'\(\left(x_0\right)\)\(\Rightarrow-3=\dfrac{-3}{\left(x_0+1\right)^2}\Leftrightarrow\left(x_0+1\right)^2=1\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_0=0\\x_0=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(x_0=0\) ta có pt tiếp tuyến:
\(d:3x+y-2=0\)
Với \(x_0=-2\) ta có pt tiếp tuyến:
\(d:3x+y+10=0\)
a: Tọa độ giao điểm của (d) với trục Ox là:
y=0 và (-x+2)=0
=>x=2 và y=0
\(y'=\dfrac{\left(-x+2\right)'\left(x+1\right)-\left(-x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)'}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\left(x+1\right)+x-2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{-3}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
Khi x=2 thì y'=-3/(2+1)^2=-3/9=-1/3
y-f(x0)=f'(x0)(x-x0)
=>y-0=-1/3(x-2)
=>y=-1/3x+2/3
b: Tọa độ giao của (d) với trục Oy là;
x=0 và y=(-0+2)/(0+1)=2
Khi x=0 thì \(y'=\dfrac{-3}{\left(0+1\right)^2}=-3\)
y-f(x0)=f'(x0)(x-x0)
=>y-2=-3(x-0)
=>y=-3x+2

f'(x)=y'=-3x^2+2x
f'(2)=-3*2^2+2*2=-3*4+4=-8
f(2)=-2^3+2^2-1=-8-1+4=-9+4=-5
y=f(2)+f'(2)(x-2)
=-5+(-8)(x-2)
=-8x+16-5
=-8x+11

\(y'\left(1\right)=-\dfrac{1}{1^2}=-1\)
Phương trình tiếp tuyến của đồ thị hàm số tại điểm N(1;1) là:
\(y=-1\left(x-1\right)+1=-x+2\)