tìm n là số nguyên để phân thức sau nhận giá trị nguyên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a) Để A là phân số thì : \(n-2\ne0=>n\ne2\)
b) Để A nhận giá trị nguyên âm lớn nhất
\(=>A=-1\\ =>\dfrac{n-6}{n-2}=-1\\ =>n-6=-\left(n-2\right)\\ =>n-6=-n+2\\ =>n+n=6+2\\ =>2n=8\\ =>n=4\left(TMDK\right)\)
c) \(A=\dfrac{n-6}{n-2}=\dfrac{n-2-4}{n-2}=1-\dfrac{4}{n-2}\)
Để A nhận gt số nguyên thì : \(\dfrac{4}{n-2}\in Z=>4⋮\left(n-2\right)\\ =>n-2\inƯ\left(4\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm4\right\}\\ =>n\in\left\{3;1;4;0;6;-2\right\}\)
Đến đây bạn lập bảng giá trị rồi thay từng gt n vào bt A, giá trị nào cho A là STN thì bạn nhận gt đó ạ.
d) Mình nghĩ bạn thiếu đề ạ

Để phân số này là số nguyên thì \(2x-5\in\left\{1;-1;19;-19\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;2;12;-7\right\}\)

\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3x^2-6x+5x-10+14}{x-2}=3x+5+\dfrac{14}{x-2}\in Z\\ \Rightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(14\right)=\left\{-14;-7;-2;-1;1;2;7;14\right\}\\ \Rightarrow x\in\left\{-12;-5;0;1;3;4;9;16\right\}\)
Để phân số này là số nguyên thì \(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;7;-7;14;-14\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;1;4;0;9;-5;16;-12\right\}\)

Để 5n+1/3n+2 nhận giá trị nguyên
thì 5n+1 phải chia hết cho 3n+2
ta có:
5n+1 chia hết 3n+2

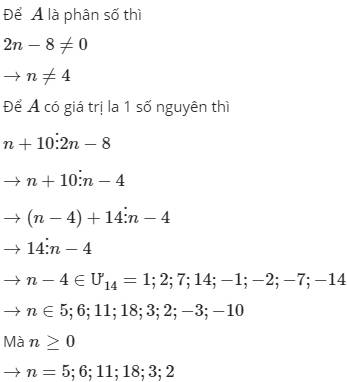
\(C\in Z\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{n-2}{2n+3}\in Z\left(1\right)\\\dfrac{n^2+2n+4}{2n+3}\in Z\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow n-2⋮2n+3\\ \Leftrightarrow2n-4⋮2n+3\\ \Leftrightarrow2n+3\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{-7;-1;1;7\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{-5;-2;-1;2\right\}\left(3\right)\\ \left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow2n^2+4n+8⋮2n+3\\ \Leftrightarrow2n\left(n+3\right)-\left(2n+3\right)+11⋮2n+3\\ \Leftrightarrow2n+3\inƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{-11;-1;1;11\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{-7;-2;-1;4\right\}\left(4\right)\\ \left(3\right)\left(4\right)\Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{-2;-1\right\}\)
Vậy ...