Cho hàm số
với a, b là các số thực và . Tính
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Hàm số a,b là các hàm số logarit
a: \(log_{\sqrt{3}}x\)
Cơ số là \(\sqrt{3}\)
b: \(log_{2^{-2}}x\)
Cơ số là \(2^{-2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)

Ta có công thức hàm số: \(f\left(a+b\right)=f\left(ab\right)\)
Áp dụng ta được:
\(f\left(-2\right)=f\left(-2+0\right)=f\left(-2.0\right)=f\left(0\right)=2013\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2013\right)=f\left(2013+0\right)=f\left(2013.0\right)=f\left(0\right)=2013\)
Vậy f(2013) = 2013

\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x\cdot ln10}\)
=>\(f'\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot ln10}=\dfrac{2}{ln10}\)

tham khảo:
a)\(y'\left(x\right)=5\left(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\right)^4.\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(2\right)-\left(2x-1\right).1}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{10\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)^3}{\left(x+2\right)^4}=\dfrac{20x-50}{\left(x+2\right)^4}\)
b)\(y'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2\left(x^2+1\right)-2x\left(2x\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)^2}\)\(=\dfrac{2\left(1-x^2\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)^2}\)
c)\(y'\left(x\right)=e^x.2sinxcosx+e^xsin^2x.2cosx\)
\(=2e^xsinx\left(cosx+sinxcosx\right)\)
\(=2e^xsinxcos^2x\)
d)\(y'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x\sqrt{x}}.\left(+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}\left(3\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)

Đáp án D
Ta có Đáp án D
Ta có y’ = –f’(1 – x) + 2018 = –[1–(1–x)][(1–x)+2]g(1–x) – 2018 + 2018
= –x(3–x)g(1–x)
Suy ra 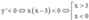 (vì g(1–x) < 0,
∀
x
∈
R
)
(vì g(1–x) < 0,
∀
x
∈
R
)
Vậy hàm số đã cho nghịch biến trên khoảng 3 ; + ∞