giải giúp em bài ni vs ạ, em cảm tạ
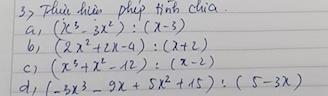
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Bài 5:
\(a,\dfrac{2}{2x-4}=\dfrac{2}{2\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x-2};\dfrac{3}{3x-6}=\dfrac{3}{3\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x-2}\\ b,\dfrac{1}{x+4}=\dfrac{2\left(x-4\right)}{2\left(x+4\right)\left(x-4\right)};\dfrac{1}{2x+8}=\dfrac{x-4}{2\left(x+4\right)\left(x-4\right)}\\ \dfrac{3}{x-4}=\dfrac{6\left(x+4\right)}{2\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}\\ c,\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)};\dfrac{2}{x-1}=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\\ \dfrac{2}{x+1}=\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\\ d,\dfrac{1}{2x}=\dfrac{x-2}{2x\left(x-2\right)};\dfrac{2}{x-2}=\dfrac{4x}{2x\left(x-2\right)};\dfrac{3}{2x\left(x-2\right)}\text{ giữ nguyên}\)
Bài 4:
\(a,\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{x^2-2x}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}\\ \dfrac{x+1}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{1}{x-1}=\dfrac{x}{x\left(x-1\right)}\\ b,\dfrac{x^3-2^3}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+2x+4}{x+2};\dfrac{3}{x+2}\text{ giữ nguyên}\)


Do MN là đường trung bình tam giác ABC \(\Rightarrow MN||AB\) mà \(AB||CD\Rightarrow MN||CD\)
MN và (ABCD) không có điểm chung \(\Rightarrow MN||\left(ABCD\right)\)
MN và (SCD) không có điểm chung \(\Rightarrow MN||\left(SCD\right)\)
MN nằm trên (SAB) nên MN không song song (SAB)
Vậy MN song song với cả (ABCD) và (SCD)

a: Xét ΔABC có \(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2\)
hay ΔABC vuông tại A
Ta có: ΔABC vuông tại A
mà AM là đường trung tuyến ứng với cạnh huyền BC
nên \(AM=\dfrac{BC}{2}=\dfrac{10}{2}=5\left(cm\right)\)

Ta có: \(3x=4y\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{20}=\dfrac{y}{15}\)
\(2y=5z\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{z}{2}\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{15}=\dfrac{z}{6}\)
Áp dụng t/c dtsbn:
\(\dfrac{x}{20}=\dfrac{y}{15}=\dfrac{z}{6}=\dfrac{x+z}{20+6}=\dfrac{52}{26}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=20.2=40\\y=15.2=30\\z=6.2=12\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: \(\dfrac{x^3-3x^2}{x-3}=\dfrac{x^2\left(x-3\right)}{x-3}=x^2\)
b: \(\dfrac{2x^2+2x-4}{x+2}=\dfrac{2\left(x^2+x-2\right)}{x+2}=2\left(x-1\right)=2x-2\)
c: \(\dfrac{x^3+x^2-12}{x-2}=\dfrac{x^3-2x^2+3x^2-6x+6x-12}{x-2}=x^2+3x+6\)
d: \(\dfrac{-3x^3-9x+5x^2+15}{5-3x}=\dfrac{3x^3-5x^2+9x-15}{3x-5}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2\left(3x-5\right)+3\left(3x-5\right)}{3x-5}=x^2+3\)