Cho hai điểm phân biệt A và B. Tìm điểm K sao cho
3 + 2
=
.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a)
Cách 1:
Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {KA} + 2\overrightarrow {KB} = \overrightarrow 0 \).
\( \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {KA} = - 2\overrightarrow {KB} \)
Suy ra vecto \(\overrightarrow {KA} \) và vecto\(\;\overrightarrow {KB} \) cùng phương, ngược chiều và \(KA = 2.KB\)
\( \Rightarrow K,A,B\)thẳng hàng, K nằm giữa A và B thỏa mãn: \(KA = 2.KB\)
Cách 2:
Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {KA} + 2\overrightarrow {KB} = \overrightarrow 0 \).
\(\begin{array}{l} \Leftrightarrow \left( {\overrightarrow {KB} + \overrightarrow {BA} } \right) + 2\overrightarrow {KB} = \overrightarrow 0 \\ \Leftrightarrow 3.\overrightarrow {KB} + \overrightarrow {BA} = \overrightarrow 0 \\ \Leftrightarrow 3.\overrightarrow {KB} = \overrightarrow {AB} \\ \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {KB} = \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {AB} \end{array}\)
Vậy K thuộc đoạn AB sao cho \(KB = \frac{1}{3}AB\).
b)
Với O bất kì, ta có:
\(\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {OA} + \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {OB} = \frac{1}{3}\left( {\overrightarrow {OK} + \overrightarrow {KA} } \right) + \frac{2}{3}\left( {\overrightarrow {OK} + \overrightarrow {KB} } \right) = \left( {\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {OK} + \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {OK} } \right) + \left( {\frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {KA} + \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {KB} } \right) = \overrightarrow {OK} + \frac{1}{3}\left( {\overrightarrow {KA} + 2\overrightarrow {KB} } \right) = \overrightarrow {OK}\)
Vì \(\overrightarrow {KA} + 2\overrightarrow {KB} = \overrightarrow 0 \)
Vậy với mọi điểm O, ta có \(\overrightarrow {OK} = \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {OA} + \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {OB} .\)

a: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là: \(x^2-mx+m-1=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-m\right)^2-4\cdot\left(m-1\right)=m^2-4m+4=\left(m-2\right)^2\)
Để (P) cắt (d) tại hai điểm phân biệt thì m-2<>0
hay m<>2
b: \(\left|x_A-x_B\right|< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-4\left(m-1\right)< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)^2-3< 0\)
=>(m+1)(m-5)<0
=>-1<m<5

Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm:
\(x^2+2mx-3m=-2x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x-3m-3=0\)
Hai đồ thị cắt nhau tại hai điểm phân biệt A, B khi phương trình \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x-3m-3=0\) có hai nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=m^2+5m+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>-1\\m< -4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x=-m-1\pm\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\)
\(x=-m-1+\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\Rightarrow y=2m+5-2\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\)
\(\Rightarrow A\left(-m-1+\sqrt{m^2+5m+4};2m+5-2\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\right)\)
\(x=-m-1-\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\Rightarrow y=2m+5+2\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\)
\(\Rightarrow B\left(-m-1-\sqrt{m^2+5m+4};2m+5+2\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-2\sqrt{m^2+5m+4};4\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{4\left(m^2+5m+4\right)+16\left(m^2+5m+4\right)}=2\sqrt{5\left(m^2+5m+4\right)}=4\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{m^2+5m+4}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+5m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\left(tm\right)\\m=-5\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (d): y = -2x + 3 và
(P) : x2 + 2mx - 3m = 0
x2 + 2mx - 3m = -2x + 3
⇔ x2 + 2(m+1) - 3(m+1) = 0 (*)
Để (d) cắt (P) taị 2 điểm phân biệt thì (*) có hai nghiệm phân biệt. Khi đó Δ' > 0
⇔ (m+1)2 + 3(m+1) > 0
⇔ (m+1)(m+4) > 0
⇔ m ∈ R \ (-4 ; -1) (!)
Do A,B là giao điểm của (d) và (P) nên hoành độ của chúng là nghiệm của (*)
Theo định lí Viet : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_A+x_B=-2m-2=-2\left(m+1\right)\\x_A.x_B=-3m-3=-3\left(m+1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do A,B ∈ d nên hoành độ và tung độ của chúng thỏa mãn
y = -2x + 3 hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y_A=-2x_A+3\\y_B=-2x_B+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để giải được bài này thì mình sẽ sử dụng công thức tính độ dài của vecto AB (nếu bạn chưa học đến thì xin lỗi)
AB = |\(\overrightarrow{AB}\)| = 4\(\sqrt{5}\)
⇒ (xA - xB)2 + (yA - yB)2 = 80
⇒ (xA - xB)2 + (-2xA + 2xB)2 = 80
Sau đó bạn thay m vào rồi biến đổi, kết quả ta được
(m+1)(m+4) = 4 \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)(thỏa mãn (!) )
Vậy tập hợp các giá trị của m thỏa mãn yêu cầu bài toán là
M = {0 ; -5}

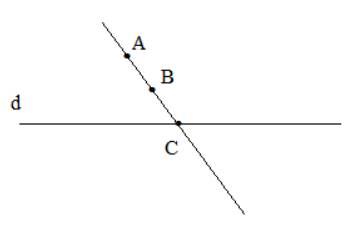
Điểm C là giao điểm của 2 đường thẳng d và AB
Khi AB song song d thì không có điểm C thỏa mãn
Ta có: 3 + 2
+ 2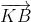 =
= 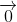 => 3
=> 3 = -2
= -2 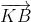 =>
=>  = –
= – 
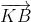
Đẳng thức này chứng tỏ hi vec tơ ,
,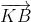 là hai vec tơ ngược hướng, do đó K thuộc đoạn AB
là hai vec tơ ngược hướng, do đó K thuộc đoạn AB
Ta lại có: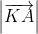 = –
= – 
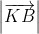 => KA =
=> KA =  KB
KB
Vậy K là điểm chia trong đoạn thẳng AB theo tỉ số