Biết là các điểm cực trị của đồ thị hàm số Tính giá trị của hàm số tại
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a/ \(\left(x+5\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+5=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ........
b/ \(x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c/ \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x+5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+5>0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x< -5\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>-5\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -5\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ..

\(x^3-3x+2-2m=0\)
=>\(2m=x^3-3x+2\)
Chúng ta sẽ vẽ đồ thị \(y=x^3-3x+2\)
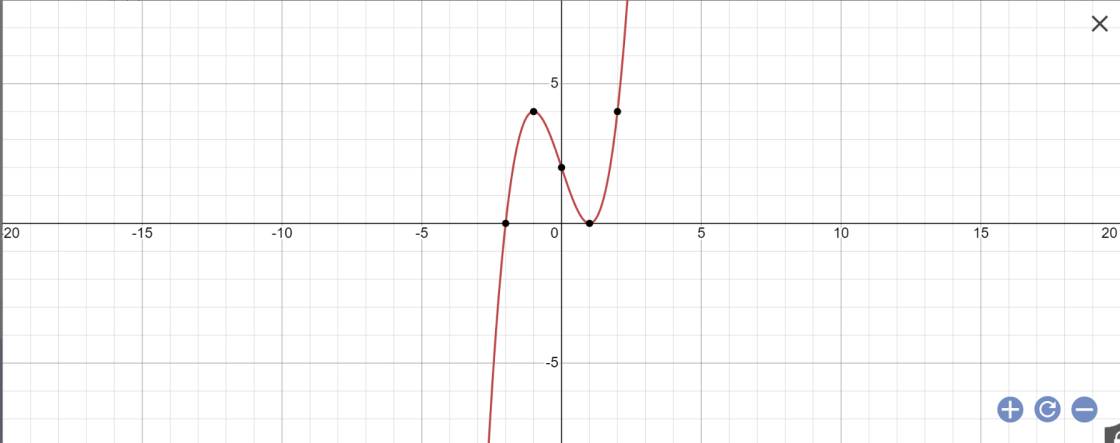
Trên đồ thị, chúng ta sẽ thấy khi \(y\in\left(0;4\right)\) thì \(y=x^3-3x+2\) sẽ cho 3 nghiệm phân biệt
=>\(2m\in\left(0;4\right)\)
=>\(m\in\left(0;2\right)\)
=>Chọn B

Phương trình m x 2 + (3m − 1)x + 2m − 1 = 0 (m 0) có
a = m; b = 3m – 1; c = 2m – 1
Vì a – b + c = m – 3m + 1 + 2m – 1 = 0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm
x 1 = − 1 ; x 2 = 1 − 2 m m
Đáp án: A

\(\frac{m-5}{m+3}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m-5>0\\m+3>0\end{cases}}\) hoặc \(\hept{\begin{cases}m-5< 0\\m+3< 0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>5\\m>-3\end{cases}}\) hoặc \(\hept{\begin{cases}m< 5\\m< -3\end{cases}}\)
=> -3 > m > 5
=.= hk tốt!!
\(\frac{m-5}{m+3}>0\)
th1 :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}m-5>0\\m+3>0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m>5\\m>-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}m>5}\)
th2 :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}m-5< 0\\m+3< 0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}m< 5\\m< -3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}m< 5\left(m\ne-3\right)}\)

1.
Ta thấy $(x-13)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x$
$\Rightarrow T=(x-13)^2-26\geq 0-26=-26$
Vậy GTNN của $T$ là $-26$.
Giá trị này đạt tại $x-13=0\Leftrightarrow x=13$
2.
Ta thấy: $(x-14)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x$
$\Rightarrow M=20-(x-14)^2\leq 20-0=20$
Vậy $M_{\max}=20$. Giá trị này đạt tại $x-14=0$
Hay $x=14$.

1.
Đặt \(x^2-2x+m=t\), phương trình trở thành \(t^2-2t+m=x\)
Ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x+m=t\\t^2-2t+m=x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-t\right)\left(x+t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=t\\x=1-t\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=x^2-2x+m\\x=1-x^2+2x-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-x^2+3x\\m=-x^2+x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của \(y=-x^2+x+1\) và \(y=-x^2+3x\):
\(-x^2+x+1=-x^2+3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Đồ thị hàm số \(y=-x^2+3x\) và \(y=-x^2+x+1\):
Dựa vào đồ thị, yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi \(m< \dfrac{5}{4}\)
Mà \(m\in\left[-10;10\right]\Rightarrow m\in[-10;\dfrac{5}{4})\)
Có cách nào lm bài này bằng cách lập bảng biến thiên k ạ


a) Ta có: \(f\left(0\right)=5\Rightarrow a.0^2+b.0+c=5\)
\(\Rightarrow c=5\)
\(f\left(1\right)=0\Rightarrow a.1^2+b.1+c=0\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b+c=0\left(1\right)\)
Thay \(c=5\) vào (1) được:
\(a+b+5=0\Rightarrow a+b=-5\left(2\right)\)
\(f\left(5\right)=0\Rightarrow a.5^2+5b+c=0\)
\(\Rightarrow25a+5b+c=0\)
\(\Rightarrow5\left(5a+b+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow5a+b+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow5a+b=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow b=-1-5a\left(3\right)\)
Thay \(\left(3\right)\rightarrow\left(2\right):a+\left(-1-5a\right)=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow a-1-5a=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow-1-4a=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow4a=4\)
\(\Rightarrow a=1\)
Khi đó: \(1+b=-5\Rightarrow b=-6\)
Vậy \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=-6\\c=5\end{matrix}\right.\).
b) Kết hợp \(y=-3\) với câu a) ta có:
\(x^2-6x+5=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-3x-3x+5=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-3x-3x+ 9-4=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-3\right)-3\left(x-3\right)-4=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=1\\x-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\).
a) thay f(0) = 5 vào hàm số ta có : \(5=a0^2+b0+c\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(c=5\)
thay f(1) = 0 và f(5) = 0 vào hàm số ta có hệ phương trình
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b+5=0\\25a+5b+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=-5\\25a+5b=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5a+5b=-25\\25a+5b=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}20a=20\\a+b=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\1+b=-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(a=1;b=-6;c=5\)
Đáp án C
y ' = 3 a x 2 + 2 b x + c .
Ta có hệ phương trình
a .0 3 + b .0 2 + c .0 + d = 2 a .2 3 + b .2 2 + c .2 + d = − 2 3 a .0 2 + 2 b .0 + c = 0 3 a .2 2 + 2 b .2 + c = 0 ⇔ a = 1 b = − 3 c = 0 d = 2 .
Vậy hàm số đó là y = x 3 − 3 x 2 + 2. Ta có y − 1 = − 2 .