
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Số tiền Linh dùng mua bút bi:
50000 - 20000 = 30000 (đồng)
Giá tiền mỗi bút chì sau khi giảm:
x - 1000 (đồng)
Phân thức biểu thị số bút chì Linh mua được:

Phân thức biểu thị số bút bi Linh mua được:

b) Với x = 3000, số bút bi Linh mua được:
30000 : 3000 = 10 (bút)

a: ta có: EI⊥BF
AC⊥BF
Do đó: EI//AC
=>\(\hat{IEB}=\hat{ACB}\) (hai góc đồng vị)
mà \(\hat{ABC}=\hat{ACB}\) (ΔABC cân tại A)
nên \(\hat{KBE}=\hat{IEB}\)
Xét ΔKBE vuông tại K và ΔIEB vuông tại I có
BE chung
\(\hat{KBE}=\hat{IEB}\)
Do đó: ΔKBE=ΔIEB
=>EK=BI
b: Điểm D ở đâu vậy bạn?

1: \(\frac{1-a\cdot\sqrt{a}}{1-\sqrt{a}}=\frac{\left(1-\sqrt{a}\right)\left(1+\sqrt{a}+a\right)^{}}{1-\sqrt{a}}=1+\sqrt{a}+a\)
2: \(\frac{\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}}{\sqrt{x+3}-\sqrt{x-3}}=\frac{\left(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}\right)\left(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x+3}-\sqrt{x-3}\right)\left(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}\right)^2}{x+3-\left(x-3\right)}=\frac{x+3+x-3+2\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}}{6}\)
\(=\frac{2x+2\sqrt{x^2-9}}{6}=\frac{x+\sqrt{x^2-9}}{3}\)
4: \(\frac{3}{2\sqrt{9x}}=\frac{3}{2\cdot3\sqrt{x}}=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{2}\)
5: \(\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}=\frac{1\cdot\sqrt{x}}{2\sqrt{x}\cdot\sqrt{x}}=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{2x}\)
7: \(\frac{\sqrt{a^3}+a}{\sqrt{a}-1}=\frac{a\cdot\sqrt{a}+a}{\sqrt{a}-1}=\frac{a\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\sqrt{a}-1}=\frac{a\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{a\left(a+2\sqrt{a}+1\right)}{a-1}=\frac{a^2+2a\cdot\sqrt{a}+a}{a-1}\)
8: \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{2b}}=\frac{2\cdot\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{2b}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{2b}\right)\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{2b}\right)}=\frac{2\sqrt{a}-2\sqrt{2b}}{a-2b}\)
10: \(\frac{25}{\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}}=\frac{25\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\right)}=\frac{25\sqrt{a}+25\sqrt{b}}{a-b}\)
11: \(-\frac{ab}{\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}}=-\frac{ab\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\right)}=\frac{-ab\cdot\sqrt{a}-ab\cdot\sqrt{b}}{a-b}\)

Bài 1:
a: \(A=x^2-4x+9\)
\(=x^2-4x+4+5\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+5\ge5\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
b: \(B=x^2-x+1\)
\(=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac12+\frac14+\frac34\)
\(=\left(x-\frac12\right)^2+\frac34\ge\frac34\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x-\frac12=0\)
=>\(x=\frac12\)
Bài 2:
a: \(M=4x-x^2+3\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
b: \(P=2x-2x^2-5\)
\(=-2\cdot\left(x^2-x+\frac52\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x^2-x+\frac14+\frac94\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x-\frac12\right)^2-\frac92\le-\frac92\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x-\frac12=0\)
=>\(x=\frac12\)
Bài 3:
a: \(A=x^2-4x+24\)
\(=x^2-4x+4+20\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+20\ge20\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
b: \(B=2x^2-8x+1\)
\(=2\left(x^2-4x+\frac12\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2-4x+4-\frac72\right)\)
\(=2\left(x-2\right)^2-7\ge-7\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
c: \(C=3x^2+x-1\)
\(=3\left(x^2+\frac13x-\frac13\right)\)
\(=3\left(x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\frac16+\frac{1}{36}-\frac{13}{36}\right)\)
\(=3\left(x+\frac16\right)^2-\frac{13}{12}\ge-\frac{13}{12}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x+\frac16=0\)
=>\(x=-\frac16\)
Bài 4:
a: \(A=-5x^2-4x+1\)
\(=-5\left(x^2+\frac45x-\frac15\right)\)
\(=-5\left(x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\frac25+\frac{4}{25}-\frac{9}{25}\right)\)
\(=-5\left(x+\frac25\right)^2+\frac95\le\frac95\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x+\frac25=0\)
=>\(x=-\frac25\)
b: \(B=-3x^2+x+1\)
\(=-3\left(x^2-\frac13x-\frac13\right)\)
\(=-3\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac16+\frac{1}{36}-\frac{13}{36}\right)\)
\(=-3\left(x-\frac16\right)^2+\frac{13}{12}\le\frac{13}{12}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x-\frac16=0\)
=>\(x=\frac16\)

\(E=\frac23x^2-\frac54x+1\)
\(=\frac23\left(x^2-\frac{15}{8}x+\frac32\right)\)
\(=\frac23\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac{15}{16}+\frac{225}{256}+\frac{159}{156}\right)\)
\(=\frac23\left(x-\frac{15}{16}\right)^2+\frac{53}{128}\ge\frac{53}{128}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x-\frac{15}{16}=0\)
=>\(x=\frac{15}{16}\)
\(K=-\frac54x^2-2x-1\)
\(=-\frac54\left(x^2+\frac85x+\frac45\right)\)
\(=-\frac54\left(x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\frac45+\frac{16}{25}+\frac{4}{25}\right)\)
\(=-\frac54\left(x+\frac45\right)^2-\frac15\le-\frac15\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x+\frac45=0\)
=>\(x=-\frac45\)

a; ABCD là hình thang cân
=>\(\hat{A}=\hat{B};\hat{C}=\hat{D}\)
\(\hat{A}+\hat{B}=\frac12\left(\hat{C}+\hat{D}\right)\)
=>\(2\cdot\hat{B}=\frac12\left(\hat{C}+\hat{C}\right)=\frac12\cdot2\cdot\hat{C}=\hat{C}\)
Ta có: AB//CD
=>\(\hat{B}+\hat{C}=180^0\)
=>\(\hat{B}+2\cdot\hat{B}=180^0\)
=>\(3\cdot\hat{B}=180^0\)
=>\(\hat{B}=60^0\)
\(\hat{C}=2\cdot\hat{B}=2\cdot60^0=120^0\)
\(\hat{D}=\hat{C}=120^0\)
\(\hat{A}=\hat{B}=60^0\)
b: ΔCAB vuông tại C
=>\(\hat{CAB}+\hat{CBA}=90^0\)
=>\(\hat{CAB}=90^0-60^0=30^0\)
Ta có: tia AC nằm giữa hai tia AD và AB
=>\(\hat{DAC}+\hat{BAC}=\hat{DAB}\)
=>\(\hat{DAC}=60^0-30^0=30^0\)
ta có: \(\hat{DAC}=\hat{BAC}\left(=30^0\right)\)
=>AC là phân giác của góc BAD
c: ta có: DC//AB
=>\(\hat{DCA}=\hat{CAB}\) (hai góc so le trong)
=>\(\hat{DCA}=30^0=\hat{DAC}\)
=>ΔDAC cân tại D
=>DC=DA
=>AD=a
Ta có: ABCD là hình thang cân
=>AD=BC
=>BC=a
Xét ΔCAB vuông tại C có \(\sin BAC=\frac{BC}{AB}\)
=>\(\frac{a}{AB}=\sin30=\frac12\)
=>AB=2a
ΔCAB vuông tại C
=>\(CA^2+CB^2=AB^2\)
=>\(CA^2=\left(2a\right)^2-a^2=3a^2\)
=>\(CA=a\sqrt3\)
Diện tích tam giác DAC là:
\(S_{DAC}=\frac12\cdot DA\cdot DC\cdot\sin ADC=\frac12\cdot a\cdot a\cdot\sin120=\frac{a^2\sqrt3}{4}\)
Diện tích tam giác ACB là:
\(S_{ACB}=\frac12\cdot CA\cdot CB=\frac12\cdot a\sqrt3\cdot a=\frac{a^2\sqrt3}{2}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABCD là:
\(S_{ABCD}=S_{DAC}+S_{CAB}=\frac{a^2\sqrt3}{4}+\frac{a^2\sqrt3}{2}=\frac{3a^2\sqrt3}{4}\)

a: ΔAEH vuông tại E
mà EO là đường trung tuyến
nên EO=OA=OH
=>E nằm trên (O)
ΔADH vuông tại D
mà DO là đường trung tuyến
nên DO=OE=OA
=>D nằm trên (O)
b: ΔDBC vuông tại D
mà DM là đường trung tuyến
nên DM=MB
=>ΔMBD cân tại M
=>\(\hat{MDB}=\hat{MBD}=\hat{DBC}\)
OD=OH nên ΔODH cân tại O
=>\(\hat{ODH}=\hat{OHD}\)
mà \(\hat{OHD}=\hat{AHD}=\hat{ACK}=\hat{DCB}\left(=90^0-\hat{HAC}\right)\)
nên \(\hat{ODH}=\hat{DCB}\)
\(\hat{ODM}=\hat{ODH}+\hat{MDH}\)
\(=\hat{DCB}+\hat{DBC}=90^0\)
=>OD⊥MD tại D
=>MD là tiếp tuyến tại D của (O)
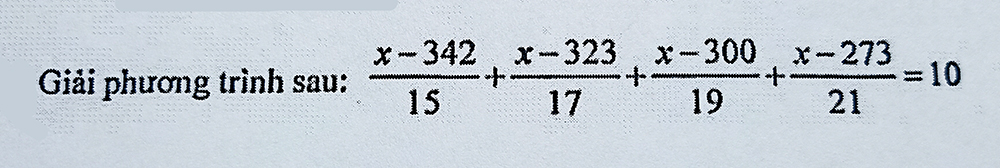









x
−
342
15
+
x
−
323
17
+
x
−
300
19
+
x
−
273
21
=
10
⇔
x
−
342
15
−
1
+
x
−
323
17
−
2
+
x
−
300
19
−
3
+
x
−
273
21
−
4
=
0
⇔
x
−
357
15
+
x
−
357
17
+
x
−
357
19
+
x
−
357
21
=
0
⇔
(
x
−
357
)
(
1
15
+
1
17
+
1
19
+
1
21
)
=
0
Vì
1
15
+
1
17
+
1
19
+
1
21
khác 0 nên x – 357 = 0 hay x = 357.
Vậy x = 357.
\(\dfrac{x-342}{15}+\dfrac{x-323}{17}+\dfrac{x-300}{19}+\dfrac{x-273}{21}=10\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{x-342}{15}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x-323}{17}-2\right)+\left(\dfrac{x-300}{19}-3\right)+\left(\dfrac{x-273}{21}-4\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-357\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{15}+\dfrac{1}{17}+\dfrac{1}{19}+\dfrac{1}{21}\right)=0\)
=>x-357=0
=>x=357