

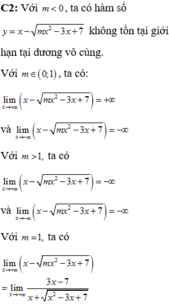


Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


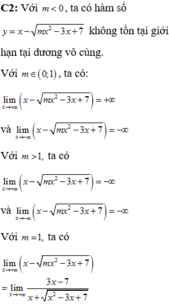



hoành độ giao điểm là nghiệm của pt
\(x^3-3mx^2+3\left(2m-1\right)x+1=2mx-4m+3\Leftrightarrow x^3-3mx^2+4mx-3x-2+4m=0\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x-2-m\left(3x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
giải hệ pt ta có \(C_m\) luôn đi qua điểm A là nghiệm của hệ pt sau
\(\begin{cases}3x^2-4x+4=0\\x^3-3x-2=0\end{cases}\)
ta đc điều phải cm

Đáp án B
Với m=1 ta có y = x + x 2 + x + 1 và lim x → + ∞ y = + ∞ lim x → − ∞ y = − 1 2
=> Đồ thị hàm số có tiệm cận ngang y = − 1 2 .
Với m = − 1 ta có y = − x + x 2 + x + 1 và lim x → + ∞ y = 1 2 lim x → − ∞ y = + ∞
=> Đồ thị hàm số có tiệm cận ngang y = 1 2 .
Với m ≠ ± 1 đồ thị hàm số không có tiệm cận ngang.

Ta có ![]() đồ thị hàm số luôn có TCN y = 1
đồ thị hàm số luôn có TCN y = 1
Do đó để ycbt thỏa mãn 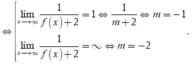
Chọn C.

giả sử : \(\frac{mx+m}{\left(m+1\right)x-m+2}>0\)\(,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{m.0+m}{\left(m+1\right).0-m+2}>0\) \(\Rightarrow\frac{m}{2-m}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow0\)\(<\)\(m<\)\(2\)
ngược lại \(0<\)\(m<2\) thì:
\(mx+m>0,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\left(m+1\right)x\ge0>m-2,\)\(\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(m+1\right)x-m+2>0,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{mx+m}{\left(m+1\right)x-m+2}>0,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
vậy: \(0\)\(<\)\(m<\)\(2\) là kết quả cần tìm