Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{AO}+\overrightarrow{OB}\right|=\left|-5\overrightarrow{i}+\left(-3\right)\overrightarrow{i}\right|=\left|8\overrightarrow{i}\right|=8\).
\(\left|\overrightarrow{BA}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{AB}\right|=8\).
\(\left|\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{AO}+\overrightarrow{OC}\right|=\left|-5\overrightarrow{i}+\left(-4\right)\overrightarrow{i}\right|=\left|9\overrightarrow{i}\right|=9\).
\(\left|\overrightarrow{BC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{BO}+\overrightarrow{OC}\right|=\left|3\overrightarrow{i}+\left(-4\right)\overrightarrow{i}\right|=\left|-\overrightarrow{i}\right|=1\).

A B C D O M N
a)
Các véc tơ cùng phương với \(\overrightarrow{AB}\) là:
\(\overrightarrow{MO};\overrightarrow{OM};\overrightarrow{MN};\overrightarrow{NM};\overrightarrow{NO};\overrightarrow{ON};\overrightarrow{DC};\overrightarrow{CD};\overrightarrow{BA};\overrightarrow{AB}\).
Hai véc tơ cùng hướng với \(\overrightarrow{AB}\) là:
\(\overrightarrow{MO};\overrightarrow{ON}\).
Hai véc tơ ngược hướng với \(\overrightarrow{AB}\) là:
\(\overrightarrow{OM};\overrightarrow{ON}\).
b) Một véc tơ bằng véc tơ \(\overrightarrow{MO}\) là: \(\overrightarrow{ON}\).
Một véc tơ bằng véc tơ \(\overrightarrow{OB}\) là: \(\overrightarrow{DO}\).

a) \(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}=\left(2;-2\right)+\left(1;4\right)=\left(3;2\right)\).
\(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}=\left(2;-2\right)-\left(1;4\right)=\left(1;-6\right)\).
\(2\overrightarrow{a}+3\overrightarrow{b}=2\left(2;-2\right)+3\left(1;4\right)=\left(4;-4\right)+\left(3;12\right)\)\(=\left(7;8\right)\).
c) Gọi x và y là hai số thực để:
\(\overrightarrow{c}=x\overrightarrow{a}+y\overrightarrow{b}=x\left(2;-2\right)+y\left(1;4\right)=\left(2x+y;-2x+4y\right)\)
Từ đó suy ra: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=5\\-2x+4y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\).
Vậy \(\overrightarrow{c}=2\overrightarrow{a}+1\overrightarrow{b}\).

\(\left|\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2=\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)
\(=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2+2\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}\)
\(=5^2+12^2+2.5.12.cos\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)
\(=169+120cos\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{b}\right)=13^2\)
Suy ra: \(cos\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)=0\).
\(\overrightarrow{a}\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\left(\overrightarrow{a}\right)^2+\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=5^2+5.12.0=25\).
Mặt khác \(\overrightarrow{a}\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|.\left|\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right|.cos\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)
\(=5.13.cos\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\).
Vì vậy \(25=5.13.cos\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\).
\(cos\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\dfrac{5}{13}\).
Vậy góc giữa hai véc tơ \(\overrightarrow{a}\) và \(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\) là \(\alpha\) sao cho \(cos\alpha=\dfrac{5}{13}\).

a) \(\overrightarrow{a}=2\overrightarrow{u}+3\overrightarrow{v}=2\left(3;-4\right)+3\left(2;5\right)=\left(6;-8\right)+\left(6;15\right)\)\(=\left(12;7\right)\).
b) \(\overrightarrow{b}=\overrightarrow{u}-\overrightarrow{v}=\left(3;-4\right)-\left(2;5\right)=\left(1;-9\right)\).
c) Hai véc tơ \(\overrightarrow{c}=\left(m;10\right)\) và \(\overrightarrow{v}\) cùng phương khi và chỉ khi:
\(\dfrac{m}{2}=\dfrac{10}{5}=2\Rightarrow m=4\).

TenAnh1
A = (-4.3, -5.94)
A = (-4.3, -5.94)
A = (-4.3, -5.94)
B = (11.06, -5.94)
B = (11.06, -5.94)
B = (11.06, -5.94)
Do các tam giác OAB, OCD, OED, OEF, OFA , OBC cùng là tam giác đều nên OA = OB = OC = OD = OE = OF = 6cm.
Do \(\overrightarrow{i}\) và \(\overrightarrow{OD}\) cùng hướng nên D(6;0), A (0;-6).
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông ta được:\(EC=2.DC.sin60^o=2.6.\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=6\sqrt{3}\).
\(\overrightarrow{EC}\) cùng hướng với \(\overrightarrow{j}\) nên:
Suy ra \(y_B=y_C=3\sqrt{3}\); \(y_E=y_F=-3\sqrt{3}\).
Do BC = 6cm và BC // OD nên \(x_E=x_C=3;x_F=x_B=-3\).
Vậy \(A\left(-6;0\right);D\left(6;0\right);B\left(-3;3\sqrt{3}\right),C\left(3;3\sqrt{3}\right)\);\(E\left(3;-3\sqrt{3}\right)\)\(F\left(-3;-3\sqrt{3}\right)\) .
a)
b) Đáp số: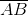 = 3;
= 3; 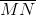 = -5. Từ đây ta có
= -5. Từ đây ta có 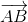 = 3
= 3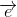 ,
, 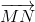 = -5
= -5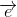 và suy ra
và suy ra 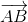 = -
= - 
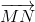 =>
=> 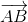 và
và 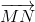 là hai vectơ ngược hướng.
là hai vectơ ngược hướng.