
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Cách 1: Ta có:
y' = 6sin5x.cosx - 6cos5x.sinx + 6sinx.cos3x - 6sin3x.cosx = 6sin3x.cosx(sin2x - 1) + 6sinx.cos3x(1 - cos2x) = - 6sin3x.cos3x + 6sin3x.cos3x = 0.
Vậy y' = 0 với mọi x, tức là y' không phụ thuộc vào x.
Cách 2:
y = sin6x + cos6x + 3sin2x.cos2x(sin2x + cos2x) = sin6x + 3sin4x.cos2x + 3sin2x.cos4x + cos6x = (sin2x + cos2x)3 = 1
Do đó, y' = 0.
b) Cách 1:
Áp dụng công thức tính đạo hàm của hàm số hợp
(cos2u)' = 2cosu(-sinu).u' = -u'.sin2u
Ta được
y' =[sin - sin
] + [sin
- sin
] - 2sin2x = 2cos
.sin(-2x) + 2cos
.sin(-2x) - 2sin2x = sin2x + sin2x - 2sin2x = 0,
vì cos = cos
=
.
Vậy y' = 0 với mọi x, do đó y' không phụ thuộc vào x.
Cách 2: vì côsin của hai cung bù nhau thì đối nhau cho nên
cos2 = cos2
'
cos2 = cos2
.
Do đó
y = 2 cos2 + 2cos2
- 2sin2x = 1 +cos
+ 1 +cos
- (1 - cos2x) = 1 +cos
+ cos
+ cos2x = 1 + 2cos
.cos(-2x) + cos2x = 1 + 2
cos2x + cos2x = 1.
Do đó y' = 0.

tham khảo:
a)\(y'=xsin2x+sin^2x\)
\(y'=sin^2x+xsin2x\)
b)\(y'=-2sin2x+2cosx\\ y'=2\left(cosx-sin2x\right)\)
c)\(y=sin3x-3sinx\)
\(y'=3cos3x-3cosx\)
d)\(y'=\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}-\dfrac{1}{sin^2x}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{sin^2x-cos^2x}{sin^2x.cos^2x}\)

a) Hàm số \(y = \sin 2x + \tan 2x\) có nghĩa khi \(tan 2x\) có nghĩa
\(\cos 2x \ne 0\;\; \Leftrightarrow 2x \ne \frac{\pi }{2}\;\;\;\; \Leftrightarrow x \ne \frac{\pi }{4} + \frac{{k\pi }}{2}\) \
Vây tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\;\backslash \left\{ {\frac{\pi }{4} + \frac{{k\pi }}{2}} \right\}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(f\left( { - x} \right) = \sin \left( { - 2x} \right) + \tan \left( { - 2x} \right) = - \sin 2x - \tan 2x = - \left( {\sin 2x + \tan 2x} \right) = - f\left( x \right),\;\forall x \in D\).
Vậy \(y = \sin 2x + \tan 2x\) là hàm số lẻ
b) Tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(f\left( { - x} \right) = \cos \left( { - x} \right) + {\sin ^2}\left( { - x} \right) = \cos x + {\sin ^2}x = f\left( x \right),\;\forall x \in D\)
Vậy \(y = \cos x + {\sin ^2}x\) là hàm số chẵn
c) Tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(f\left( { - x} \right) = \sin \left( { - x} \right)\cos \left( { - 2x} \right) = - \sin x.\cos 2x = - f\left( x \right),\;\forall x \in D\)
Vậy \(y = \sin x\cos \;2x\) là hàm số lẻ
d) Tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(f\left( { - x} \right) = \sin \left( { - x} \right) + \cos \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x + \cos x \ne f\left( x \right),\;\forall x \in D\)
Vậy \(y = \sin x + \cos x\) không là hàm số chẵn cũng không là hàm số lẻ

a/ \(\Leftrightarrow2cosx.cos2x=cos2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cosx.cos2x-cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos2x\left(2cosx-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=0\\cosx=\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\x=\pm\frac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{4}+\frac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\pm\frac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
b/ \(\Leftrightarrow2sinx.sin2x=sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sinx.sin2x-sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(2sin2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=0\\sin2x=\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\2x=\frac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\2x=\frac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\x=\frac{\pi}{12}+k\pi\\x=\frac{5\pi}{12}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
c/ \(\Leftrightarrow sin3x-sinx+sin4x-sin2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos2x.sinx+2cos3x.sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(cos2x+cos3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sinx.2cos\frac{5x}{2}.cos\frac{x}{2}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=0\\cos\frac{5x}{2}=0\\cos\frac{x}{2}=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\\frac{5x}{2}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\\frac{x}{2}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\x=\frac{\pi}{5}+\frac{k4\pi}{5}\\x=\pi+k4\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
d/ \(\Leftrightarrow sin3x-sinx-\left(sin4x-sin2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos2x.sinx-2cos3x.sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(cos2x-cos3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=0\\cos2x=cos3x\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\2x=3x+k2\pi\\2x=-3x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k\pi\\x=\frac{k2\pi}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Dễ thấy cosx = 0 không thỏa mãn phương trình đã cho nên chiaw phương trình cho cos2x ta được phương trình tương đương 2tan2x + tanx - 3 = 0.
Đặt t = tanx thì phương trình này trở thành
2t2 + t - 3 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {1 ; ![]() }.
}.
Vậy ![]()
b) Thay 2 = 2(sin2x + cos2x), phương trình đã cho trở thành
3sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 5cos2x = 2sin2x + 2cos2x
⇔ sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 3cos2x = 0
⇔ tan2x - 4tanx + 3 = 0
⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
c) Thay sin2x = 2sinxcosx ; ![]() =
= ![]() (sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
(sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
![]() sin2x + 2sinxcosx -
sin2x + 2sinxcosx - ![]() cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔
cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
d) 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x - 4sin2x = -4
⇔ 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x + 4 - 4sin2x = 0
⇔ 6cos2x - 6√3sinxcosx = 0 ⇔ cosx(cosx - √3sinx) = 0
⇔ 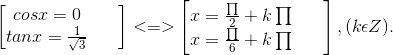

\(a,sin2x-2sinx+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sinxcosx-2sinx+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sinx\left(cosx-1\right)+cosx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-1\right)\left(2sinx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}cosx=1\\sinx=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2k\pi\\x=\frac{-\pi}{6}+2k\pi\end{cases}}}\)
\(b,\sqrt{2}\left(sinx-2cosx\right)=2-sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sinx-2\sqrt{2}cosx-2+2sinxcosx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sinx\left(1+\sqrt{2}cosx\right)-2.\left(\sqrt{2}cosx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{2}cosx+1\right)\left(\sqrt{2}sinx-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}cosx=\frac{-\sqrt{2}}{2}\\sinx=\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(l\right)\end{cases}}\)(vì \(-1\le sinx\le1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3\pi}{4}+2k\pi\\x=\frac{5\pi}{4}+2k\pi\end{cases}}\)
\(c,\frac{1}{cosx}-\frac{1}{sinx}=2\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{sinx-cosx}{sinx.cosx}=2\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)}{sinx.cosx}=2\sqrt{2}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin2x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\frac{3\pi}{2}+2k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3\pi}{4}+k\pi\)
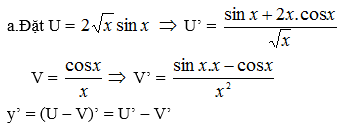
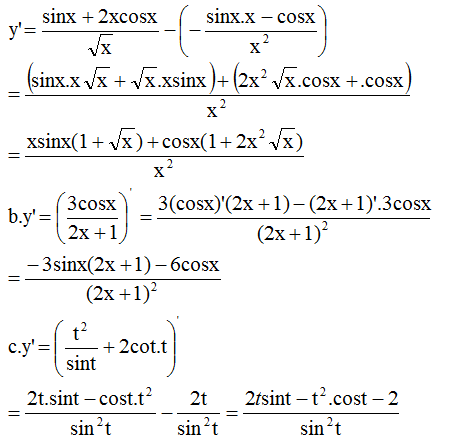
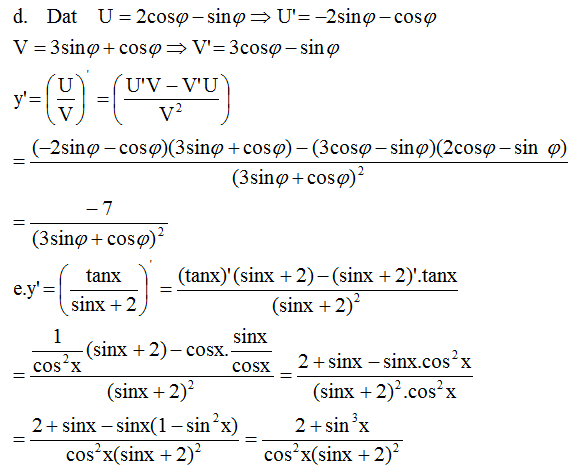
Chọn A.
Áp dụng u / , với u = sin x + 2 x
y ' = sin x + 2 x / 2 sin x + 2 x = cos x + 2 2 sin x + 2 x .