
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


x,y là số nguyên tố đúng ko? bn có nhiueeuf câu hỏi nên mik trả lời nhầm.(ko phait thì thui nhé)
\(\left(3x^2+6x+3\right)+\left(3y^2+3y+1\right)+y^2-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+1\right)^2+3\left(y+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{9}{4}-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\left(x+1\right)^2+3\left(y+1\right)^2=41\)
\(\Rightarrow12\left(x+1\right)^2\le41\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\le3\Rightarrow x+1\in\left\{1;0;-1\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;-1;-2\right\}\)
Bạn làm nốt

\(Pt\Leftrightarrow3x^2+12x+4y^2+3y+5=0\)
Coi pt trên là pt bậc 2 ẩn x
Ta có : \(\Delta'=36-12y^2-9y-15\)
\(=-12y^2-9y+21\)
Pt có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=-12y^2-9y+21\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\frac{7}{4}\le y\le1\)
Mà \(y\inℤ\Rightarrow y\in\left\{-1;0;1\right\}\)
Rồi làm nốt

\(3\left(x+1\right)^2=-4y^2-3y+7\)
\(\Rightarrow-4y^2-3y+7\ge0\Rightarrow-\frac{7}{4}\le y\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\left\{-1;0;1\right\}\)
- Với \(y=-1\Rightarrow3\left(x+1\right)^2=6\Rightarrow\) ko có x nguyên t/m
- Với \(y=0\Rightarrow3\left(x+1\right)^2=7\) ko có x nguyên t/m
- Với \(y=1\Rightarrow3\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)

Với câu a)bạn nhân cả 2 vế cho 12 rồi ép vào dạng bình phương 3 số
Câu b)bạn nhân cho 8 mỗi vế rồi ép vào bình phương 3 số

a) \(5x-3y=2xy-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2xy-5x+3y-11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4xy-10x+6y-22=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(2y-5\right)+3\left(2y-5\right)=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\left(2y-5\right)=7=1.7=\left(-1\right).\left(-7\right)\)
Xét các TH sau:
Nếu \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x+3=1\\2y-5=7\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-1\\y=6\end{cases}}\)
Nếu \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x+3=7\\2y-5=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2\\y=3\end{cases}}\)
Nếu \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x+3=-1\\2y-5=-7\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-2\\y=-1\end{cases}}\)
Nếu \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x+3=-7\\2y-5=-1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-5\\y=2\end{cases}}\)
KL:...


a) (I): 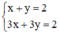
Xét (d): x + y = 2 hay (d): y = -x + 2 có a = -1; b = 2.
(d’) 3x + 3y = 2 hay (d’): y = -x + 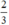 có a’ = -1 ; b’ =
có a’ = -1 ; b’ = 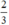
Ta có: a = a’ ; b ≠ b’ ⇒ (d) // (d’)
⇒ Hệ (I) vô nghiệm.
b) (II): 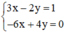
Xét: (d): 3x – 2y = 1 hay (d):
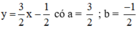
(d’): -6x + 4y = 0 hay (d’):
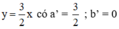
Ta có: a = a’ ; b ≠ b’ ⇒ (d) // (d’)
⇒ Hệ (II) vô nghiệm.
Kiến thức áp dụng
+ Xét hệ (I): 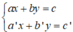
Gọi (d): ax + by = c và (d’): a’x + b’y = c’.
Số nghiệm của hệ (I) phụ thuộc vào vị trí tương đối của (d) và (d’).
(d) cắt (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) có nghiệm duy nhất.
(d) // (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) vô nghiệm
(d) ≡ (d’) ⇒ hệ (I) có vô số nghiệm.
+ Cho đường thẳng (d): y = ax + b và (d’): y = a’x + b’.
(d) cắt (d’) ⇔ a ≠ a’
(d) // (d’) ⇔ a = a’ và b ≠ b’
(d) trùng (d’) ⇔ a = a’ và b = b’.

\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+1\right)^2+4y^2+3y-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4y^2+3y-7=-3\left(x+1\right)^2\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow4y^2+3y-7\le0\Rightarrow-\frac{7}{4}\le y\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\left\{-1;0;1\right\}\)
Thay lần lượt y vào pt ban đầu thấy chỉ có \(y=1\) thỏa mãn, khi đó \(x=-1\)
cảm ơn bn nhìu nhoaaa