Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Tìm MTC:
2x + 6 = 2(x + 3)
x2 – 9 = (x – 3)(x + 3)
MTC = 2(x – 3)(x + 3) = 2(x2 – 9)
Nhân tử phụ:
2(x – 3)(x + 3) : 2(x + 3) = x – 3
2(x – 3)(x + 3) : (x2 – 9) = 2
Qui đồng:
b) Tìm MTC:
x2 – 8x + 16 = (x – 4)2
3x2 – 12x = 3x(x – 4)
MTC = 3x(x – 4)2
Nhân tử phụ:
3x(x – 4)2 : (x – 4)2 = 3x
3x(x – 4)2 : 3x(x – 4) = x – 4
Qui đồng:

a: \(\dfrac{5}{2x+6}=\dfrac{5\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
3/x^2-9=6/2(x+3)(x-3)
b: \(\dfrac{2x}{x^2-8x+16}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-4\right)^2}=\dfrac{6x^2}{3x\left(x-4\right)^2}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{3x^2-12x}=\dfrac{x}{3x\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x-4\right)}{3x\left(x-4\right)^2}\)
c: \(\dfrac{x+y}{x}=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)\cdot\left(x-y\right)}{x\left(x-y\right)}\)
x/x-y=x^2/x(x-y)
e: \(\dfrac{1}{x+2}=\dfrac{2x-x^2}{x\left(x+2\right)\left(2-x\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{8}{2x-x^2}=\dfrac{8\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}\)

a) Tìm MTC: x3 – 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nên MTC = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nhân tử phụ:
(x3 – 1) : (x3 – 1) = 1
(x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) : (x2 + x + 1) = x – 1
(x – 1)(x2+ x + 1) : 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Qui đồng:
b) Tìm MTC: x + 2
2x – 4 = 2(x – 2)
6 – 3x = 3(2 – x)
MTC = 6(x – 2)(x + 2)
Nhân tử phụ:
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : (x + 2) = 6(x – 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : 2(x – 2) = 3(x + 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : -3(x – 2) = -2(x + 2)
Qui đồng:

Bài 7:(Sbt/25) Dùng tính chất cơ bản của phân thức hoặc quy tắc đổi dấu để biến mỗi cặp phân thức sau thành một cặp phân thức bằng nó và có cùng mẫu thức :
a. \(\dfrac{3x}{x-5}\) và \(\dfrac{7x+2}{5-x}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{3x}{x-5}=\dfrac{-\left(3x\right)}{-\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{-3x}{5-x}\)
\(\dfrac{7x+2}{5-x}\)
Vậy .....
b.\(\dfrac{4x}{x+1}\) và \(\dfrac{3x}{x-1}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{4x}{x+1}=\dfrac{4x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{4x^2-4x}{x^2-1}\)
\(\dfrac{3x}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3x^2+3x}{x^2-1}\)
Vậy ..........
c. \(\dfrac{2}{x^2+8x+16}\) và \(\dfrac{x-4}{2x+8}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2+8x+16}=\dfrac{4}{2\left(x+4\right)^2}\)
\(\dfrac{x-4}{2x+8}=\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}{2\left(x+4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-16}{2\left(x+4\right)^2}\)
Vậy .........
d. \(\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\) và \(\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2-4x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-9}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
Vậy .........

a) \(\dfrac{3x}{2x+4}\) và \(\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-4}\)
Phân tích các mẫu thức thành nhân tử :
\(2x+4 = 2(x+2)\)
\(x^2 - 4 = (x-2)(x+2)\)
MTC : \(2(x+2)(x-2)\)
Nhân tử phụ của mẫu thức : \(2x + 4\) là \((x - 2)\)
\(x^2 - 4\) là \(2\)
QĐ: \(\dfrac{3x}{2x+4}=\dfrac{3x}{2\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{3x\left(x-2\right)}{2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+3\right)}{2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
b) \(\dfrac{x+5}{x^2+4x+4}\) và \(\dfrac{x}{3x+6}\)
Phân tích các mẫu thức thành nhân tử :
\(x^2+4x+4 = (x+2)^2\)
\(3x + 6\) \(= 3(x+2)\)
MTC : \(3(x+2)^2\)
Nhân tử phụ của mẫu thức : \(x^2 + 4x +4 \) là \(3\)
\(3x + 6\) là \((x+2)\)
QĐ : \(\dfrac{x+5}{x^2+4x+4}=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2}=\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{3x+6}=\dfrac{x}{3\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}\)

Bài giải
a) \(\dfrac{1}{x+2}=\dfrac{x.\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right).x}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{8}{2x-x^2}=\dfrac{8}{x\left(2-x\right)}=-\dfrac{8}{x\left(x-2\right)}=-\dfrac{8.\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
b) \(x^2+1=\dfrac{x^2+1}{1}=\dfrac{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{x^4-1}{x^2-1}\)
\(\dfrac{x^4}{x^2-1}\) giữ nguyên.
c) \(\dfrac{x^3}{x^3-3x^2y+3xy^2-y^3}=\dfrac{x^3}{\left(x-y\right)^3}=\dfrac{x^3.y}{\left(x-y\right)^3.y}=\dfrac{x^3y}{y\left(x-y\right)^3}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{y^2-xy}=\dfrac{x}{y.\left(y-x\right)}=-\dfrac{x}{y.\left(x-y\right)}=-\dfrac{x\left(x-y\right)^2}{y.\left(x-y\right).\left(x-y\right)^2}=\dfrac{x\left(x-y\right)^2}{y.\left(x-y\right)^3}\)
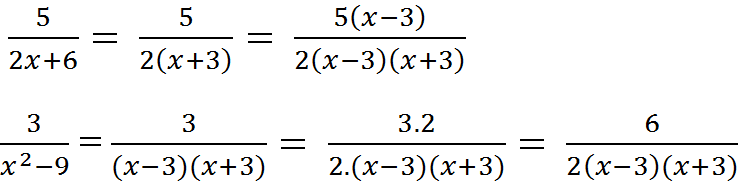
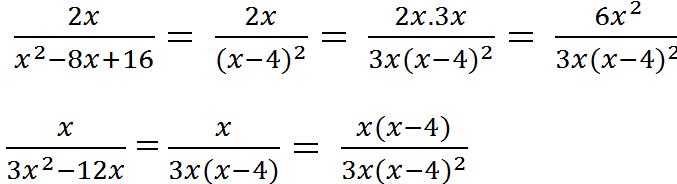



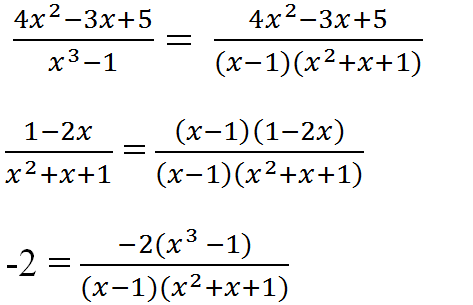
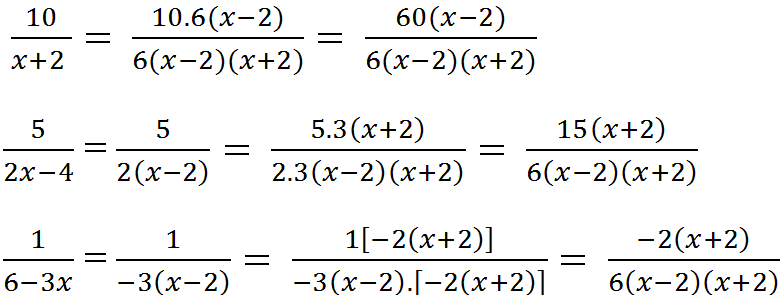


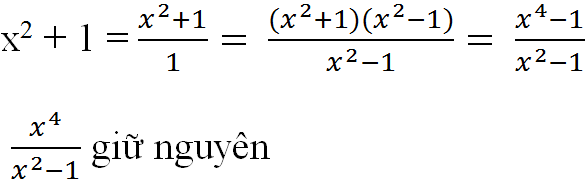
x2-8x+16=(x+4)2
3x2-12x=3x(x-4)
MTC: 3x(x-4)2
\(\dfrac{2x}{x^2-8x+16}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-4\right)^2}=\dfrac{2x.3x}{\left(x-4\right)^2.3x}=\dfrac{6x^2}{3x\left(x-4\right)^2}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{3x^2-12x}=\dfrac{x}{3x\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{x.\left(x-4\right)}{3x\left(x-4\right)\left(x-4\right)}\)