Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

(Lưu ý: Các phần giải thích các bạn có thể không trình bày vào bài làm)
2 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 5 x = − 2
(Chuyển 2 sang vế phải)
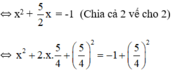
(Tách 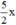 thành
thành 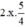 và thêm bớt
và thêm bớt 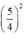 để vế trái thành bình phương).
để vế trái thành bình phương).
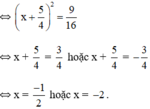
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm 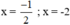

(Lưu ý: Các phần giải thích các bạn có thể không trình bày vào bài làm)
2x2 + 5x + 2 = 0
⇔ 2x2 + 5x = -2 (Chuyển 2 sang vế phải)
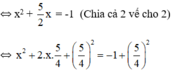
(Tách 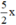 thành
thành 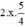 và thêm bớt
và thêm bớt 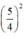 để vế trái thành bình phương).
để vế trái thành bình phương).
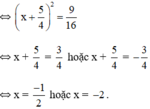
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm 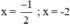

\(2x^2+5x+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2+5x+\frac{50}{16}-\frac{18}{16}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x^2+2.\frac{5}{4}x+\frac{25}{16}\right)=\frac{9}{8}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+\frac{5}{4}\right)^2=\frac{9}{16}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{5}{4}=\frac{3}{4}\\x+\frac{5}{4}=\frac{-3}{4}\end{cases}}\)\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{2}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Ta có :
\(2x^2+5x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+5x=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+\frac{5}{2}x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2.x.\frac{5}{4}=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2.x.\frac{5}{4}+\left(\frac{5}{4}\right)^2=-1+\left(\frac{5}{4}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\frac{5}{4}\right)^2=-1+\frac{25}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\frac{5}{4}\right)^2=\frac{9}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{5}{4}=\frac{3}{4}\\x+\frac{5}{4}=-\frac{3}{4}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{2}\\x=-2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có hai nghiệm là........

a) Phương trình 4x2 + 2x – 5 = 0 có nghiệm vì a = 4, c = -5 trái dấu nhau nên
x1 + x2 = \(-\dfrac{1}{2}\), x1x2 = \(-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
b) Phương trình 9x2 – 12x + 4 = 0 có ∆' = 36 - 36 = 0
x1 + x2 = \(\dfrac{12}{9}\) = \(\dfrac{4}{3}\), x1x2 = \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)
c) Phương trình 5x2+ x + 2 = 0 có ∆ = 12 - 4 . 5 . 2 = -39 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm, nên không tính được tổng và tích các nghiệm.
d) Phương trình 159x2 – 2x – 1 = 0 có hai nghiệm phân biệt vì a và c trái dấu
x1 + x2 = \(\dfrac{2}{159}\), x1x2 = \(-\dfrac{1}{159}\)
a) Phương trình 4x2 + 2x – 5 = 0 có nghiệm vì a = 4, c = -5 trái dấu nhau nên
x1 + x2 = , x1x2 =
b) Phương trình 9x2 – 12x + 4 = 0 có ∆' = 36 - 36 = 0
x1 + x2 = =
, x1x2 =
c) Phương trình 5x2+ x + 2 = 0 có ∆ = 12 - 4 . 5 . 2 = -39 < 0
Phương trình vô nghiệm, nên không tính được tổng và tích các nghiệm.
d) Phương trình 159x2 – 2x – 1 = 0 có hai nghiệm phân biệt vì a và c trái dấu
x1 + x2 = , x1x2 =

a, 2x2+5x-3=0
<=> 2x2+6x-x-3=0
<=> 2x(x+3)-(x+3)=0
<=> (x+3)(2x-1)=0
\(=>\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\2x-1=0\end{cases}=>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy...
a, 2x2+5x-3=0
<=> 2x2+6x-x-3=0
<=> 2x(x+3)-(x+3)=0
<=>(x+3)(2x-1)=0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}}\)



#)Sửa đề : x4+2x3+5x2+4x-12=0
#)Giải :
\(x^4+2x^3+5x^2+4x-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-x^3\right)+\left(3x^3-3x^2\right)+\left(8x^2-8x\right)+\left(12x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+8x+12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x^3+2x^2\right)+\left(x^2+2x\right)+\left(6x+12\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)

Ta có : \(2x^4-5x^3-27x^2+25x+50=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+2x^3-10x^2-7x^3-7x^2+35x-10x^2-10x+50=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x^2+x-5\right)-7x\left(x^2+x-5\right)-10\left(x^2+x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x-5\right)\left(2x^2-7x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+x-5=0\\2x^2-7x-10=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt{21}}{2}\\x=\frac{7\pm\sqrt{129}}{4}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là : \(S=\left\{\frac{-1-\sqrt{21}}{2};\frac{7-\sqrt{129}}{4};\frac{-1+\sqrt{21}}{2};\frac{7+\sqrt{129}}{4}\right\}\)

Bài giải
2x2 + 5x + 2 = 0 ⇔ 2x2 + 5x = -2 ⇔ x2 + x = -1
x = -1
⇔ x2 + 2 . x . +
+ 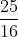 = -1 +
= -1 + 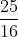 ⇔ (x +
⇔ (x +  )2 =
)2 = 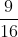
=> x + =
=  => x =
=> x = 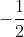
Hoặc x + =
= 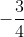 => x = -2.
=> x = -2.