6/x-3 =9/2x-7
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) (x+6)(3x-1)+x+6=0
⇔(x+6)(3x-1)+(x+6)=0
⇔(x+6)(3x-1+1)=0
⇔3x(x+6)=0
2) (x+4)(5x+9)-x-4=0
⇔(x+4)(5x+9)-(x+4)=0
⇔(x+4)(5x+9-1)=0
⇔(x+4)(5x+8)=0
3)(1-x)(5x+3)÷(3x-7)(x-1)
=\(\frac{\left(1-x\right)\left(5x+3\right)}{\left(3x-7\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{\left(1-x\right)\left(5x+3\right)}{\left(7-3x\right)\left(1-x\right)}=\frac{\left(5x+3\right)}{\left(7-3x\right)}\)

Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\left(2x+1\right)-\left(2x+5\right)\left(2x+7\right)=1-\left(6x^2+9x-9\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+2x+6x+3-\left(4x^2+14x+10x+35\right)=1-6x^2-9x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+8x+3-4x^2-24x-35-1+6x^2+9x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-7x-42=0\)
\(\Delta=49-4\cdot6\cdot\left(-42\right)=1057\)
Vì \(\Delta>0\) nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{1057}}{12}\\x_2=\dfrac{7+\sqrt{1057}}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{7-\sqrt{1057}}{12};\dfrac{7+\sqrt{1057}}{12}\right\}\)

* Trả lời:
\(\left(1\right)\) \(-3\left(1-2x\right)-4\left(1+3x\right)=-5x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3+6x-4-12x=-5x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-12x+5x=3+4+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=12\)
\(\left(2\right)\) \(3\left(2x-5\right)-6\left(1-4x\right)=-3x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-15-6+24x=-3x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+24x+3x=15+6+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow33x=28\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{28}{33}\)
\(\left(3\right)\) \(\left(1-3x\right)-2\left(3x-6\right)=-4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-3x-6x+12=-4x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x-6x+4x=-1-12-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x=-18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{5}\)
\(\left(4\right)\) \(x\left(4x-3\right)-2x\left(2x-1\right)=5x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-3x-4x^2+2x=5x-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-5x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{6}\)
\(\left(5\right)\) \(3x\left(2x-1\right)-6x\left(x+2\right)=-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-6x^2-12x=-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-15x+3x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)

a, \(-2x=2\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
b, \(2x-3+5x=4x+12\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
c, \(5+x-6=12-8x\Leftrightarrow9x=13\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{13}{9}\)
d, \(5x-15-4=2x-2+7\Leftrightarrow3x=24\Leftrightarrow x=8\)

20) -5-(x + 3) = 2 - 5x ⇔ -5 - x - 3 = 2 -5x ⇔ 4x = 10 ⇔ x = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy...

1) \(\left|4-2x\right|.\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\left|4-2x\right|=\dfrac{1}{3}:\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\left|4-2x\right|=\dfrac{1}{3}.3\)
\(\left|4-2x\right|=1\)
=>\(4-2x=\pm1\)
+)\(TH1:4-2x=1\) +)\(TH2:4-2x=-1\)
\(2x=4-1\) \(2x=4-\left(-1\right)\)
\(2x=3\) \(2x=4+1\)
\(x=3:2\) \(2x=5\)
\(x=1,5\) \(x=5:2\)
Vậy x=1,5 \(x=2,5\)
Vậy x=2,5
2) \(\left(-3\right)^2:\left|x+\left(-1\right)\right|=-3\)
\(9:\left|x+\left(-1\right)\right|=-3\)
\(\left|x+\left(-1\right)\right|=9:\left(-3\right)\)
\(\left|x+\left(-1\right)\right|=-3\)
=> \(x+\left(-1\right)\) sẽ không có giá trị nào ( Vì giá trị tuyệt đối luôn luôn lớn hơn hoặc bằng 0 )
Vậy x = \(\varnothing\)
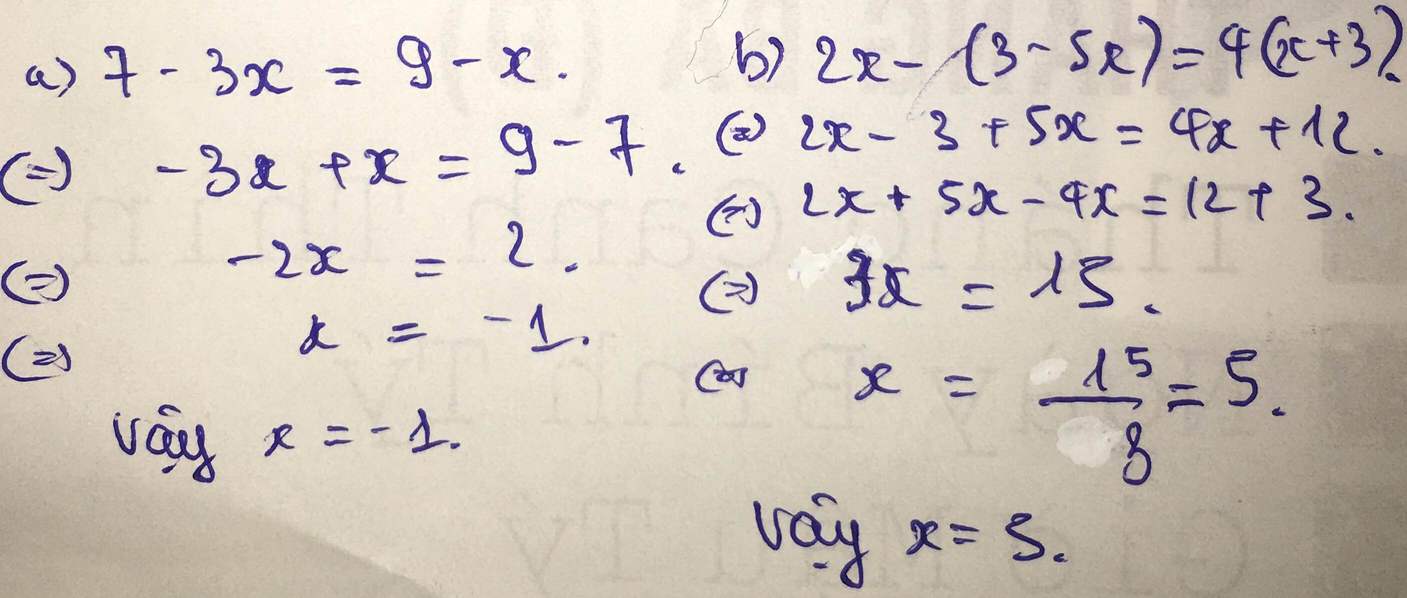
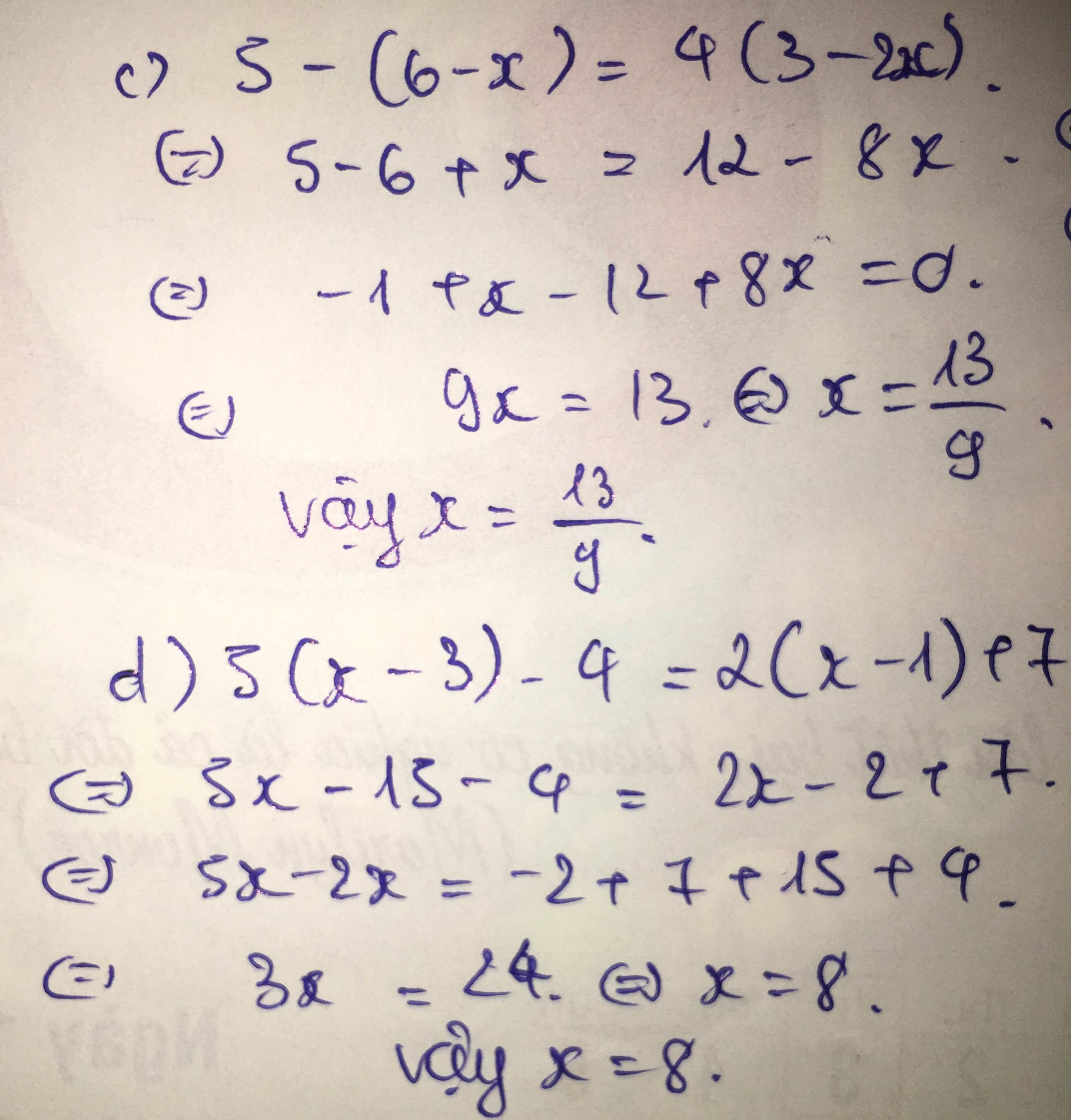
ước 1: Nhân chéo để loại mẫu số Nhân chéo cả hai vế của phương trình để loại bỏ mẫu số: 6 ( 2 𝑥 − 7 ) = 9 ( 𝑥 − 3 ) 6(2x−7)=9(x−3) Bước 2: Phân phối và rút gọn Mở rộng các vế: 12 𝑥 − 42 = 9 𝑥 − 27 12x−42=9x−27 Bước 3: Đưa các hạng tử chứa 𝑥 x về một phía Di chuyển các hạng tử chứa 𝑥 x sang một phía và các hạng tử còn lại sang phía còn lại: 12 𝑥 − 9 𝑥 = 42 − 27 12x−9x=42−27 3 𝑥 = 15 3x=15 Bước 4: Giải phương trình Chia cả hai vế cho 3: 𝑥 = 15 3 = 5 x= 3 15 =5 Kết luận: Giá trị của 𝑥 x là 𝑥 = 5 x=5.
Ta có: \(\dfrac{6}{x-3}=\dfrac{9}{2x-7}\)
=>\(6\left(2x-7\right)=9\left(x-3\right)\)
=>12x-42=9x-27
=>12x-9x=-27+42
=>3x=15
=>\(x=\dfrac{15}{3}=5\left(nhận\right)\)