tìm nghiệm của phương trình: m2 (x-1)=2(2x-3)+m , theo tham sô m
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1: Ta có: \(\text{Δ}=\left[-2\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-4\cdot\left(m+2\right)\left(3-m\right)\)
\(=\left(2m-2\right)^2+4\left(m+2\right)\left(m-3\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4+4\left(m^2-3m+2m-6\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4+4m^2-4m-24\)
\(=-12m-20\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì Δ>0
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m-20>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m>20\)
hay \(m< \dfrac{-5}{3}\)
Để phương trình có nghiệm kép thì Δ=0
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m-20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m=20\)
hay \(m=\dfrac{-5}{3}\)
Để phương trình vô nghiệm thì Δ<0
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m-20< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m< 20\)
hay \(m>\dfrac{-5}{3}\)
2: ĐKXĐ: \(m\ne-2\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2\left(m-1\right)}{m+2}=\dfrac{2m-2}{m+2}\\x_1\cdot x_2=\dfrac{3-m}{m+2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1+x_2=x_1x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2m-2}{m+2}=\dfrac{3-m}{m+2}\)
Suy ra: 2m-2=3-m
\(\Leftrightarrow2m+m=3+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3m=5\)
hay \(m=\dfrac{5}{3}\)(thỏa ĐK)

Thay x=2 vào pt ta có:
\(\left(m^2+2m+3\right)x-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left(m^2+2m+3\right)-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2m^2+4m+6-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2m+4m=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2m\left(m+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...

a.
Pt có 2 nghiệm pb khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1\ne0\\\Delta'=\left(m+3\right)^2-\left(m+1\right)\left(-m+2\right)>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne-1\\2m^2+7m+7>0\left(\text{luôn đúng}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ne-1\)
b.
BPT vô nghiệm khi \(\left(m^2-4m-5\right)x^2+2\left(m-5\right)-1< 0\) nghiệm đúng với mọi x
- Với \(m=-1\) ko thỏa mãn
- Với \(m=5\) thỏa mãn
- Với \(m\ne\left\{-1;5\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2-4m-5< 0\\\Delta'=\left(m-5\right)^2+m^2-4m-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< m< 5\\\left(m-5\right)\left(2m-4\right)< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< m< 5\\2< m< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2< m< 5\)
Kết hợp lại ta được: \(2< m\le5\)

ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;1\right\}\)
a) Thay m=1 vào phương trình, ta được:
\(\dfrac{2x+1}{x}=1+\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{x}=\dfrac{x-1+x+1}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x+1}{x}=\dfrac{2x}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=2x^2-2x+x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x^2+2x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1(loại)
Vậy: Khi m=1 thì \(S=\varnothing\)

`a,m=1`
`=>(2x+1)/x=(2x)/(x-1)`
`<=>2x^2-x-1=2x^2`
`<=>-x-1=0`
`<=>x=-1`
`b,(2x+m)/x=(2x)/(x-1)`
`<=>2x^2=2x^2-2x+mx-m`
`<=>mx-2x=m`
`<=>x(m-2)=m`
PT có nghiệm duy nhất
`<=>m-2 ne 0<=>m ne 2`
PT vô nghiệm
`<=>m-2=0,m ne 0`
`<=>m=2`
PT có vô số nghiệm
`<=>m=2,m=2` vô lý.

a: TH1: m=3
=>2x-5=0
=>x=5/2(nhận)
TH2: m<>3
Δ=2^2-4*(m-3)*(-5)
=4+20(m-3)
=4+20m-60=20m-56
Để phương trình có nghiệm kép thì 20m-56=0
=>m=2,8
=>-0,2x^2+2x-5=0
=>x^2-10x+25=0
=>x=5
b: Để phươg trình có hai nghiệm pb thì 20m-56>0
=>m>2,8

a: Thay m=3 vào pt, ta được:
\(x^2-2\cdot\left(3-1\right)x+3^2-2\cdot3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+3=0\)
=>(x-1)(x-3)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=3
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left[-2\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-4\left(m^2-2m\right)\)
\(=\left(2m-2\right)^2-4\left(m^2-2m\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-4m^2+8m=4>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Thay x=-2 vào pt, ta được:
\(\left(-2\right)^2-2\cdot\left(-2\right)\cdot\left(m-1\right)+m^2-2m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+4+4\left(m-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+4+4m-4=0\)
=>m(m+2)=0
=>m=0 hoặc m=-2
Theo hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2-2=2\cdot\left(-1\right)=-2\\x_2-2=2\cdot\left(-3\right)=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2=0\\x_2=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(x_1^2+x_2^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-2\right)^2-2\left(m^2-2m\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m^2+4m-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-4m=0\)
=>2m(m-2)=0
=>m=0 hoặc m=2

Lời giải:
$x+y=1\Leftrightarrow y=1-x$. Thay vô pt $(2)$:
$2x-(1-x)=m-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 3x-1=m-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 3x=m(*)$
Để pt ban đầu có nghiệm $x,y$ nguyên duy nhất thì pt $(*)$ phải có nghiệm nguyên $x$ duy nhất
Điều này xảy ra khi $m=3k$ với $k\in\mathbb{Z}$
Khi đó: $3x=3k\Leftrightarrow x=k$
$y=1-x=1-k$
Vậy để hpt có nghiệm thỏa đề thì $m=3k$ với $k\in\mathbb{Z}$
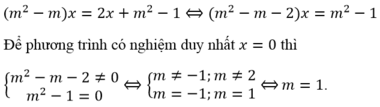
\(m^2(x-1)=2(2x-3)+m\\\Leftrightarrow m^2x-m^2=4x-6+m\\\Leftrightarrow m^2x-4x=m^2+m-6\\\Leftrightarrow (m^2-4)x=(m-2)(m+3)\text{ (1) }\)
+, Xét \(m^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow m=\pm2\)
*) Với \(m=2\) thì pt (1) trở thành:
\(\left(2^2-4\right)x=\left(2-2\right)\left(2+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\) (luôn đúng)
\(\Rightarrow m=2\) thì pt (1) có vô số nghiệm
*) Với \(m=-2\) thì pt (1) trở thành:
\(\left[\left(-2\right)^2-4\right]x=\left(-2-2\right)\left(-2+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=-4\) (vô lí)
\(\Rightarrow m=-2\) thì pt vô nghiệm
+, Xét \(m^2-4\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\pm2\)
Khi đó, pt (1) tương đương:
\(\left(m-2\right)\left(m+2\right)x=\left(m-2\right)\left(m+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{m+3}{m+2}\) (do \(m\ne\pm2\)) \(\Rightarrow m\ne\pm2\) thì pt có nghiệm \(x=\dfrac{m+3}{m+2}\).
Vậy: ...
giúp nhanh mình với mai mình kiểm tra r