Tìm các giá trị của x để biểu thức sau có nghĩa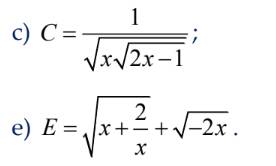
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Để biểu thức có nghĩa thì : x2 - 5x + 6 > 0
=> (x - 2)(x - 3) > 0
Xét 2 trường hợp:
+ Với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-2>0\\x-3>0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x>2\\x>3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}x>3}\)
+ Với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-2< 0\\x-3< 0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x< 2\\x< 3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}x< 2}\)
Vậy x < 2 hoặc x > 3 thì biểu thức có nghĩa

Lời giải:
a.
\(A=\frac{(x\sqrt{x}-4x)-(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x\geq 0\\ \sqrt{x}-4\neq 0\\ \sqrt{x}-2\neq 0\\ \sqrt{x}-1\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x\geq 0\\ x\neq 16\\ x\neq 4\\ x\neq 1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\frac{x(\sqrt{x}-4)-(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{2}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}=\frac{(x-1)(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}\)
\(=\frac{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{2(\sqrt{x}-2)}\)
b.
Với $x$ nguyên, để $A\in\mathbb{Z}$ thì $\sqrt{x}+1\vdots 2(\sqrt{x}-2)}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}+1\vdots \sqrt{x}-2$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}-2+3\vdots \sqrt{x}-2$
$\Leftrightarrow 3\vdots \sqrt{x}-2$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}-2\in\left\{\pm 1;\pm 3\right\}$
$\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;9;25\right\}$
Thử lại thấy đều thỏa mãn.

bài 1:
\(\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right).\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)>0\)
Để biểu thức \(\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right)\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)\) nhận giá trị dương thì \(-\frac{3}{2}\)và \(\frac{1}{3}-x\)phải cùng âm
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{3}-x< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{1}{3}\)
Vậy \(x>\frac{1}{3}\)thì biểu thức\(\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right)\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)\) nhận giá trị dương
bài 2:
a)Để \(\frac{x^2-2}{5x}\) nhận giá trị âm thì x2-2<0 hoặc 5x<0
+)Nếu x2-2<0
=>x2<2
=>x<\(\sqrt{2}\)
+)Nếu 5x<0
=>x<0
Vậy x<\(\sqrt{2}\)hoặc x<0 thì biểu thức \(\frac{x^2-2}{5x}\)nhận giá trị âm
b)Để E nhận giá trị âm thì \(\frac{x-2}{x-6}\)nhận giá trị âm
=>x-2<0 hoặc x-6<0
+)Nếu x-2<0
=>x<2
+)Nếu x-6<0
=>x<6
Vậy x<2 hoặc x<6 thì biểu thức E nhận giá trị âm

Bài 1:
a: \(x^2+5x=x\left(x+5\right)\)
Để biểu thức này âm thì \(x\left(x+5\right)< 0\)
hay -5<x<0
b: \(3\left(2x+3\right)\left(3x-5\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{3}{2}< x< \dfrac{5}{3}\)


 (Với x > 0; x 1; x4)
(Với x > 0; x 1; x4)
c
Để biểu thức C có nghĩa thì
\(\sqrt{x\sqrt{2x-1}}>0\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\2x-1>0\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy để biểu thức C có nghĩa thì \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Giải câu e:
Điều kiện để biểu thức E có nghĩa:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{2}{x}\ge0\\-2x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x^2+2}{x}\ge0\\x\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy không tồn tại x để biểu thức E có nghĩa.
bạn ctv xem lại dấu vào câu e nhé: )