tìm x
a) x+2\(\sqrt{2}\)x2+2x3=0
b) (x2+x)(x2+x+1)=6
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: Ta có: \(2x^3-18x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x+1\right)-6x\left(x+2\right)=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+3x-4x-2-6x^2-12x=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-13x=13\)
hay x=-1
c: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^3-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)=3\left(1-x^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3-8=3-3x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=12\)
hay x=4
a) 2x3-18x=0
⇔ 2x(x2-9)=0
⇔ 2x(x-3)(x+3)=0
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)(3x-1)(2x+1)-6x(x+2)=11
⇔ 6x2+x-1-6x2-12x=11
⇔ -11x=12
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{12}{11}\)
c) (x-1)3-(x+2).(x2-2x+4)=3.(1-x2)
⇔ x3-3x2+3x-1-x3-8-3+3x2=0
⇔ 3x=12
⇔ x=4

b: 4x^2-20x+25=(x-3)^2
=>(2x-5)^2=(x-3)^2
=>(2x-5)^2-(x-3)^2=0
=>(2x-5-x+3)(2x-5+x-3)=0
=>(3x-8)(x-2)=0
=>x=8/3 hoặc x=2
c: x+x^2-x^3-x^4=0
=>x(x+1)-x^3(x+1)=0
=>(x+1)(x-x^3)=0
=>(x^3-x)(x+1)=0
=>x(x-1)(x+1)^2=0
=>\(x\in\left\{0;1;-1\right\}\)
d: 2x^3+3x^2+2x+3=0
=>x^2(2x+3)+(2x+3)=0
=>(2x+3)(x^2+1)=0
=>2x+3=0
=>x=-3/2
a: =>x^2(5x-7)-3(5x-7)=0
=>(5x-7)(x^2-3)=0
=>\(x\in\left\{\dfrac{7}{5};\sqrt{3};-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)

\(a,Sửa:2021x-1+2022x\left(1-2021x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2021x-1\right)\left(1-2022x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2021}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2022}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: ta có: \(x^2+3x-\left(2x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(5x+20-x^2-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(5-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: Ta có: \(2x\left(x-3\right)+x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(x^2\left(x-6\right)-x^2+36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x^2-x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Ta có: \(x^3+x^2+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
nên x+1=0
hay x=-1
Vậy: S={-1}
b) Ta có: \(x^3-6x^2+11x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-5x^2+5x+6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-5x\left(x-1\right)+6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={1;2;3}
c) Ta có: \(x^3-x^2-21x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+2x^2-6x-15x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-3\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)-15\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+2x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+5x-3x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2\cdot\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-5}
d) Ta có: \(x^4+2x^3-4x^2-5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+4x^3-8x^2+4x^2-8x+3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-2\right)+4x^2\cdot\left(x-2\right)+4x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+4x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[x^2\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+x+1>0\forall x\)
nên (x-2)(x+3)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={2;-3}


b) x.(x+1). ( x+ 4). (x+ 5) = 12
⇔ [ x. (x + 5)]. [(x+1). (x+ 4)] = 12
⇔ x 2 + 5 x ⋅ x 2 + 4 x + x + 4 − 12 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 5 x ⋅ x 2 + 5 x + 4 − 12 = 0 ( * )
Đặt t = x 2 + 5 x + 2
= > x 2 + 5 x = t – 2 v à x 2 + 5 x + 4 = t + 2
Khi đó phương trình (*) trở thành:
( t – 2). (t+ 2) - 12 = 0
⇔ t 2 − 4 − 12 = 0 ⇔ t 2 − 16 = 0 ⇔ t 2 = 16 ⇔ t = ± 4
+ Với t = 4 ta có: x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 4
⇔ x 2 + 5 x – 2 = 0 ( * * )
Có a= 1, b = 5, c = - 2 và ∆ = 5 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 2 ) = 33 > 0
Nên (**) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt là:
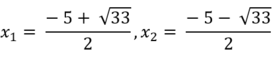
* Với t = - 4 ta có: x 2 + 5 x + 2 = - 4
⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 6 = 0 ( * * * )
Có a= 1, b = 5, c= 6 và ∆ = 5 2 – 4 . 1 . 6 = 1 > 0
Phương trình (***) có 2 nghiệm là:
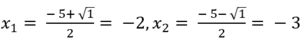
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
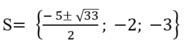


b) x.(x+1). ( x+ 4). (x+ 5) = 12
⇔ [ x. (x + 5)]. [(x+1). (x+ 4)] = 12
⇔ x 2 + 5 x ⋅ x 2 + 4 x + x + 4 − 12 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 5 x ⋅ x 2 + 5 x + 4 − 12 = 0 ( * )
Đặt t = x 2 + 5 x + 2
= > x 2 + 5 x = t – 2 v à x 2 + 5 x + 4 = t + 2
Khi đó phương trình (*) trở thành:
( t – 2). (t+ 2) - 12 = 0
⇔ t 2 - 4 - 12 = 0 ⇔ t 2 - 16 = 0 ⇔ t 2 = 16 ⇔ t = ± 4
+ Với t = 4 ta có: x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 4
⇔ x2 +5x – 2 = 0 (**)
Có a= 1, b = 5, c = - 2 và ∆ = 5 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 2 ) = 33 > 0
Nên (**) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt là:
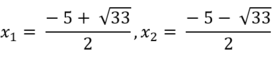
* Với t = - 4 ta có: x 2 + 5 x + 2 = - 4
⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 6 = 0 ( * * * )
Có a= 1, b = 5, c= 6 và ∆ = 5 2 – 4 . 1 . 6 = 1 > 0
Phương trình (***) có 2 nghiệm là:
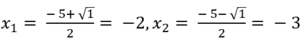
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
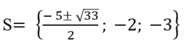

a) \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)+\left(x+2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x^2-x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\\left[x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\right]+\dfrac{23}{4}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\left(N\right)\\\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}\ge\dfrac{23}{4}>0\left(L\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-2\right\}\)
b) \(9x^2-4-\left(3x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)-\left(3x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left[\left(3x+2\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2-3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\cdot4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)