Chúng minh đa thức: 3x2+2x+2 không có nghiệm
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Với P(x)=0 thì
2x^2+12x+23=0
Vì 2x^2 lớn hơn hoặc bằng 0 với mọi x
=) 2x^2+12x lớn hơn hoặc bằng 0 với mọi x =) 2x^2+12x+23 lớn hơn hoặc bằng 23 với mọi x(vô lí)
Vậy đa thức P(x) vô nghiệm

Bài 1:
1.
$6x^3-2x^2=0$
$2x^2(3x-1)=0$
$\Rightarrow 2x^2=0$ hoặc $3x-1=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=\frac{1}{3}$
Đây chính là 2 nghiệm của đa thức
2.
$|3x+7|\geq 0$
$|2x^2-2|\geq 0$
Để tổng 2 số bằng $0$ thì: $|3x+7|=|2x^2-2|=0$
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{-7}{3}$ và $x=\pm 1$ (vô lý)
Vậy đa thức vô nghiệm.
Bài 2:
1. $x^2+2x+4=(x^2+2x+1)+3=(x+1)^2+3$
Do $(x+1)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x$ nên $x^2+2x+4=(x+1)^2+3\geq 3>0$ với mọi $x$
$\Rightarrow x^2+2x+4\neq 0$ với mọi $x$
Do đó đa thức vô nghiệm
2.
$3x^2-x+5=2x^2+(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4})+\frac{19}{4}$
$=2x^2+(x-\frac{1}{2})^2+\frac{19}{4}\geq 0+0+\frac{19}{4}>0$ với mọi $x$
Vậy đa thức khác 0 với mọi $x$
Do đó đa thức không có nghiệm.

Ta có P(x) - Q(x) = (3x2 + 5x - 1) - (3x2 + 2x + 2) = 3x - 3
Vì 3x - 3 = 0 ⇒ x = 1 nên x = 1 là nghiệm cần tìm. Chọn A

`@` `\text {dnv4510}`
`A)`
`P(x)+Q(x)=`\((2x^4+3x^2-3x^2+6)+(x^4+x^3-x^2+2x+1)\)
`= 2x^4+3x^2-3x^2+6+x^4+x^3-x^2+2x+1`
`= (2x^4+x^4)+x^3+(3x^2-3x^2-x^2)+2x+(6+1)`
`= 3x^4+x^3-x^2+2x+7`
`B)`
`P(x)+M(x)=2Q(x)`
`-> M(x)= 2Q(x) - P(x)`
`2Q(x)=2(x^4+x^3-x^2+2x+1)`
`= 2x^4+2x^3-2x^2+4x+2`
`-> 2Q(x)-P(x)=(2x^4+2x^3-2x^2+4x+2)-(2x^4+3x^2-3x^2+6)`
`= 2x^4+2x^3-2x^2+4x+2-2x^4-3x^2+3x^2-6`
`= (2x^4-2x^4)+2x^3+(-2x^2-3x^2+3x^2)+4x+(2-6)`
`= 2x^3-2x^2+4x-4`
Vậy, `M(x)=2x^3-2x^2+4x-4`
`C)`
Thay `x=-4`
`M(-4)=2*(-4)^3-2*(-4)^2+4*(-4)-4`
`= 2*(-64)-2*16-16-4`
`= -128-32-16-4`
`= -180`
`->` `x=-4` không phải là nghiệm của đa thức.

Bài 1
Gợi ý bạn làm : Bạn thay \(x=-4;x=-3;x=0;x=1\) vào \(f\left(x\right);g\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Nếu kết quả ra giống nhau thì là nghiệm , ra khác nhau thì không là nghiệm
VD : Thay \(x=-4\) vào \(f\left(x\right)\) và \(g\left(x\right)\)
\(f\left(-4\right)=4.\left(-4\right)^4-5\left(-4\right)^3+3.\left(-4\right)+2=1334\)
\(g\left(x\right)=-4.\left(-4\right)^4+5\left(-4\right)^3+7=-1337\)
Ra hai kết quả khác nhau
\(\Rightarrow x=-4\) không là nghiệm
Bài 2
\(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)=\left(-x^5+3x^2+4x+8\right)-\left(-x^5-3x^2+4x+2\right)\\ =-x^5+3x^2+4x+8+x^5+3x^2-4x-2\\ =\left(-x^5+x^5\right)+\left(3x^2+3x^2\right)+\left(4x-4x\right)+\left(8-2\right)\\ =6x^2+6\\ =x^2+1\\ =x^2+2.\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\\ =\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\) phương trình vô nghiệm

c. x = 3, x = -3 có là nghiệm của N(x) vì N(3) = N(-3) = 0 (0.5 điểm)

Bài 1:
a) \(3x^2\left(2x^3-x+5\right)-6x^5-3x^3+10x^2\)
\(=6x^5-3x^3+10x^2-6x^5-3x^3+10x^2\)
\(=10x^2+10x^2\)
\(=20x^2\)
b) \(-2x\left(x^3-3x^2-x+11\right)-2x^4+3x^3+2x^2-22x\)
\(=-2x^4+6x^3+2x^2-22x-2x^4+3x^3+2x^2-22x\)
\(=-4x^4+9x^3+4x^2-44x\)

x2+2x+2=(x2+2x+1)+1=(x+1)2+1>0 với mọi x
suy ra đa thức đã cho vô nghiệm
tinh denta phay = 1^2 - 4.1.2 = -7 . vi denta < 0 nen pt vo nghiem

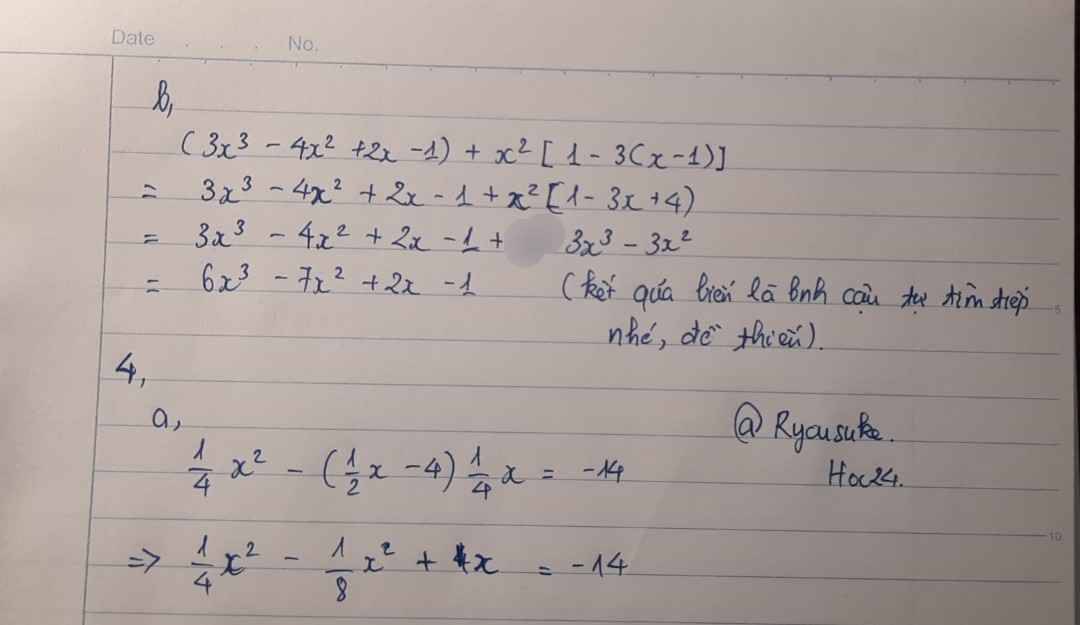

Do \(3x^2+2x\ge0\) với mọi \(x\)
\(\Rightarrow3x^2+2x+2>0\)
Vậy đa thức\(3x^2+2x+2\)không có nghiệm
Đặt \(A=3x^2+2x+2\).
\(A=x^2+2x^2+2x+1+1\).
\(A=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+2x^2+1\).
\(A=\left(x^2+x+x+1\right)+2x^2+1\).
\(A=\left[\left(x^2+x\right)+\left(x+1\right)\right]+2x^2+1\).
\(A=\left[x\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)\right]+2x^2+1\).
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)+2x^2+1\).
\(A=\left(x+1\right)^2+2x^2+1\).
Ta có:
\(\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\);
\(x^2\ge0\forall x\)\(\Rightarrow2x^2\ge0\forall x\).
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2+2x^2\ge0\forall x\).
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2+2x^2+1\ge1\forall x\).
\(\Rightarrow A\ge1\).
Mà \(1>0\).
\(\Rightarrow A>0\Rightarrow A\ne0\).
Do đó biểu thức A vo nghiệm.