2X2+4X-18=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(2x^2-4x+2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(2x^2-4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}x=1}\)

\(2x^2-4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy....

Ta có:
\(C=2x^2-4x+6\)
\(C=2\cdot\left(x^2-2x+3\right)\)
\(C=2\cdot\left(x^2-2x+1+2\right)\)
\(C=2\cdot\left[\left(x-1\right)^2+2\right]\)
\(C=2\left(x-1\right)^2+4\)
Mà: \(2\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow C=2\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4>0\forall x\)
Vậy tất cả các số thực đều thỏa mãn:
\(\Rightarrow x\in R\)
`C = 2x^2 - 4x + 6`
`2C = 4x^2 - 8x + 12`
`2C = ( 2x )^2 - 2 . 2x . 2 + 2^2 + 12 - 2^2`
`2C = ( 2x - 2 )^2 + 8`
Vì ` ( 2x - 2 )^2 >= 0 AAx` nên :
`( 2x - 2 )^2 + 8 >= 8 > 0 AAx`
Hay `2C > 0 AAx` . Vì `2C > 0 AAx => C > 0 AAx` .
Vậy `C > 0 AAx` ( đpcm ) .

\(2x^2-2x+2y+y^2-4x+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-6x+y^2+2y+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{9}{2}+y^2+2y+1+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\left(y+1\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{2}=0\)(vô lý)

a, \(x^2\) + 4\(x\) - y2 + 4
= (\(x^2\) + 4\(x\) + 4) - y2
= (\(x\) + 2)2 - y2
= (\(x\) + 2 - y)(\(x\) + 2 + y)
b, 2\(x^2\) - 18
= 2.(\(x^2\) -9)
= 2.(\(x\) -3).(\(x\) + 3)

đây bạn nếu bạn ko hiểu thì lên mạng gõ cách lm bất phương trình mũ 2
 nhows
nhows

Ta xét các phương án:
(I) có:
![]()
(II) có:
![]()
(III) tương đương : x2+ y2 – 2x - 3y + 0,5= 0.
phương trình này có:
![]()
Vậy chỉ (I) và (III) là phương trình đường tròn.
Chọn D.
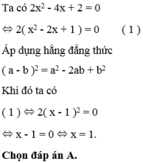


2X2+4X-18=0
<=>2(x2+2x-9)=0
=>x2+2x-9=0
denta:22-(-4(1.9))=40
vì 40>0=>pt có 2 nghiệm pb
x1=(-2+\(\sqrt{40}\)):2=\(\sqrt{10}-1\)
x2=(-2-\(\sqrt{40}\)):2=\(-\sqrt{10}-1\)