giải phương trình : -3x(x-5)+5(x-1)+3x2=4-x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,x-5\left(x-2\right)=6x\\ \Leftrightarrow x-5x+10-6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-10x+10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\\ b,2^3+3x^2-32x=48\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-32x+8=48\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-32x-40=0\)
Nghiệm xấu lắm bn
\(c,\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow c,\left(3x+1\right)\left[\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x-3\right)^2\right]\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-5-x+3\right)\left(2x-5+x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(3x-8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=2\\x=\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,9x^2-1=\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1\right)-\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(4x+1-3x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x^3+3x^2-32x-48=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3-8x^2\right)+\left(11x^2-44x\right)+\left(12x-48\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x-4\right)+11x\left(x-4\right)+12\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(2x^2+11x+12\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[\left(2x^2+8x\right)+\left(3x+12\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left[2x\left(x+4\right)+3\left(x+4\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) – 2x = x(x – 1)(x + 1)
⇔ x3 – 1 – 2x = x(x2 – 1)
⇔ x2 – 1 – 2x = x3 – x
⇔ -2x + x = 1 ⇔ - x = 1 ⇔ x = -1
Tập nghiệm của phương trình: S = { -1}
b) x2 – 3x – 4 = 0
⇔ x2 – 4x + x – 4 = 0 ⇔ x(x – 4) + (x – 4) = 0
⇔ (x – 4)(x + 1) = 0 ⇔ x – 4 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
⇔ x = 4 hoặc x = -1
Tập nghiệm của phương trình: S = {4; -1}
c) ĐKXĐ : x – 1 ≠ 0 và x2 + x + 1 ≠ 0 (khi đó : x3 – 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) ≠ 0)
⇔ x ≠ 1
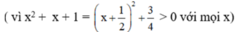
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế:
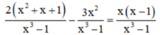
Khử mẫu, ta được: 2x2 + 2x + 2 – 3x2 = x2 – x
⇔ -2x2 + 3x + 2 = 0 ⇔ 2x2 – 3x – 2 = 0
⇔ 2x2 – 4x + x – 2 = 0 ⇔ 2x(x – 2) + (x – 2) = 0
⇔ (x – 2)(2x + 1) = 0 ⇔ x – 2 = 0 hoặc 2x + 1 = 0
⇔ x = 2 hoặc x = -1/2(thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = {2 ; -1/2}
d) ĐKXĐ : x – 5 ≠ 0 và x – 1 ≠ 0 (khi đó : x2 – 6x + 5 = (x – 5)(x – 1) ≠ 0)
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế :
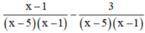
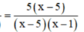
Khử mẫu, ta được : x – 1 – 3 = 5x – 25 ⇔ -4x = -21
⇔ x = 21/4 (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = {21/4}

1) Ta có: \(2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Ta có: \(\left(x^2-4\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3) Ta có: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left(2x+5\right)^2=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x-1-4x^2-20x-25=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24x=11+1+25=37\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{37}{24}\)
5) Ta có: \(3x^2-5x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-8x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-8\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
8) Ta có: \(\left|x-5\right|=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=3\\x-5=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
10) Ta có: \(\left|2x+1\right|=\left|x-1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=x-1\\2x+1=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-x=-1-1\\2x+x=1-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)

a. (3x - 1)2 - (x + 3)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1+x+3\right)\left(3x-1-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+2\right)\left(2x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=0\) hoặc \(2x-4=0\)
1. \(4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow4x=-2\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2. \(2x-4=0\Leftrightarrow2x=4\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
S=\(\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};2\right\}\)
b. \(x^3=\dfrac{x}{49}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49x^3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(49x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(7x+1\right)\left(7x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\) hoặc \(7x+1=0\) hoặc \(7x-1=0\)
1. x=0
2. \(7x+1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{7}\)
3. \(7x-1=0\Leftrightarrow7x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)

\(a)x^2-9x+20=0 \\<=>(x-4)(x-5)=0 \\<=>x=4\ hoặc\ x=5 \\b)x^2-3x-18=0 \\<=>(x+3)(x-6)=0 \\<=>x=-3\ hoặc\ x=6 \\c)2x^2-9x+9=0 \\<=>(x-3)(2x-3)=0 \\<=>x=3\ hoặc\ x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-6x-2x+4=0\)
=>(x-2)(3x-2)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=2/3
e: \(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)=0\)
=>x(x-3)(x+1)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{0;3;-1\right\}\)
f: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=6\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\sqrt{6}+2;-\sqrt{6}+2\right\}\)

a) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0
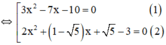
+ Giải (1):
3 x 2 – 7 x – 10 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -7; c = -10
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 10 / 3 .
+ Giải (2):
2 x 2 + ( 1 - √ 5 ) x + √ 5 - 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 1 - √5; c = √5 - 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
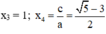
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 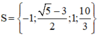
b)
x 3 + 3 x 2 - 2 x - 6 = 0 ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 - ( 2 x + 6 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x + 3 ) - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0
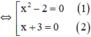
+ Giải (1): x 2 – 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 2 ⇔ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
+ Giải (2): x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3; -√2; √2}
c)
x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = x ⋅ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) − x ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) x 2 − 1 − x = 0
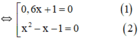
+ Giải (1): 0,6x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 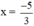
+ Giải (2):
x 2 – x – 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = -1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm 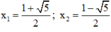
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 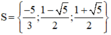
d)
x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 − x 2 − x + 5 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 − x 2 − x + 5 ⋅ x 2 + 2 x − 5 + x 2 − x + 5 = 0 ⇔...
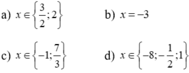


\(-3x^2+15x+5x-5+3x^2=4-x\)
<=> 21x=9
<=> x=3/7