Cho n > 1 là một số nguyên dương. Giá trị của bằng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

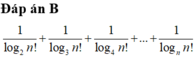
![]()

Đáp án B.
Đặt t = 2 + log u 1 - 2 log u 10 ≥ 0
⇔ 2 log u 1 - 2 log u 10 = t 2 - 2 ,
khi đó giả thiết trở thành:
log u 1 - 2 log u 10 + 2 + log u 1 - 2 log u 10 = 0
⇔ t 2 + t - 2 = 0
<=> t = 1 hoặc t = -2
⇒ log u 1 - 2 log u 10 = - 1
⇔ log u 1 + 1 = 2 log u 10
⇔ log 10 u 1 = log u 10 2 ⇔ 10 u 1 = u 10 2 ( 1 )
Mà un+1 = 2un => un là cấp số nhân với công bội q = 2
=> u10 = 29 u1 (2)
Từ (1), (2) suy ra
10 u 1 = 9 9 u 1 2 ⇔ 2 18 u 1 2 = 10 u 1 ⇔ u 1 = 10 2 18
⇒ u n = 2 n - 1 . 10 2 18 = 2 n . 10 2 19 .
Do đó u n > 5 100 ⇔ 2 n . 10 2 19 > 5 100
⇔ n > log 2 5 100 . 2 19 10 = - log 2 10 + 100 log 2 5 + 19 ≈ 247 , 87
Vậy giá trị n nhỏ nhất thỏa mãn là n = 248.

\(a,A=log_23\cdot log_34\cdot log_45\cdot log_56\cdot log_67\cdot log_78\\ =log_28\\ =log_22^3\\ =3\\ b,B=log_22\cdot log_24...log_22^n\\ =log_22\cdot log_22^2...log_22^n\\ =1\cdot2\cdot...\cdot n\\ =n!\)

\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)

Chọn B
Cách giải: Ta có:
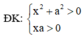
log 2 x 2 + a 2 + log 2 x 2 + a 2 + log 2 x 2 + a 2 + . . . + log . . . 2 ⏝ n c ă n x 2 + a 2 - 2 n + 1 - 1 log 2 x a + 1 = 0
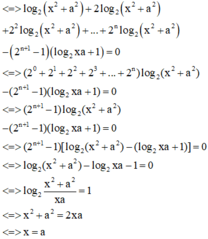
![]()