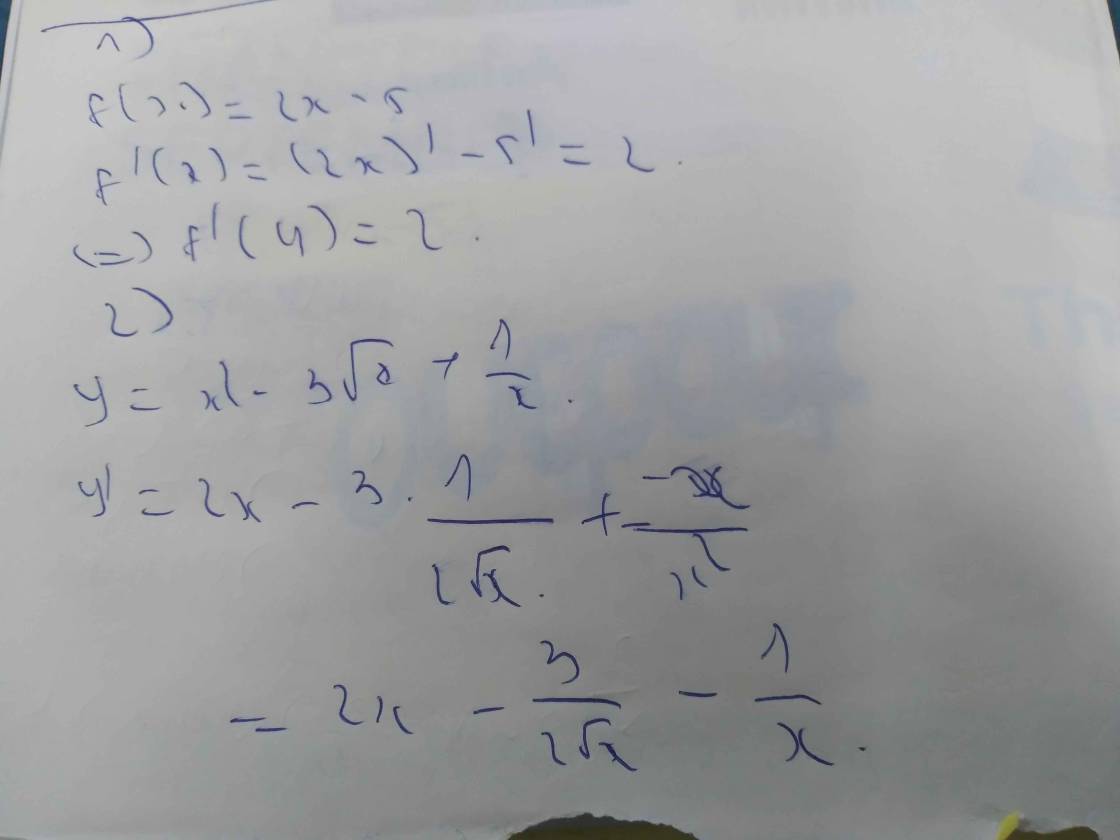Tìm đạo hàm của hàm số sau:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

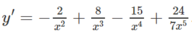

\(a,y'=\left(x^3-4x^2+5\right)'=3x^2-8x\\ b,y''=\left(3x^2-8x\right)'=6x-8\)

1) \(f\left(x\right)=2x-5\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(4\right)=2\)
2) \(y=x^2-3\sqrt[]{x}+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=2x-\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt[]{x}}-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
3) \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+9}{x+3}+4\sqrt[]{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1.\left(x+3\right)-1.\left(x+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+3-x-9}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{12}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{x}}\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(1-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{1}}\right]=2\left(\dfrac{3}{2}+1\right)=2.\dfrac{5}{2}=5\)

1. \(y'=3x^2\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{x^3-5}{2\sqrt{x}}=\dfrac{7x^3-5}{2\sqrt{x}}\)
2. \(y'=3x^5+\dfrac{3}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
3. \(y'=2-\dfrac{2}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)

a, \(y=3x^4-7x^3+3x^2+1\)
\(y'=12x^3-21x^2+6x\)
b, \(y=\left(x^2-x\right)^3\)
\(y'=3\left(x^2-x\right)^2\left(2x-1\right)\)
c, \(y=\dfrac{4x-1}{2x+1}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{4+2}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{6}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
a: y=3x^4-7x^3+3x^2+1
=>y'=3*4x^3-7*3x^2+3*2x
=12x^3-21x^2+6x
b: \(y'=\left[\left(x^2-x\right)^3\right]'\)
\(=3\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-x\right)^2\)
c: \(y'=\dfrac{\left(4x-1\right)'\left(2x+1\right)-\left(4x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)'}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(4x-1\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{6}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)

\(a,y'=8x^3-10x\\ \Rightarrow y''=24x^2-10\\ b,y'=e^x+xe^x\\ \Rightarrow y''=e^x+e^x+xe^x=2e^x+xe^x\)

Ta có
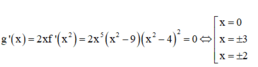
Bảng biến thiên của hàm số y= g( x)
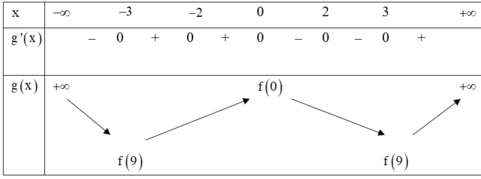
Dựa vào bảng biến thiên ta thấy hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng ( 3: + ∞) hàm số nghịch biến trong khoảng (-∞; -3) .
Hàm số có 3 cực trị, hàm số đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất tại x= ±3
Vậy có 3 khẳng định đúng là khẳng định I, II, IV
Chọn C.

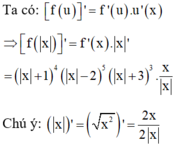
Do đó hàm số f(|x|) có 3 điểm cực trị tại x= 2; x= -2 và x= 0
Chọn B.

Đáp án: B.
Xét f(x) = x 3 + m x 2 + x - 5
Vì 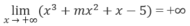
và f(0) = -5 với mọi m ∈ R cho nên phương trình f(x) = 0 luôn có nghiệm dương.

1) \(y=x^2-3\sqrt[]{x}+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y=2x-\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt[]{x}}-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
2) \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+9}{x+3}+4\sqrt[]{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1.\left(x+3\right)-1\left(x+9\right)}{\left(x+3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+3-x-9}{\left(x+3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{-6}{\left(x+3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=\dfrac{-6}{\left(1+3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{1}}=-\dfrac{3}{8}+2=\dfrac{13}{8}\)