Tìm nguyên hàm của hàm số:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(j\left(x\right)=3x-6+7=3x+1\)
\(j\left(-1\right)=3\cdot\left(-1\right)+1=-3+1=-2\)
j(2)=6+1=7
b: j(x)=-3/5 nên 3x+1=-3/5
=>3x=-8/5
hay x=-8/15

c2 ;nhan vo duocx2(sinx/2 .cosx/2)=x2/2(sinx+cosx) lai nhan vo roi tung phan nhe

Ý bạn là \(f(x)=\frac{1}{9+x^2}+\frac{3}{9+x^2}\) hay thế nào? Bạn cần viết đề bằng công thức toán (biểu tượng $\sum$ góc trái khung soạn thảo để được hỗ trợ tốt hơn).

Lời giải:
Đặt \(u=\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1}); dv=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}dx\)
\(\Rightarrow du=\frac{dx}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}; v=\int \frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\int \frac{d(x^2+1)}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}=\sqrt{x^2+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow \int \frac{x\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1})}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}dx=\int udv=uv-vdu=\sqrt{x^2+1}\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1})-\int dx\)
\(=\sqrt{x^2+1}\ln (x+\sqrt{x^2+1})-x+C\)

\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-1}{x^2}=1-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
\(\int f\left(x\right)dx=\int\left(1-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)dx=\int1dx-\int x^{-2}dx\)
=\(x-\dfrac{x^{-2+1}}{-2+1}+C=x-\dfrac{x^{-1}}{-1}+C=x+\dfrac{1}{x}+C\)
C=-1 ta được phương án A(ko tm câu hỏi)
C=0 ta được phương án B(ko tm câu hỏi)
C=2 ta được phương án C(ko tm câu hỏi)
=>chọn D

2.
\(I=\int e^{3x}.3^xdx\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=3^x\\dv=e^{3x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=3^xln3dx\\v=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}.3^x-\dfrac{ln3}{3}\int e^{3x}.3^xdx=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}.3^x-\dfrac{ln3}{3}.I\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{ln3}{3}\right)I=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}.3^x\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{3+ln3}.e^{3x}.3^x+C\)
1.
\(I=\int\left(2x-1\right)e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx=\int2x.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx-\int e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx\)
Xét \(J=\int2x.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}\\dv=2xdx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=-\dfrac{e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}}{x^2}dx\\v=x^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow J=x^2.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}+\int e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}dx\)
\(\Rightarrow I=x^2.e^{\dfrac{1}{x}}+C\)
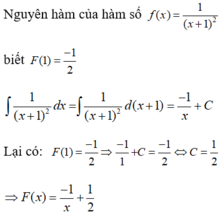
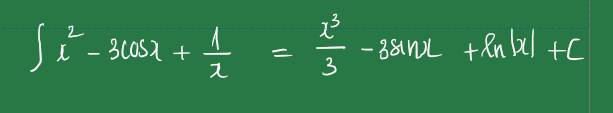
Chọn D.
Ta có: