Cho biểu thức P = -2x2 + 8x - 9
Chứng minh P < 0 với mọi giá trị x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(x^2-5x+10\)
\(=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{5}{2}+\dfrac{25}{4}+\dfrac{15}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{4}>0\forall x\)
b: \(2x^2+8x+15\)
\(=2\left(x^2+4x+\dfrac{15}{2}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2+4x+4+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x+2\right)^2+7>0\forall x\)

a)\(\frac{-1}{4x+2}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x>-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{-1}{2}\)
Vậy ...
b)\(\frac{-x^2-2x-3}{x^2+1}\)
Ta có: \(-x^2-2x-3=-\left(x+1\right)^2-2\)
Vì \(-\left(x+1\right)^2\le0;\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(x+1\right)^2-2\le-2< 0;\forall x\)
Lại có \(x^2\ge0;\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+1\ge1>0;\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{-x^2-2x-3}{x^2+1}< 0;\forall x\)

\(a,x^2y-8x+xy-8=xy\left(x+1\right)-8\left(x+1\right)=\left(xy-8\right)\left(x+1\right)\\ b,=\left(x+3y\right)^2-9=\left(x+3y-3\right)\left(x+3y+3\right)\)
\(A=3x^2\left(2x^2-7x-2\right)-6x^2\left(x^2-4x-1\right)-3x^3+15\\ A=6x^4-21x^3-6x^2-6x^4+24x^3+6x^2-3x^3+15\\ A=15\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(Sửa:\left(6x^3-7x^2+2x\right):\left(2x+1\right)\\ =\left(6x^3+3x^2-10x^2-5x\right):\left(2x+1\right)\\ =\left[3x^2\left(2x+1\right)-5x\left(2x+1\right)\right]:\left(2x+1\right)\\ =3x^2-5x\)

a) Ta có: 2x2 + 8 = 2(x2 + 4).
8 – 4x + 2x2 – x3
= (8 – x3) - ( 4x - 2x2)
= (2 – x).(4 + 2x + x2) - 2x.(2 - x)
= (2 – x).(4 + 2x + x2 – 2x)
= (2 - x). (4 + x2 )
* Do đó:
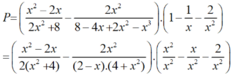
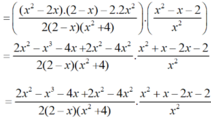
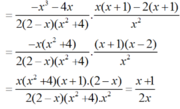
b) Tại x = 1 2 hàm số đã cho xác định nên thay x = 1 2 vào biểu thức rút gọn của P ta được:
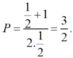

Ta có :
\(x^2-4x+5=\left(x^2-2.2x+2^2\right)+1=\left(x-2\right)^2+1\ge1>0\)
Vậy đa thức \(x^2-4x+5\) vô nghiệm với mọi giá trị của x
Chúc bạn học tốt ~

a) Ta có \(2x^2-8x+13=2x^2-8x+8+5\)
\(=2\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+5\)
\(=2\left(x-2\right)^2+5\ge5\forall x\)
Giả sử trước khi làm nhé
\(a)\)\(2x^2-8x+13>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(4x^2-16x+26>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(4x^2-16+16\right)+10>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(2x-4\right)^2+10\ge10>0\) ( luôn đúng )
Vậy ...
\(b)\)\(-2+2x-x^2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^2-2x+2>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(x-1\right)^2+1\ge1>0\) ( luôn đúng )
Vậy ...
Chúc bạn học tốt ~

Điều kiện x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 1
Ta có:
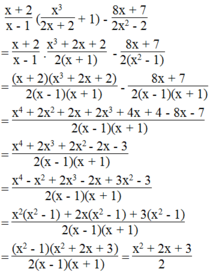
Biểu thức dương khi x 2 + 2 x + 3 > 0
Ta có: x 2 + 2 x + 3 = x 2 + 2 x + 1 + 2 = x + 1 2 + 2 > 0 với mọi giá trị của x.
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức dương với mọi giá trị x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 1

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-3;2\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2-5x-6}{x^2+x-6}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+3x^2-x^2-3x-2x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x+3\right)-2\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x-2}=x+1\)
Với mọi x nguyên thỏa ĐKXĐ, ta luôn có: x+1 là số nguyên
hay P là số nguyên(đpcm)
Ta có P = -2x2 + 8x - 9
= \(-2\left(x^2-4x+\frac{9}{2}\right)=-2\left(x^2-4x+4+\frac{1}{2}\right)=-2\left[\left(x-2\right)^2+\frac{1}{2}\right]\)
\(=-2\left(x-2\right)^2-1\le-1< 0\forall x\)
=> P < 0 \(\forall x\)(đpcm)
Ta có :
P = -2x2 + 8x - 9
= -2( x2 - 4x + 4 ) - 1
= -2( x - 2 )2 - 1 ≤ -1 < 0 ∀ x
=> P < 0 ∀ x ( đpcm )