Cos13x + sin14x =1
Giải phương trình sau
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



c/
Đặt \(3cosx-4sinx-6=t\)
Pt trở thành:
\(t^2+2=-3t\Leftrightarrow t^2+3t+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-1\\t=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3cosx-4sinx-6=-1\\3cosx-4sinx-6=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3cosx-4sinx=5\\3cosx-4sinx=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx.\frac{3}{5}-sinx.\frac{4}{5}=1\\cosx.\frac{3}{5}-sinx.\frac{4}{5}=\frac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos\left(x+a\right)=1\\cosx\left(x+a\right)=\frac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\) (với góc \(a\in\left[0;\pi\right]\) sao cho \(cosa=\frac{3}{5}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+a=k2\pi\\x+a=\pm\left(\frac{\pi}{2}-a\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-a+k2\pi\\x=-a\pm\left(\frac{\pi}{2}-a\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
a/
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx.\frac{1}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=cos\left(\frac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx.cos\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)-sinx.sin\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(\frac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(\frac{\pi}{3}-x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\frac{\pi}{3}=\frac{\pi}{3}-x+k2\pi\\x+\frac{\pi}{3}=-\frac{\pi}{3}+x+k2\pi\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=k\pi\)
b/
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sin\left(5x+\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=\sqrt{2}cos13x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(\frac{\pi}{4}-5x\right)=cos13x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}13x=\frac{\pi}{4}-5x+k2\pi\\13x=-\frac{\pi}{4}+5x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{72}+\frac{k\pi}{9}\\x=-\frac{\pi}{32}+\frac{k\pi}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a: Khi m=2 thì pt sẽ là x^2-6x-3=0
=>\(x=3\pm2\sqrt{3}\)

a: 7x+35=0
=>7x=-35
=>x=-5
b: \(\dfrac{8-x}{x-7}-8=\dfrac{1}{x-7}\)
=>8-x-8(x-7)=1
=>8-x-8x+56=1
=>-9x+64=1
=>-9x=-63
hay x=7(loại)
a, \(7x=-35\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
b, đk : x khác 7
\(8-x-8x+56=1\Leftrightarrow-9x=-63\Leftrightarrow x=7\left(ktm\right)\)
vậy pt vô nghiệm
2, thiếu đề

4x2 – 1 = (2x + 1)(3x – 5)
⇔ 4x2 – 1 – (2x + 1)(3x – 5) = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)(2x + 1) – (2x + 1)(3x – 5) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)[(2x – 1) – (3x – 5)] = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(2x – 1 – 3x + 5) = 0
⇔ (2x + 1)(4 – x) = 0
⇔ 2x + 1= 0 hoặc 4 – x = 0
+ 2x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = -1 ⇔ x = -1/2.
+ 4 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 4.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 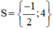

Cách 1:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 22. (x -1)2 = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 – [ 2(x – 1)]2 =0
⇔ [(x+ 1) + 2( x- 1)]. [(x+ 1) - 2( x- 1)]= 0
⇔ ( x+1+ 2x -2) . (x+1 – 2x + 2) =0
⇔ ( 3x- 1).( 3- x) = 0
⇔ 3x – 1 = 0 hoặc 3 – x= 0
+) 3x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 1 ⇔ x = 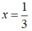
+) 3 – x = 0 ⇔ x= 3
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
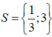
* Cách 2: Ta có:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ x2 + 2x +1- 4x2 + 8x – 4 = 0
⇔ - 3x2 + 10x – 3 = 0
⇔ (- 3x2 + 9x) + (x – 3) = 0
⇔ -3x (x – 3)+ ( x- 3) = 0
⇔ ( x- 3). ( - 3x + 1) = 0
⇔ x - 3 = 0 hoặc -3x + 1= 0
+) x - 3 = 0 x = 3
+) - 3x + 1 = 0 - 3x = - 1 ⇔ x = 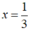
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
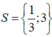
\(\left(x+1\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(< =>\left(x+1\right)^2=\left(2x-2\right)^2\)
\(< =>\left(x+1-2x+2\right)\left(x+1+2x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}-x+3=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Lời giải:
Vì $\sin x,\cos x\in [-1;1]$ nên:
$\cos ^{13}x\leq \cos ^2x; \sin ^{14}x\leq \sin ^2x$
$\Rightarrow \cos ^{13}x+\sin ^{14}x\leq \cos ^2x+\sin ^2x$
$\Leftrightarrow \cos ^{13}x+\sin ^{14}x\leq 1$
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\left\{\begin{matrix} \cos ^{13}x=\cos ^2x\\ \sin ^{14}x=\sin ^2x\end{matrix}\right.\)
$\Leftrightarrow x=2k\pi$ hoặc $x=k\pi -\frac{\pi}{2}$ với $k$ nguyên.