Bài toán : x/(x-1) + (2*y)/(y+1) = 3 , x/(x+1) + y/(y-1) = 2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
a.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} x\neq 0\\ 2x-1\geq 0\\ x^2-3x+2=(x-1)(x-2)\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x\neq 0\\ x\geq \frac{1}{2}\\ x\neq 1; x\neq 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
$\Leftrightarrow x\geq \frac{1}{2}; x\neq 1; x\neq 2$
b. \(\left\{\begin{matrix}
x^2-1=(x-1)(x+1)\neq 0\\
7-2x\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
x\neq \pm 1\\
x\leq \frac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} x\neq 0\\ 4-2x+x^2\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x\neq 0\\ (x-1)^2+3\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\neq 0\)
d.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} 25-x^2=(5-x)(5+x)\geq 0\\ x\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} -5\leq x\leq 5\\ x\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow 0\leq x\leq 5\)
a) \(y=\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{\sqrt[]{2x-1}}{x^2-3x+2}\)
Điều kiện \(\) \(2x-1\ge0;x\ne0;x^2-3x+2\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{2};x\ne0;\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{2};x\ne0;x\ne1;x\ne2\)

(x+y+z)^2=x^2+y^2+z^2
=>x^2+y^2+z^2+2(xy+yz+xz)=x^2+y^2+z^2
=>2(xy+yz+xz)=0
=>xy+yz+xz=0
1/x+1/y+1/z
=(xz+yz+xy)/xyz
=0/xyz=0

Bài 11:
Ta có: \(n^3-n^2+2n+7⋮n^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n^3+n-n^2-1+n+8⋮n^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n^2-64⋮n^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n^2+1\in\left\{1;5;13;65\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n^2\in\left\{0;4;64\right\}\)
hay \(n\in\left\{0;-2;2;8;-8\right\}\)

10:
Vì n là số lẻ nên n=2k-1
Số số hạng là (2k-1-1):2+1=k(số)
Tổng là (2k-1+1)*k/2=2k*k/2=k^2 là số chính phương
11:
n^3-n^2+2n+7 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^3+n-n^2-1+n+8 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n+8 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2-64 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2+1-65 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2+1 thuộc {1;5;13;65}
=>\(n\in\left\{0;2;-2;2\sqrt{3};-2\sqrt{3};8;-8\right\}\)

Bài 7:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double a,b,c;
int main()
{
cin>>a>>b>>c;
if ((a+b>c) && (a+c>b) && (b+c>a)) cout<<"Day la ba canh trong mot tam giac";
else cout<<"Day khong la ba canh trong mot tam giac";
return 0;
}

bài 1 : a,ta có 3/x-1 =4/y-2=5/z-3 => x-1/3=y-2/4=z-3/5
áp dụng .... => x-1+y-2+z-3 / 3+4+5 = x+y+z-1-2-3/3+4+5 = 12/12=1
do x-1/3 = 1 => x-1 = 3 => x= 4 ( tìm y,z tương tự
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: 3/x - 1 = 4/y - 2 = 5/z - 3 => x - 1/3 = y - 2/4 = z - 3/5 áp dụng ... =>x - 1 + y - 2 + z - 3/3 + 4 + 5 = x + y + z - 1 - 2 - 3/3 + 4 + 5 = 12/12 = 1 do x - 1/3 = 1 => x - 1 = 3 => x = 4 ( tìm y, z tương tự )

Bài 1 :
Cách 1 : Dùng hằng đẳng thức : \(A^3-B^3=\left(A-B\right)\left(A^2+AB+B^2\right)\)
Áp dụng hằng đẳng thức trên ta suy ra được : đpcm.
Cách 2 :
\(VT=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(=x^3+x^2+x-x^2-x-1\)
\(=x^3-1\left(VP\right)\)
suy ra : đpcm.
Bài 2 :
Hình như sai đề rồi á bạn . Đáp án đúng phải là \(x^4-y^4\) á cậu.
Cách 1 : Ta biến đổi vế phải thành vế trái .
Ta có : \(VP=x^4-y^4=\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(x^2-y^2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=\left(x^3+x^2y+xy^2+y^3\right)\left(x-y\right)\left(VT\right)\)
Suy ra : đpcm.
Cách 2 : Bạn cũng có thể dùng hằng đẳng thức hoặc nhân bung vế trái ra á.
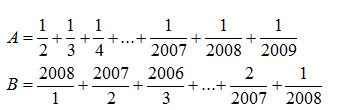
\(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{x}{x-1}+\frac{2y}{y+1}=3\\\frac{x}{x+1}+\frac{y}{y-1}=2\end{cases}}\)\(ĐKXĐ:x,y\ne\pm1\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{x\left(y+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(y+1\right)}+\frac{\left(x-1\right)2y}{\left(x-1\right)\left(y+1\right)}=3\\\frac{x\left(y-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(y-1\right)}+\frac{y\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(y-1\right)}=2\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{xy+x}{xy+x-y-1}+\frac{2xy-2y}{xy+x-y-1}=3\\\frac{xy-x}{xy-x+y-1}+\frac{xy+y}{xy-x+y-1}=2\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{xy+x+2xy-2y}{xy+x-y-1}=3\\\frac{xy-x+xy+y}{xy-x+y-1}=2\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{3xy+x-2y}{xy+x-y-1}=3\\\frac{2xy-x+y}{xy-x+y-1}=2\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}3xy+x-2y=3xy+3x-3y-3\\2xy-x+y=2xy-2x+2y-2\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}3xy+x-2y-3xy-3x+3y+3=0\\2xy-x+y-2xy+2x-2y+2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}-2x+y+3=0\\x-y+2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\hept{\begin{cases}-2\left(-2+y\right)+y+3=0\left(1\right)\\x=-2+y\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\left(1\right)< =>4-2y+y+3=0\)
\(< =>7-y=0< =>y=7\left(tmđk\right)\)
\(\left(2\right)< =>x=-2+7=5\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy nghiệm của hệ phương trình trên là \(\left\{5;7\right\}\)