x2 + 5x – 6 (phân tích thành nhân tử)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Cách 1: Tách một hạng tử thành tổng hai hạng tử để xuất hiện nhân tử chung.
a) x2 – 3x + 2
= x2 – x – 2x + 2 (Tách –3x = – x – 2x)
= (x2 – x) – (2x – 2)
= x(x – 1) – 2(x – 1) (Có x – 1 là nhân tử chung)
= (x – 1)(x – 2)
Hoặc: x2 – 3x + 2
= x2 – 3x – 4 + 6 (Tách 2 = – 4 + 6)
= x2 – 4 – 3x + 6
= (x2 – 22) – 3(x – 2)
= (x – 2)(x + 2) – 3.(x – 2) (Xuất hiện nhân tử chung x – 2)
= (x – 2)(x + 2 – 3) = (x – 2)(x – 1)
b) x2 + x – 6
= x2 + 3x – 2x – 6 (Tách x = 3x – 2x)
= x(x + 3) – 2(x + 3) (có x + 3 là nhân tử chung)
= (x + 3)(x – 2)
c) x2 + 5x + 6 (Tách 5x = 2x + 3x)
= x2 + 2x + 3x + 6
= x(x + 2) + 3(x + 2) (Có x + 2 là nhân tử chung)
= (x + 2)(x + 3)
Cách 2: Đưa về hằng đẳng thức (1) hoặc (2)
a) x2 – 3x + 2
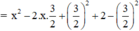
(Vì có x2 và 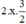 nên ta thêm bớt
nên ta thêm bớt 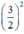 để xuất hiện HĐT)
để xuất hiện HĐT)
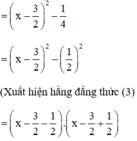
= (x – 2)(x – 1)
b) x2 + x - 6

= (x – 2)(x + 3).
c) x2 + 5x + 6

= (x + 2)(x + 3).

`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`a)`
`6x^2 - 3xy`
`= 3x(2x - y)`
`b)`
Bạn ghi lại đầy đủ thông tin
`c)`
`x^2 - 5x + 6`
`= x^2 - 2x - 3x +6`
`= (x^2 - 2x) - (3x - 6)`
`= x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2)`
`= (x - 3)(x - 2)`
a: =3x*2x-3x*y
=3x(2x-y)
c: =x^2-2x-3x+6
=x(x-2)-3(x-2)
=(x-2)(x-3)
b: Bạn ghi đầy đủ đề nha bạn

a) (x - 2)(x - 3). b) 3(x - 2)(x + 5).
c) (x - 2)(3x + 1). d) (x-2y)(x - 5y).
e) (x + l)(x + 2)(x - 3). g) (x-1)(x + 3)( x 2 + 3).
h) (x + y - 3)(x - y + 1).

Bài 2:
a: \(x^2+5x-6=\left(x+6\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
b: \(5x^2+5xy-x-y\)
\(=5x\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(5x-1\right)\)
c:\(-6x^2+7x-2\)
\(=-6x^2+3x+4x-2\)
\(=-3x\left(2x-1\right)+2\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-1\right)\left(-3x+2\right)\)
1.
a) \(=x^2\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=x^2\left(x+1\right)^2\)
b) \(=\left(x+y\right)^3-\left(x+y\right)=\left(x+y\right)\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-1\right]\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\left(x+y+1\right)\)
c) \(=5\left[\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)-4z^2\right]=5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4z^2\right]\)
\(=5\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\)
2.
a) \(=x\left(x+2\right)+3\left(x+2\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
b) \(=5x\left(x+y\right)-\left(x+y\right)=\left(x+y\right)\left(5x-1\right)\)
c) \(=-\left[3x\left(2x-1\right)-2\left(2x-1\right)\right]=-\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)\)
3.
b) \(=2x\left(x-1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+5\right)\)
c) \(=-\left[5x\left(x-3\right)-1\left(x-3\right)\right]=-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-1\right)\)
4.
a) \(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\Rightarrow2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(2-x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

x2 + 5x + 4
= x2 + x + 4x + 4
(Tách 5x = x + 4x)
= x(x + 1) + 4(x + 1)
(có x + 1 là nhân tử chung)
= (x + 1)(x + 4)

\(x^2+xy-5x-5y=\left(x^2+xy\right)-\left(5x+5y\right)\)
\(=x\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x+y\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(x+y\right)\)
x(x+y)-5(x+y) = (x-5)(x+y) bài này mik hok qua rùi mik đang ôn tập nên là mik tự làm chứ ko chép mấy câu trả lời khác

-Đặt \(t=\left(x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(\left(x^2-x+1\right)^2-5x\left(x^2-x+1\right)+4x^2\)
\(=t^2-5xt+4x^2\)
\(=t^2-4xt-xt+4x^2\)
\(=t\left(t-4x\right)-x\left(t-4x\right)\)
\(=\left(t-4x\right)\left(t-x\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-x+1-4x\right)\left(x^2-x+1-x\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-5x+1\right)\left(x^2-2x +1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-5x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2\)
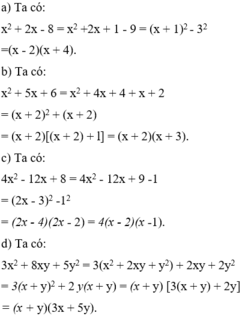

\(x^2+5x-6=\left(x+6\right)\left(x-1\right)\)