0,ab x 87 = 1a,b1
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta chứng minh BĐT
( a + b + c ) ( 1 a + 1 b + 1 c ) ≥ 9 ( * ) ( * ) < = > 3 + ( a b + b a ) + ( b c + c b ) + ( c a + a c ) ≥ 9
Áp dụng BĐT Cô – si cho hai số dương ta có:
a b + b a ≥ 2 b c + c b ≥ 2 c a + a c ≥ 2 =>(*) đúng
= > 9 a + b + c ≤ 1 a + 1 b + 1 c ≤ 3 = > a + b + c ≥ 3
Trở lại bài toán: Áp dụng BĐT Cô si cho hai số dương ta có 1 + b 2 ≥ 2 b
Ta có: a 1 + b 2 = a − a b 2 1 + b 2 ≥ a − a b 2 2 b = a − a b 2 ( 1 )
Tương tự ta có:
b 1 + c 2 ≥ b − b c 2 ( 2 ) c 1 + a 2 ≥ c − c a 2 ( 3 )
Cộng từng vế của (1), (2) và (3) ta có:
a 1 + b 2 + b 1 + c 2 + c 1 + a 2 ≥ a + b + c − 1 2 ( a b + b c + c a ) = > a 1 + b 2 + b 1 + c 2 + c 1 + a 2 + 1 2 ( a b + b c + c a ) ≥ a + b + c ≥ 3

\(a,A=\left(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+1}-3\right)\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\left(đk:x\ge0;x\ne1\right)\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{3\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}+1-3\left(x-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+2\sqrt{x}+1-3x+3}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+4}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(---\)
\(b,A< 0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}< 1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp với điều kiện của \(x\), ta được:
\(0\le x< 1\)
Vậy: ...
\(Toru\)
a) \(A=\left(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+1}-3\right)\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(A=\left[\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{3\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}+1-3x+3}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+4}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
b) \(A< 0\) khi
\(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}< 0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}< 1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp với đk:
\(0\le x< 1\)

a) \(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x-\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\right):\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{x-2\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(A=\left[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}+\dfrac{1.\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\right].\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(A=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}.\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
b) \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}-3=\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{9}{4}\)

a: Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{x^2-\sqrt{x}}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{2x+\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=x-\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}-1+2\sqrt{x}+2\)
\(=x-\sqrt{x}+1\)
Lời giải:
a.
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-1)(x+\sqrt{x}+1)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\frac{\sqrt{x}(2\sqrt{x}+1)}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{2(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-1)-(2\sqrt{x}+1)+2(\sqrt{x}+1)\)
\(=x-\sqrt{x}+1\)
b.
\(A=x-\sqrt{x}+1=(\sqrt{x}-\frac{1}{2})^2+\frac{3}{4}\geq \frac{3}{4}\)
Vậy $A_{\min}=\frac{3}{4}$ khi $\sqrt{x}=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{4}$

a: \(=\dfrac{x\sqrt{x}+26\sqrt{x}-19-2x-6\sqrt{x}+x-4\sqrt{x}+3}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\sqrt{x}-x+16\sqrt{x}-16}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}=\dfrac{x+16}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
b: Để A=4 thì \(x+16-4\sqrt{x}-12=0\)
=>x=4

Bài 1:
a: Ta có: \(x^2-2\sqrt{5}x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\sqrt{5}=0\)
hay \(x=\sqrt{5}\)
b: Ta có: \(\sqrt{x+3}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=1\)
hay x=-2

Bài 1 :
a, ĐKXĐ : \(\dfrac{1}{2-x}\ge0\)
Mà 1 > 0
\(\Rightarrow2-x>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x< 2\)
Vậy ...
b, Ta có : \(\sqrt[3]{125}.\sqrt[3]{216}-\sqrt[3]{512}.\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{1}{8}}\)
\(=5.6-\dfrac{8.1}{2}=26\)
1a) Để căn thức bậc 2 có nghĩa thì \(\dfrac{1}{2-x}\ge0\Rightarrow2-x>0\Rightarrow x< 2\)
b) \(\sqrt[3]{125}.\sqrt[3]{-216}-\sqrt[3]{512}.\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{1}{8}}=\sqrt[3]{5^3}.\sqrt[3]{\left(-6\right)^3}-\sqrt[3]{8^3}.\sqrt[3]{\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3}\)
\(=5.\left(-6\right)-8.\dfrac{1}{2}=-34\)
\(\dfrac{\sqrt{ab}-b}{b}-\sqrt{\dfrac{a}{b}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{b}\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{b}\right)^2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}}{\sqrt{b}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
\(=-\dfrac{\sqrt{b}}{\sqrt{b}}=-1< 0\)

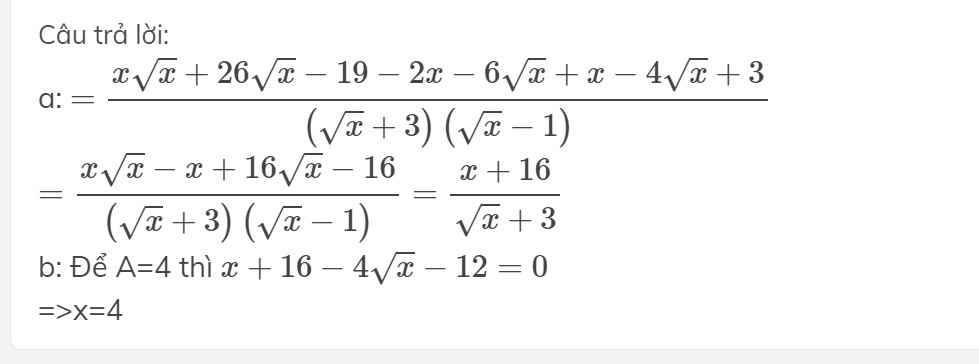
a=1
b=3
a=1
b=3