( x2+8x+12 )( x2-7x+12 ) = 16x2
Tìm x
Helppppp
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, 7x - 14
= 7(x-2)
b, 2x - 2y + \(x^2\)- xy
= (2x-2y) + (\(x^2\)-xy)
= 2(x-y) + x(x-y)
= (x-y)(2+x)
c, 6x + 12
= 6(x+2)
\(a,=7\left(x-2\right)\\ b,=2\left(x-y\right)+x\left(x-y\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(x-y\right)\\ c,=6\left(x+2\right)\\ d,\text{Sai đề}\)

a) x 2 – 7 x + 12 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -7; c = 12
⇒ Δ = b 2 – 4 a c = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . 12 = 1 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt x 1 ; x 2 thỏa mãn:
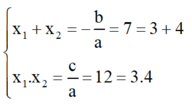
Vậy dễ dàng nhận thấy phương trình có hai nghiệm là 3 và 4.
b) x2 + 7x + 12 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 7; c = 12
⇒ Δ = b2 – 4ac = 72 – 4.1.12 = 1 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1; x2 thỏa mãn:
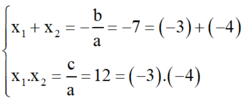
Vậy dễ dàng nhận thấy phương trình có hai nghiệm là -3 và -4.

\(\left(x-3\right)\left(4-x\right)>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3>0\\4-x>0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\hept{\begin{cases}x>3\\x< 4\end{cases}}\) (vô lí)
hoặc \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-3< 0\\4-x< 0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\hept{\begin{cases}x< 3\\x>4\end{cases}}\)(vô lí)
Vậy \(x=\Phi\)

\(a.x^2-7x-3x+21=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-7x\right)-\left(3x-21\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-7\right)-3\left(x-7\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b.x^2+6x+2x+12=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+6x\right)+\left(2x+12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+6\right)+2\left(x+6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c.x^2+4x+5x+20=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+4x\right)+\left(5x+20\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+4\right)+5\left(x+4\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+...+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>1/x+2-1/x+6=1/8
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>x^2+8x+12=32
=>x^2+8x-20=0
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>x=-10 hoặc x=2

a: \(x^2-6x+5=\left(x-5\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
b: \(x^2-x-12=\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
c: \(x^2+8x+15=\left(x+5\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
d: \(2x^2-5x-12=\left(x-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)\)
e: \(x^2-13x+36=\left(x-9\right)\left(x-4\right)\)
Ta có:
\(\left(x^2+8x+12\right)\left(x^2-7x+12\right)=16x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-7x+12+15x\right)\left(x^2-7x+12\right)=16x^2\)
Đặt \(x^2-7x+12=a\)
Khi đó phương trình trở thành:
\(\left(a+15x\right)a=16x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2+15ax=16x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2+15ax-16x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-ax+16ax-16x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(a-x\right)+16x\left(a-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-x\right)\left(a+16x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a-x=0\\a+16x=0\end{cases}}\)
+) Với \(a-x=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+12-x=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-8x+12=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
+) Với \(a+16x=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+12+16x=0\Leftrightarrow x^2+9x+12=0\)(vô nghiệm)
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{2;6\right\}\)