Tìm GTNN , GTLN
\(\sqrt{x-2}\)+ \(\sqrt{4-x}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
TXĐ: $[-1;1]$
$y'=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}-\frac{1}{2\sqrt{1-x}}+\frac{x}{2}$
$y'=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$
$f(0)=2$;
$f(1)=f(-1)=\sqrt{2}+\frac{1}{4}$
Vậy $f_{\min}=2; f_{\max}=\frac{1}{4}+\sqrt{2}$

Câu 2:
\(C=-x+\sqrt{x}\)
\(=-\left(x-\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(=-\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{4}\le\dfrac{1}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)

Lời giải:
Ta có:
$A^2=x+4+6-x+2\sqrt{(x+4)(6-x)}=10+2\sqrt{(x+4)(6-x)}\geq 10$
$\Rightarrow A\geq \sqrt{10}$ (do $A\geq 0$)
Vậy $A_{\min}=\sqrt{10}$. Giá trị này đạt được khi $(x+4)(6-x)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-4$ hoặc $x=6$
----------------------
Áp dụng BĐT Bunhiacopkxy:
$A^2\leq (x+4+6-x)(1+1)=10.2=20$
$\Rightarrow A\leq \sqrt{20}$
Vậy $A_{\max}=\sqrt{20}$

\(Q\le\sqrt{2\left(x-2+4-x\right)}=2\)
Bên cạnh đó \(2\le x\le4\)
=> \(Q\ge\sqrt{2}\)
Vậy GTLN là 2 đạt được khi x = 3
GTNN là \(\sqrt{2}\)đạt được khi x = 2 hoặc 4

\(A\le\sqrt{\left(3^2+4^2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(5-x\right)}=10\)
\(A_{max}=10\) khi \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x-1}}{3}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5-x}}{4}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{61}{25}\)
\(A=3\left(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}\right)+\sqrt{5-x}\ge3\left(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}\right)\ge3\sqrt{x-1+5-x}=6\)
\(A_{min}=6\) khi \(x=5\)

1:
a: \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}=1-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
căn x+1>=1
=>2/căn x+1<=2
=>-2/căn x+1>=-2
=>A>=-2+1=-1
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=0
b: 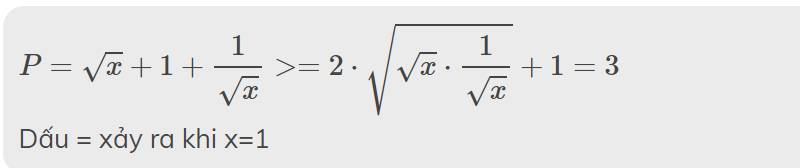
ĐK: \(2\le x\le4\)
Tìm max:
Ta có: \(\left(a-b\right)^2\ge0\Rightarrow2\left(a^2+b^2\right)\ge\left(a+b\right)^2\Rightarrow a+b\le\sqrt{2\left(a^2+b^2\right)}\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi a = b
Áp dụng vào \(\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{4-x}\le\sqrt{2\left(x-2+4-x\right)}=2\)
Tìm min: Áp dụng BĐT sau \(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\ge\sqrt{a+b}\)(tự chứng minh)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi a = 0 hoặc b = 0
\(\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{4-x}\ge\sqrt{x-2+4-x}=\sqrt{2}\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi x = 2 hoặc x = 4
\(\text{Ta co BĐT: }\sqrt{a\: }+\sqrt{b}\le\sqrt{2\left(a+b\right)}\text{ thật vậy:}\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\le\sqrt{2\left(a+b\right)}\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\right)^2\le2a+2b\left(vì:\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b};\sqrt{2\left(a+b\right)}\ge0\right)\Leftrightarrow a+2\sqrt{ab}+b\le2a+2b\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{ab}\le a+b\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)^2\ge0\left(\text{luôn đung}\right)\Rightarrow\sqrt{x\: -2}+\sqrt{4-x\: }\le\sqrt{2\left(x\: -2+4-x\: \right)}=\sqrt{4}=2\Rightarrow A_{max\: }=2\)
\(Dâu "=" \text{ra }\Leftrightarrow x\: =3\)
\(\text{Đạt: A=}\sqrt{x\: -2}+\sqrt{4-x\: }\Rightarrow A^2=x\: -2+4-x+2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(4-x\: \right)}\: =2+2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(4-x\: \right)}\ge2+0=2\left(vì:2\sqrt{\left(x\: -2\right)\left(4-x\: \right)}\ge2.0=0\right)\Rightarrow A_{min}=\sqrt{2}\left(vì:A=\sqrt{x\: -2}+\sqrt{4-x\: }\ge0+0=0\right).\text{Dâu "=" xay ra }\)\(khi:x\: =2hoac:x\: =4\)