Tìm x biết:
4x2 - 4x = 8
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b)x2-2x+1=4
⇔(x-1)2=4
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=2\\x-1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)x2-4x+4=9
⇔ (x-2)2=9
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=3\\x-2=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
d)4x2-4x+1=4
⇔ (2x-1)2=4
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=4\\2x-1=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e)x2-2x-8=0
⇔ x2-4x+2x-8=0
⇔ x(x-4)+2(x-4)=0
⇔(x-4)(x+2)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
f)9x2-6x-8=0
⇔ 9x2-12x+6x-8=0
⇔ 3x(3x-4)+2(3x-4)=0
⇔ (3x-4)(3x+2)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(x^6+2x^3+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3\right)^2+2x^3+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3=\left(-1\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
___________
\(x\left(x-5\right)=4x-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-5\right)-4\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
_____________
\(x^4-2x^2=8-4x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-2\right)+\left(4x^2-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-2\right)+4\left(x^2-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
_______________
\(\left(x^3-x^2\right)-4x^2+8x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Ta có: 1 - 4 x + 4 x 2 = 5 ⇔ 1 - 2 x 2 = 5
⇔ |1 - 2x| = 5 (3)
* Trường hơp 1: 1 - 2x ≥ 0 ⇔ 2x ≤ 1 ⇔ x ≤ 1/2 ⇒ |1 - 2x| = 1 - 2x
Suy ra: 1 - 2x = 5 ⇔ -2x = 5 - 1 ⇔ x = -2
Giá trị x = -2 thỏa mãn điều kiện x ≤ 1/2
Vậy x = -2 là nghiệm của phương trình (3).
* Trường hợp 2: 1 - 2x < 0 ⇔ 2x > 1 ⇔ x > 12 ⇒ |1 - 2x| = 2x - 1
Suy ra: 2x - 1 = 5 ⇔ 2x = 5 + 1 ⇔ x = 3
Giá trị x = 3 thỏa mãn điều kiện x > 1/2
Vậy x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (3).
Vậy x = -2 và x = 3.


4 x 2 - 4 x + 1 = 3
⇔ 2 x - 1 2 = 3 ⇔ 2 x - 1 = 3
⇔ [ 2 x - 1 = 3 2 x - 1 = - 3
Nên x = 2 hoặc x = -1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 2; x = - 1

căn
- Với x ≥ 3 thì |x - 3| = x - 3 nên ta được:
x - 3 = 9 ⇔ x = 12
- Với x < 3 thì |x - 3| = 3 - x nên ta được:
3 - x = 9 ⇔ x = -6
Vậy phương trình có hai nghiệm: x = 12; x = -6
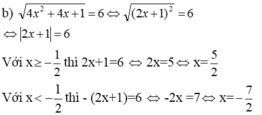

Bài 1:
a: \(49-4x^2=\left(7-2x\right)\left(7+2x\right)\)
b: \(x^3+8=\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\)
c: \(x^2+18xy+81y^2=\left(x+9y\right)^2\)

a.
\(1-4x^2=\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)\)
b.
\(8-27x^3=\left(2\right)^3-\left(3x\right)^3=\left(2-3x\right)\left(4+6x+9x^2\right)\)
c.
\(27+27x+9x^2+x^3=x^3+3.x^2.3+3.3^2.x+3^3\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)^3\)
d.
\(2x^3+4x^2+2x=2x\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)^2\)
e.
\(x^2-y^2-5x+5y=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y-5\right)\)
f.
\(x^2-6x+9-y^2=\left(x-3\right)^2-y^2=\left(x-3-y\right)\left(x-3+y\right)\)

a) \(\text{5x(x-2)+(2-x)=0}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x\left(x-2\right)-\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\5x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\text{x(2x-5)-10x+25=0}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(2x-5\right)-5\left(2x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=2,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\dfrac{25}{16}-4x^2+4x-1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{9}{16}-4x^2+4x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4x^2+4x+\dfrac{9}{16}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(-4x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)+\left(\dfrac{9}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}x\left(8x+1\right)+\dfrac{9}{16}\left(8x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}\right)\left(8x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}=0\\8x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{8}\\x=\dfrac{-1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(4x^2-4x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x-8=8-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy: x = -1 hoặc x = 2
4x2 - 4x = 8
=> 4x2 - 4x -8 = 0
=> 4( x2 - 2x -2 ) = 0
=> 4 ( x2 - x - x - 2 ) = 0
=> 4 ( x +1) ( x - 2 ) = 0
=> x + 1 = 0 hoặc x -2 = 0
x = -1 hoặc x = 2