X3+8
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) x 3 – 8 = 0
⇔ (x − 2)( x 2 + 2x + 4) = 0
⇔ x1 = 2; x2 = −1 + i 3 ; x2 = −1 - i 3
b) x 3 + 8 = 0
⇔ (x + 2)( x 2 − 2x + 4) = 0
⇔ x1 = −2; x2 = 1 + i 3 ; x3 = 1 - i 3

a)
=(x-2)3
b)\(\left(2-x\right)^3\)
c)\(\left(x+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)^3\)
d)\(\left(\dfrac{x}{2}+y\right)^3\)
e)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x-1-15\right)+25\left[3\left(x-1\right)-5\right]\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x-16\right)+25\left(3x-3-5\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x-16\right)+25\left(3x-8\right)\)

Ta có: \(x^6-2x^4+x^3+x^2-x\)
\(=x^6-x^4-x^4+x^2+x^3-x\)
\(=x^4\left(x^2-1\right)-x^2\left(x^2-1\right)+\left(x^3-x\right)\)
\(=x^2\left(x^2-1\right)^2+8\)
\(=\left(x^3-x\right)^2+8\)
=72

Lời giải:
$(x^3-3x^2+2x-6):(x-3)=[x(x-3)+2(x-3)]:(x-3)$
$=(x-3)(x+2):(x-3)=x+2$
-------------------
$(x^3-8):(x-2)=(x-2)(x^2+2x+4):(x-2)=x^2+2x+4$

a) \(\left(x^3-3x^2+2x-6\right):\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left[x^2\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)\right]:\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left[\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+2\right)\right]:\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=x^2+2\)
b) \(\left(x^3-8\right):\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right):\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=x^2+2x+4\)

a) TXĐ: R
y′ = 6x − 24 x 2 = 6x(1 − 4x)
y' = 0 ⇔ 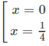
y' > 0 trên khoảng (0; 1/4) , suy ra y đồng biến trên khoảng (0; 1/4)
y' < 0 trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0 ); (14; + ∞ ), suy ra y nghịch biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ;0 ); (14; + ∞ )
b) TXĐ: R
y′ = 16 + 4x − 16 x 2 − 4 x 3 = −4(x + 4)( x 2 − 1)
y' = 0 ⇔ 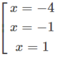
Bảng biến thiên:
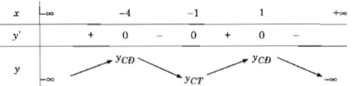
Vậy hàm số y đã cho đồng biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; -4) và (-1; 1), nghịch biến trên các khoảng (-4; -1) và (1; + ∞ )
c) TXĐ: R
y′ = 3 x 2 − 12x + 9
y' = 0
y' > 0 trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 1), (3; + ∞ ) nên y đồng biến trên các khoảng ( - ∞ ; 1), (3; + ∞ )
y'< 0 trên khoảng (1; 3) nên y nghịch biến trên khoảng (1; 3)
d) TXĐ: R
y′ = 4 x 3 + 16 = 4x( x 2 + 4)
y' = 0 ⇔ 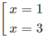
y' > 0 trên khoảng (0; + ∞ ) ⇒ y đồng biến trên khoảng (0; + ∞ )
y' < 0 trên khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0) ⇒ y nghịch biến trên khoảng ( - ∞ ; 0)

\(\left(\dfrac{1}{6}+4\right)\times\dfrac{3}{10}=\left(\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{24}{6}\right)=\dfrac{25}{6}\times\dfrac{3}{10}=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\left(\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{9}\right)\times\dfrac{3}{2}=\left(\dfrac{9}{72}-\dfrac{8}{72}\right)\times\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{1}{72}\times\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{1}{48}\)
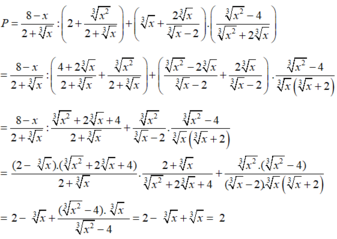
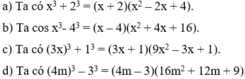
oooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo