Giải phương trình: \(\dfrac{x-1}{x}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x^{2^{ }}+x}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne-1,x\ne0\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+x}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-1+x-2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2-x-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+x-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)+\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm `S={2}`
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+x}\left(đk:x\ne0,-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{2x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+x-2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x-1+x-2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-2=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-1\right)^2-4.\left(-2\right)=9>0\Rightarrow\sqrt{\Delta}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow\)PT có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{1+3}{2}=2\left(n\right)\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{1-3}{2}=-1\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{2\right\}\)

\(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+10}=\dfrac{1}{12}\)
\(ĐK:x\ne0;-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{12\left(x+10\right)+12x}{12x\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x+10\right)}{12x\left(x+10\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\left(x+10\right)+12x-x\left(x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+120+12x-x^2-10x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+14x+120=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=20\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(o,\dfrac{x}{2x+6}-\dfrac{x}{2x-2}=\dfrac{3x+2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{3x+2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x+3\right)-2\left(3x+2\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2-3x-6x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-8x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

ĐKXĐ: `x ne 1`
`(5x-2)/(2-2x) + (2x+1)/2 = 1 - (x^2 + x -3)/(1-x)`
`<=> (5x-2)/[2(1-x)] + [(2x+1)(1-x)]/[2(1-x)] = [2(1-x)]/[2(1-x)] - [2(x^2 +x-3)]/[2(1-x)]`
`<=> (5x-2)/[2(1-x)] + (2x - 2x^2 +1 - x)/[2(1-x)] = (2-2x)/[2(1-x)] - (2x^2 +2x -6)/[2(1-x)]`
`=> 5x-2 + x - 2x^2 +1 = 2-2x - 2x^2 - 2x + 6`
`<=> (5x + x + 2x+2x) - (2x^2 + 2x^2) = 2 + 6 - 1 +2`
`<=> 10x = 9`
`<=> x= 9/10` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là `S = { 9/10}`

1: Ta có: \(\dfrac{3}{x+2}-\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
Suy ra: \(3x-6-x+1=2x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5=2x+4\left(vôlý\right)\)
2: Ta có: \(\dfrac{x-5}{2x-3}-\dfrac{x}{2x+3}=\dfrac{1-6x}{4x^2-9}\)
Suy ra: \(\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+3\right)-x\left(2x-3\right)=1-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-7x-15-2x^2+6x+6x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=16\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{16}{5}\)

a: =>(x-2)(2x+5)=0
=>x-2=0 hoặc 2x+5=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=-5/2
c: \(\dfrac{2x}{x-1}-\dfrac{x}{x+1}=1\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2+2x-x^2+x}{x^2-1}=1\)
=>x^2+3x=x^2-1
=>3x=-1
=>x=-1/3

\(a,\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = \(\left\{2;\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\Leftrightarrow2x.\left(x+1\right)-x.\left(x-1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\) ( ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-1;x\ne1\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x-x^2+x=x^2-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x^2+3x=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\) ( nhận )
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = \(\left\{-\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)

ĐKXĐ: x<>0; x<>-1
PT =>(x-1)(x+1)-x=2x-1
=>x^2-1-x=2x-1
=>x^2-x-2x=0
=>x(x-3)=0
=>x=0(loại) hoặc x=3(nhận)

Sửa đề: \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{3x+2}{x^2+2x}=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{3x+2}{x^2+2x}=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{3x+2}{x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{x}\)
=>\(x\left(2x-1\right)+3x+2=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
=>\(2x^2-x+3x+2=x^2+3x+2\)
=>\(2x^2+2x-x^2-3x=0\)
=>\(x^2-x=0\)
=>x(x-1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=1\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
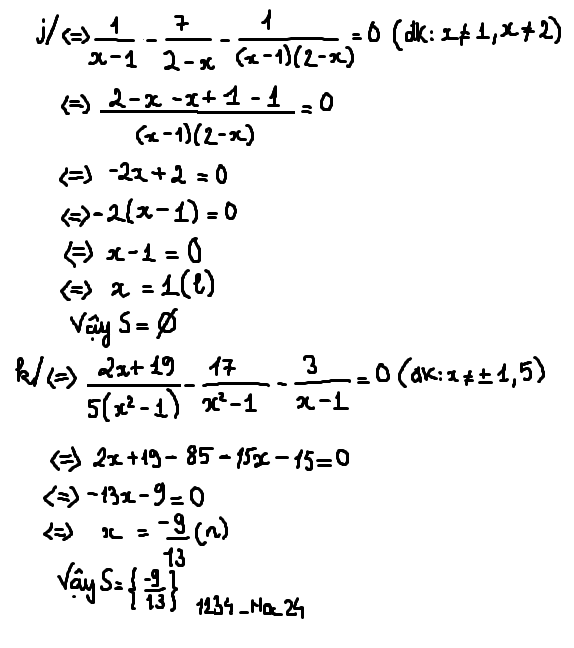
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{1.x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-1+x=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(KTM\right)\\x=1\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ..........
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x}\) ( ĐK : \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x^2+x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+x-1=2x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-2x+x-1+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là x = 1
\(\)