\(B=\left(1+\tan^2\right)\left(1-\sin^2\right)-\left(1+cotan^2\right)\left(1-\cos^2\right)\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cos2x-1\right)\left(sinx-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\sinx=3>1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
2. Bạn kiểm tra lại đề, pt này về cơ bản ko giải được.
3.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{3\left(sinx+\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}\right)}{\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}-sinx}-2cosx=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(1+cosx\right)}{1-cosx}+2\left(1+cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1+cosx\right)\left(\dfrac{3}{1-cosx}+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-1\left(loại\right)\\cosx=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt đã cho vô nghiệm

\(B=\left(1+\dfrac{sin^2a}{cos^2a}\right).cos^2a-\left(1+\dfrac{cos^2a}{sin^2a}\right).sin^2a\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(sin^2a+cos^2a\right)}{cos^2a}.cos^2a-\left(\dfrac{sin^2a+cos^2a}{sin^2a}\right).sin^2a\)
\(=1-1=0\)

a) \(4sinx-1=1\Leftrightarrow4sinx=2\Leftrightarrow sinx=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=30^o\)
b) \(2\sqrt{3}-3tanx=\sqrt{3}\Leftrightarrow3tanx=2\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{3}\Leftrightarrow tanx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=30^o\)
c) \(7sinx-3cos\left(90^o-x\right)=2,5\Leftrightarrow7sinx-3sinx=2,5\Leftrightarrow4sinx=2,5\Leftrightarrow sinx=\dfrac{5}{8}\Leftrightarrow x=30^o41'\)
d)\(\left(2sin-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(4cos-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2sin-\sqrt{2}=0\\4cos-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2sin=\sqrt{2}\\4cos=5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\cos=\dfrac{5}{4}\left(loai\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow x=45^o\)
Xin lỗi nãy đang làm thì bấm gửi, quên còn câu e, f nữa:"(
e) \(\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}-tanx=1\Leftrightarrow1+tan^2x-tanx-1=0\Leftrightarrow tan^2x-tanx=0\Leftrightarrow tanx\left(tanx-1\right)=0\Rightarrow tanx-1=0\Leftrightarrow tanx=1\Leftrightarrow x=45^o\)
f) \(cos^2x-3sin^2x=0,19\Leftrightarrow1-sin^2x-3sin^2x=0,19\Leftrightarrow1-4sin^2x=0,19\Leftrightarrow4sin^2x=0,81\Leftrightarrow sin^2x=\dfrac{81}{400}\Leftrightarrow sinx=\dfrac{9}{20}\Leftrightarrow x=26^o44'\)

b)
(sin2x + cos2x)cosx + 2cos2x - sinx = 0
⇔ cos2x (cosx + 2) + sinx (2cos2 x – 1) = 0
⇔ cos2x (cosx + 2) + sinx.cos2x = 0
⇔ cos2x (cosx + sinx + 2) = 0
⇔ cos2x = 0
⇔ 2x = 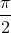 + kπ ⇔ x =
+ kπ ⇔ x = 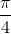 + k
+ k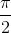 (k ∈
(k ∈ 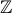 )
)
c)
Đáp án:
x=π6π6+ k2ππ
và x= 5π65π6+k2ππ (k∈Z)
Lời giải:
sin2x-cos2x+3sinx-cosx-1=0
⇔ 2sinxcosx-(1-2sin²x) +3sinx-cosx-1=0
⇔ 2sin²x+2sinxcosx+3sinx-cosx-2=0
⇔ (2sin²x+3sinx-2)+ cosx(2sinx-1)=0
⇔ (2sinx-1)(sinx+2)+cosx(2sinx-1)=0
⇔ (2sinx-1)(sinx+cosx+2)=0
⇔ sinx=1212
⇔ x=π6π6+ k2ππ
hoặc x= 5π65π6+k2ππ (k∈Z)
(sinx+cosx+2)=0 (vô nghiệm do sinx+cosx+2=√22sin(x+π4π4)+2>0)

Để chứng minh các định lượng đẳng cấp, ta sẽ sử dụng các công thức định lượng giác cơ bản và các quy tắc biến đổi đẳng thức. a) Bắt đầu với phương trình ban đầu: 1 - cos^2(π/2 - x) / (1 - sin^2(π/2 - x)) = -cot(π/2 - x) * tan( π/2 - x) Ta biết rằng: cos^2(π/2 - x) = sin^2(x) (công thức lượng giác) sin^2(π/2 - x) = cos^2(x) (công thức lượng giác) Thay vào phương trình ban đầu, ta có: 1 - sin^2(x) / (1 - cos^2(x)) = -cot(π/2 - x) * tan(π/ 2 - x) Tiếp theo, ta sẽ tính toán một số lượng giác: cot(π/2 - x) = cos(π/2 - x) / sin(π/2 - x) = sin(x) / cos(x) = tan(x) (công thức lượng giác) tan(π/2 - x) = sin(π/2 - x) / cos(π/2 - x) = cos(x) / sin(x) = 1 / tan(x) (công thức lượng giác) Thay vào phương trình, ta có: 1 - sin^2(x) / (1 - cos^2(x)) = -tan(x) * (1/tan(x)) = -1 Vì vậy, ta đã chứng minh là đúng. b) Bắt đầu với phương thức ban đầu: (1/cos^2(x) + 1) * tan(x) = tan^2(x) Tiếp tục chuyển đổi phép tính: 1/cos^2(x) + 1 = tan^2(x) / tan(x) = tan(x) Tiếp theo, ta sẽ tính toán một số giá trị lượng giác: 1/cos^2(x) = sec^2(x) (công thức) lượng giác) sec^2(x) + 1 = tan^2(x) + 1 = sin^2(x)/cos^2(x) + 1 = (sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) ))/cos^2(x) = 1/cos^2(x) Thay thế vào phương trình ban đầu, ta có: 1/cos^2(x) + 1 = 1/cos^2(x) Do đó, ta đã chứng minh được b)đúng.
ta có : \(B=\left(1+tan^2x\right)\left(1-sin^2x\right)-\left(1+cot^2x\right)\left(1-cos^2x\right)\)
\(=\left(1+\dfrac{sin^2x}{cos^2x}\right)\left(sin^2x+cos^2x-sin^2x\right)-\left(1+\dfrac{cos^2x}{sin^2x}\right)\left(sin^2x+cos^2x-cos^2x\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{sin^2x+cos^2x}{cos^2x}\left(cos^2x\right)-\dfrac{sin^2x+cos^2x}{sin^2x}\left(sin^2x\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}.cos^2x-\dfrac{1}{sin^2x}.\left(sin^2\right)x=1-1=0\)
nhớ ghi góc nha bn :) .