Tìm max:
-2x^2 - 3x +5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(B=-2\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}x\right)+5=-2\left(x^2-2x.\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{9}{16}\right)+5+\dfrac{9}{16}=-2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{25}{16}\le\dfrac{25}{16}\)
dấu = xảy ra khi x=3/4
vậy Bmax=....
tik mik nha

\(A=\dfrac{3x^2-6x+17}{x^2-2x+5}\)
\(=3+\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x+5}\)
Mà \(x^2-2x+5\ge4\)
=> \(\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x+5}\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=> A ≤ 7/2
Dấu "=" xảy ra ⇔ x = 1
Ta có : \(A=\dfrac{3x^2-6x+17}{x^2-2x+5}=\dfrac{3x^2-6x+15+2}{x^2-2x+5}=\dfrac{3\left(x^2-2x+5\right)+2}{x^2-2x+5}\)
\(=3+\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x+5}\)
- Thấy : \(x^2-2x+5=x^2-2x+1+4=\left(x-1\right)^2+4\)
Lại có : \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x+5}\le\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow3+\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x+5}\le\dfrac{7}{2}\)
\(HayA\le\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy MaxA = \(\dfrac{7}{2}\) Dấu " = " xảy ra <=> x - 1 = 0
<=> x = 1 .


a: A=-(x-7)^2-888<=-888
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=7
b: \(B=\left|2x-1\right|+\left|y-5\right|+\dfrac{8}{3}>=\dfrac{8}{3}\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=1/2 và y=5
c: \(C=\left(x+3\right)^2+\left|2y-5\right|-232>=-232\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=-3 và y=5/2

a/ Ta có ;
\(B=\left(\frac{2}{3}x-\frac{1}{5}\right)^2+3\)
Mà \(\left(\frac{2}{3}x-\frac{1}{5}\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\ge3\)
Để B đạt GTNN thì \(\left(\frac{2}{3}x-\frac{1}{5}\right)^2\) đạt GTNN
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi :
\(\left(\frac{2}{3}x-\frac{1}{5}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{3}x-\frac{1}{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{10}\)
Vậy B đạt GTNN = 3 khi x = 3/10
b, tương tự

\(D=-2x^2+3x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow D=-2\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}x\right)-1\)
\(\Rightarrow D=-2\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{4}-\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-1\)
\(\Rightarrow D=-2\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-1+\dfrac{9}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow D=-2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{7}{2}\le-\dfrac{7}{2}\left(-2\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2\le0,\forall x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow Max\left(D\right)=-\dfrac{7}{2}\left(tạix=\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)

\(B=3x^2+3x-1\)
\(=3\left(x^2+x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
\(=3\left(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{7}{12}\right)\)
\(=3\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{7}{4}>=-\dfrac{7}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x+1/2=0
=>\(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(C=-2x^2+7x+3\)
\(=-2\left(x^2-\dfrac{7}{2}x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{7}{4}+\dfrac{49}{16}-\dfrac{73}{16}\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x-\dfrac{7}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{73}{8}< =\dfrac{73}{8}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-7/4=0
=>x=7/4
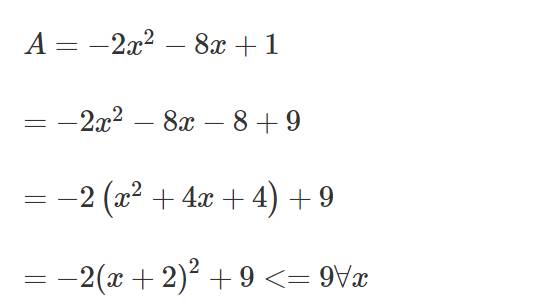
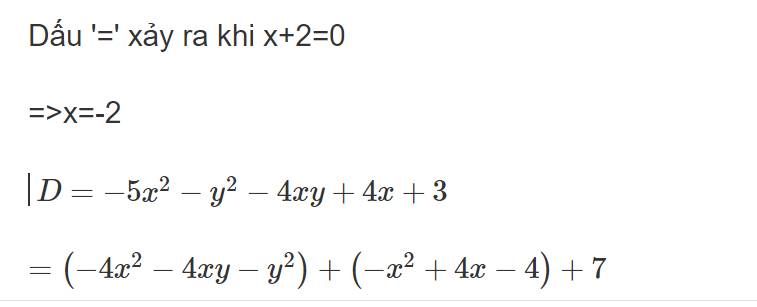
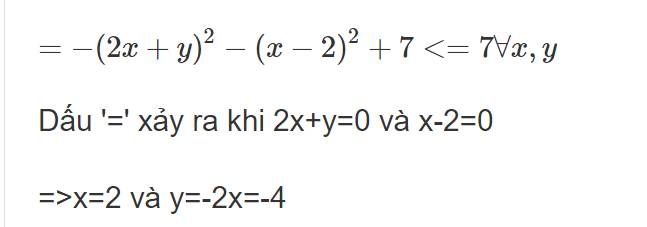

Bài 1.
A = 2x2 - x + 4 = 2( x2 - 1/2x + 1/16 ) + 31/8 = 2( x - 1/4 )2 + 31/8 ≥ 31/8 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 1/4
=> MinA = 31/8 <=> x = 1/4
Bài 2.
A = -x2 + 3x + 2 = -( x2 - 3x + 9/4 ) + 17/4 = -( x - 3/2 )2 + 17/4 ≤ 17/4 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 3/2
=> MaxA = 17/4 <=> x = 3/2
B = 3x2 + x - 5 = 3( x2 + 1/3x + 1/36 ) - 61/12 = 3( x + 1/6 )2 - 61/12 ≥ -61/12 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -1/6
=> MinB = -61/12 <=> x = -1/6
C = x2 + 3/2x - 5 = ( x2 + 3/2x + 9/16 ) - 89/16 = ( x + 3/4 )2 - 89/16 ≥ -89/16 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -3/4
=> MinC = -89/16 <=> x= -3/4
-2x2 - 3x + 5
\(=-2\left(x^2-\frac{3}{2}x+\frac{5}{2}\right)=-2\left(x^2-2.\frac{3}{4}x+\frac{9}{16}+\frac{31}{16}\right)\)
\(=-2\left(x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2-\frac{31}{8}\)
Có: \(\left(x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2\ge0,\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-2\left(x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2\le0,\forall x\)\(\Rightarrow-2\left(x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2-\frac{31}{8}\le-\frac{31}{8},\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-2x^2-3x+5\le-\frac{31}{8},\forall x\)
\(\text{Dấu "=" xảy ra }\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{3}{4}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\frac{3}{4}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow-2x^2-3x+5\text{ đạt max}\text{ }\Leftrightarrow\text{ }x=\frac{3}{4}\)
Vậy, ...