Giải PT vô tỉ sau:
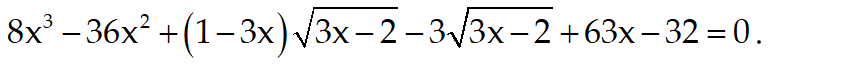
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b2
\(\left(\sqrt{2x^2-6x+2}-2x+3\right)\left(-\sqrt{2x^2-6x+2}-3x+4\right)=0\)
Dự đoán \(\frac{1}{2}\)là nghiệm của phương trình ( casio :v)
Áp dụng AM-GM:\(2VF=3.\sqrt[3]{4.8x\left(4x^2+3\right)}\le4+8x+4x^2+3=4x^2+8x+7\)
và \(4x^2+8x+7\le8x^4+2x^2+6x+8\)vì nó tương đương \(\left(2x-1\right)^2\left(2x^2+2x+1\right)\ge0\)
Do đó \(VT\ge VF\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi\(x=\frac{1}{2}\)


\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{14x+7}-7-\left(\sqrt{2x+3}-3\right)=\sqrt{5x+1}-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14x+7-49}{\sqrt{14x+7}+7}-\dfrac{2x+3-9}{\sqrt{2x+3}+3}=\dfrac{5x+1-16}{\sqrt{5x+1}+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14x-42}{\sqrt{14x+7}+7}-\dfrac{2x-6}{\sqrt{2x+3}+3}=\dfrac{5x-15}{\sqrt{5x+1}+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(\dfrac{14}{\sqrt{14x+7}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x+3}+3}-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{5x+1}+4}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\)

Lời giải:
Đặt $\sqrt[3]{2x+1}=a; \sqrt[3]{x}=b$ thì ta có:
$a+b=1$ và $a^3-2b^3=1$
$\Rightarrow a^3-2b^3=(a+b)^3$
$\Leftrightarrow a^3-2b^3=a^3+3a^2b+3ab^2+b^3$
$\Leftrightarrow 3a^2b+3ab^2+3b^3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow b(a^2+ab+b^2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow b=0$ hoặc $a^2+ab+b^2=0$
Nếu $b=0\Leftrightarrow \sqrt[3]{x}=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ (thử lại thấy tm)
Nếu $a^2+ab+b^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+\frac{b}{2})^2+\frac{3}{4}b^2=0$
$\Rightarrow a+\frac{b}{2}=b=0$
$\Rightarrow a=b=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt[3]{2x+1}=\sqrt[3]{x}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}{2}=0$ (vô lý)
Vậy $x=0$

\(\text{∆}=\left(-4m\right)^2-4.m.\left(4m-1\right)\)
\(=16m^2-16m^2+4m\)
\(=4m\)
phương trình vô nghiệm khi \(\text{∆}< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow4m< 0\)
⇒ \(m< 0\)
`\Delta'=(-2m)^2-m(4m-1)=4m^2-4m^2+m=m`
Để phương trình vô nghiệm thì `\Delta'<0 => m<0`

\(pt\Rightarrow\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{2}+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}}=2-x\\ \Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\left(2-x\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{4}=\left(x-2\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=\left(x-2\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=x-2\left(1\right)\\\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=2-x\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tới đây giải \(pt\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\), sau đó thế lại vào cái pt ban đầu, từ đó nhận hoặc loại nghiệm tìm được
( Không giải được 2 cái kia thì cmt nhắc nha )
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Ta có: \(x+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{2}+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}+2\cdot\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{4}+2\cdot\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=-2\\\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}=-\dfrac{5}{2}\left(loại\right)\\\sqrt{x+\dfrac{1}{4}}=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
hay x=2(thỏa ĐK)
Vậy: x=2

Đk: \(x\ge-5\)
2 vế dương bình phương lên
\(2^2\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)^2}=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x+5\right)=x^2+4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+20=x^2+4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=4\left(tm\right)\\x=-4\left(loai\right)\end{array}\right.\)

Đk:\(x\in\left[1;\frac{5}{2}\right]\)
Ta thấy 2 vế luôn dương, bình phương lên đc:
\(\sqrt{\left(5-2x\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-2x=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Đk:\(\frac{5}{2}\le x\le1\)
2 vế dương bình lên ta có:
\(\sqrt{\left(5-2x\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-2x=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Đề không chính xác, phương trình này không giải được em nhé
dạ để e hỏi lại