tính gí trị biểu thức (2x+3) nhân (2x -3) - (2x+1)2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


(2x+3)(2x-3) - (2x+1)^2
<=> (2x)^2 - 9 - (2x)^2 + 4x + 1
<=> 4x - 8
nếu x = 1/2
=> 4*1/2 - 8
<=> 2 - 8
<=> -6

Đặt \(y=\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{23+\sqrt{513}}{4}}+\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{23-\sqrt{513}}{4}}\) ( bạn lập phương cả 2 vế nhé )
\(\Leftrightarrow2y^3=6y+23\left(1\right)\)
theo đề bài,ta có: \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(y-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=y-1\Leftrightarrow y=3x+1\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow2y^3=54x^3+54x^2+18x+2\left(3\right)\)
Thế (2) và (3) vào (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow54x^3+54x^2+18x+2=6\left(3x+1\right)+23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow54x^3+54x^2+18x+2=18x+6+23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow54x^3+54x^2=27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+2x^2=1\)
\(A=2x^3+2x^2+1\)
\(A=1+1=2\)

Q=x^6+x^5+x^5+x^4+x^4+x^3+x^3+x^2+x^2+x+x+1
=x^4(x^2+x)+x^3(x^2+x)+x^2(x^2+x)+x(x^2+x)+1+x+1
=x^4+x^3+x^2+x+x+2
=x^4+x^3+x^2+2x+2
=x^2(x^2+x)+x^2+x+x+2
=x^2+1+x+2
=x^2+x+3
=1+3
=4
Cho x,y>0 và x+y \(\ge\)3 .Tìm gí trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức A=\(2x^2+y^2+\frac{28}{x}+\frac{1}{y}\)

Ta có:
\(A=2x^2+y^2+\frac{28}{x}+\frac{1}{y}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{14}{x}+\frac{14}{x}+\frac{7}{4}x^2\right)+\left(\frac{1}{2y}+\frac{1}{2y}+\frac{y^2}{2}\right)+\frac{x^2}{4}+\frac{y^2}{2}\)
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy cho 3 số dương và BĐT Bunyakovsky dạng cộng mẫu ta có:
\(A\ge3\sqrt[3]{\frac{14}{x}\cdot\frac{14}{x}\cdot\frac{7}{4}x^2}+3\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{2y}\cdot\frac{1}{2y}\cdot\frac{y^2}{2}}+\frac{\left(x+y\right)^2}{4+2}\)
\(\ge3\cdot7+3\cdot\frac{1}{2}+\frac{3^2}{6}=21+\frac{3}{2}+\frac{3}{2}=24\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi: x = 2 , y = 1

a: |2x-3|=1
=>2x-3=1 hoặc 2x-3=-1
=>x=1(nhận) hoặc x=2(loại)
KHi x=1 thì \(A=\dfrac{1+1^2}{2-1}=2\)
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1; x<>2
\(B=\dfrac{2x^2-4x+3x+3-2x^2-1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{x+1}\)

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(B=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{2x-2}+\dfrac{3}{2x-2}-\dfrac{x+3}{2x+2}\right):\left(1-\dfrac{x-3}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-1}{2x-2}-\dfrac{x+3}{2x+2}\right):\left(\dfrac{x+1-x-3}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{-2}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-1-x^2-2x+3}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2x+2}{2\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: Khi x=2005 thì \(B=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

a:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
b: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{2x-2}+\dfrac{3}{2x-2}-\dfrac{x+3}{2x+2}\right):\left(1-\dfrac{x-3}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{2\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3}{2\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{x+3}{2\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{x+1-x+3}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)+3\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x-2+3x+3-x^2-2x+3}{2\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2}{4\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{2\left(x-1\right)}\)
Khi x=2005 thì \(A=\dfrac{-1}{2\cdot\left(2005-1\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{4008}\)
Vì x=1 không thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
nên khi x=1 thì A không có giá trị
c: Để A=-1002 thì \(\dfrac{-1}{2\left(x-1\right)}=-1002\)
=>\(2\left(x-1\right)=\dfrac{1}{1002}\)
=>\(x-1=\dfrac{1}{2004}\)
=>\(x=\dfrac{1}{2004}+1=\dfrac{2005}{2004}\left(nhận\right)\)

Bài 1.
Ta có : B = ( x + 2 )2 + ( x - 2 )2 - 2( x + 2 )( x - 2 )
= [ ( x + 2 ) - ( x - 2 ) ]2
= ( x + 2 - x + 2 )2
= 42 = 16
=> B không phụ thuộc vào x
Vậy với x = -4 thì B vẫn bằng 16
Bài 2.
4x2 - 4x + 1 = ( 2x )2 - 2.2x.1 + 12 = ( 2x - 1 )2
Bài 3.
Ta có : \(A=\frac{3}{2}x^2+2x+3\)
\(=\frac{3}{2}\left(x^2+\frac{4}{3}x+\frac{4}{9}\right)+\frac{7}{3}\)
\(=\frac{3}{2}\left(x+\frac{2}{3}\right)^2+\frac{7}{3}\ge\frac{7}{3}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -2/3
=> MinA = 7/3 <=> x = -2/3
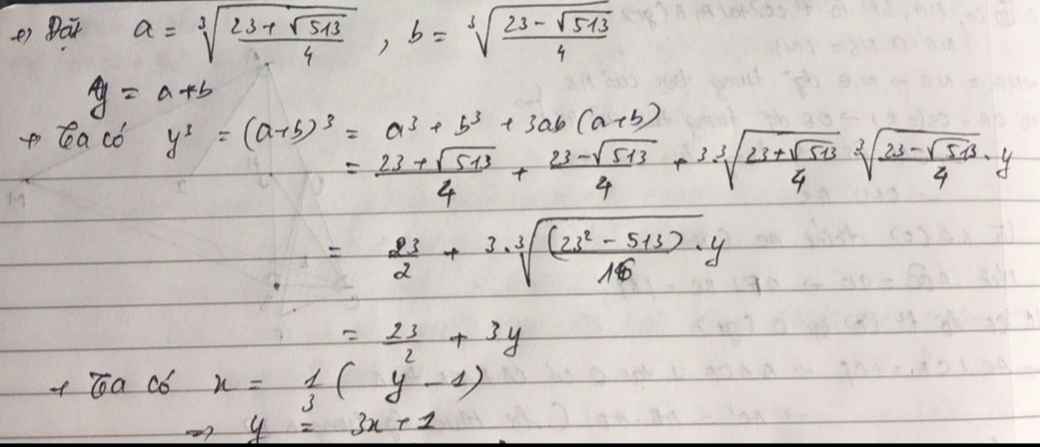
=(2x+3)2 - (2x+1)2
=(2x+3-x+1) (2x+3+2x+1)
(2x+3) (2x-3)- (2x+1)2
= (2x)^2 - 3^2 - (2x+1)2
= 4x^2 - 9 - (2x+1)2
= 4x^2 -9 - 4x2 - 4x -1
=(4x2 - 4x2) - (9+1) - 4x
= -10 -4x