Cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A. Kẻ AH vuông góc BC. Chứng minh: AB2 + CH2 = AC2 + BH2
Mọi người giúp mình bài này với nha,mình cảm ơn nhiều!
(Mọi người không cần vẽ hình đâu ạ!)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 88: Gọi độ dài của cạnh tam giác vuông cân là: a (cm) a > 0
Theo pytago ta có: a2 + a2 = 22
2a2 = 4
a2 = 2
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=\sqrt{2}\\a=-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vì a > 0 nên a = - \(\sqrt{2}\) (loại)
Độ dài cạnh góc vuông của tam giác vuông cân là \(\sqrt{2}\) cm
b, a2 + a2 = (\(\sqrt{2}\))2
2a2 = 2
a2 = 1
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\a=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì a > 0 nên a = - 1 loại
Vậy cạnh góc vuông của tam giác vuông cân là 1 cm

a) (2x - 5)2 - (5 + 2x) = 0
<=> 4x2 - 22x + 20 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-\dfrac{11}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{41}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pm\sqrt{41}+11}{4}\)
b) \(27x^3-54x^2+36x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x^2-6x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\) (Vì \(3x^2-6x+4=3\left(x-1\right)^2+1>0\forall x\))
c) x3 + 8 - (x + 2).(x - 4) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right).\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-3x+8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\) (Vì \(x^2-3x+8=\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{23}{4}>0\))
d) \(x^6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2\right)^3-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=0\) (Vì \(x^4+x^2+1>0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm1\)
\(d,x^6-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2\right)^3-1^3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+1=0\\x^4+x^2+1=0\left(Vô.lí,vì:x^4\ge0;x^2\ge0,\forall x\in R\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\left(x^3+8\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^3+8\right)-\left(x^2-2x-8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2+2x+16=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^3+2x^2-3x^2-6x+8x+16=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+2\right)-3x\left(x+2\right)+8\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x+8\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x+8=0\left(Vô.lí\right)\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)

Ta có :
\(AH^2=AB^2+BH^2\left(1\right)\) (Δ ABH vuông tại H)
\(AH^2=AC^2+CH^2\left(2\right)\) (Δ ACH vuông tại H)
\(\left(1\right),\left(2\right)\Rightarrow AB^2+BH^2=AC^2+CH^2\)
\(\Rightarrow CH^2=AB^2+BH^2-AC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow CH^2=81+676-121=636\)
\(\Rightarrow CH=\sqrt[]{636}=\sqrt[]{4.159}=2\sqrt[]{159}\left(cm\right)\)
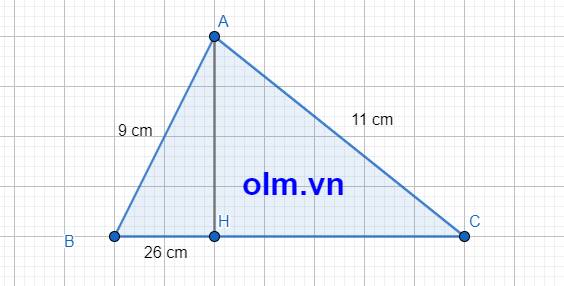
Vì AH là đường cao của tam giác ABC nên AH \(\perp\) BC \(\equiv\) H
⇒ \(\Delta\) AHB \(\perp\) \(\equiv\) H \(\Rightarrow\) AB > BH ⇒ 9 cm > 26 cm vô lý
Em có hai sựa lựa chọn: 1 là em chỉ ra cái sai của cô
2 là em xem lại đề bài của em

\(AH^2=BH.CH=18.32=576\Rightarrow AH=24\left(cm\right)\)
\(AB^2=AH^2+BH^2=576+324=900\) (Δ ABH vuông tại H)
\(\Rightarrow AB=30\left(cm\right)\)
\(AC^2=AH^2+CH^2=576+1024=1600\) (Δ ACH vuông tại H)
\(\Rightarrow AC=40\left(cm\right)\)
Xét tam giác AHB vuông tại H có:
AH2+HB2=AB2(định lý pythagore) (1)
Xét tam giác AHC vuông tại H có:
HA2+HC2=AC2 (định lý pythagore) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) ta cộng lại vế theo vế, có:
2AH2+BH2+CH2=AB2+AC2
<=>2AH2+BH2+CH2=BC2
<=> 2AH2+182+322=(18+32)2
<=>2AH2+1348=2500
<=>2AH2=2500-1348
<=>2AH2=1152
<=>AH2=1152:2
<=>AH2=576
<=>AH=\(\sqrt{576}\)
<=>AH=24(cm)
-Ta thay AH=24cm vào (1) ta có:
HB2+AH2=AB2
<=>182+242=AB2
<=>900=AB2
<=>\(AB=\sqrt{900}=30\)(cm)
-Ta thay AH=24cm vào (2) ta có:
HC2+HA2=AC2
<=>322+242=AC2
<=>1600=AC2
\(\Leftrightarrow AC=\sqrt{1600}=40\left(cm\right)\)
Vậy AB=30cm; AC=40cm

Hình a, b, c là tứ giác lồi
* Hình a:
- Các cạnh: AB, BC, CD, AD
- Các đỉnh: A, B, C, D
- Các góc: \(\widehat{ABC},\widehat{BCD},\widehat{CDA},\widehat{DAB}\)
* Hình b:
- Các cạnh: EF, FG, GH, HE
- Các đỉnh: E, F, G, H
- Các góc: \(\widehat{HEF},\widehat{EFG},\widehat{FGH},\widehat{GHE}\)
* Hình c:
- Các cạnh: \(IJ,JK,KL,LI\)
- Các đỉnh: \(I,J,K,L\)
- Các góc: \(\widehat{LIJ},\widehat{IJK},\widehat{JKL},\widehat{KLI}\)
Tứ giác lồi ABCD có 4 canh: AB,BC,CD,DA và 4 đỉnh: A,B,C,D và 4 góc \(\widehat{A},\widehat{B},\widehat{C},\widehat{D}\)
Tứ giác lồi EFGH có 4 canh: EF, FG, GH, HE và 4 đỉnh: E,F,G,H và 4 góc \(\widehat{E},\widehat{F},\widehat{G},\widehat{H}\)
Tứ giác lồi IJKL có 4 canh: IJ, JK, KL, LI và 4 đỉnh I,J,K,L và 4 góc \(\widehat{I},\widehat{J},\widehat{K},\widehat{L}\)
Hình 4 là ngũ giác và hình 5 là tam giác

E = - \(x^2\) + 2\(x\) - 1
E = - (\(x^2\) - 2\(x\) + 1)
E = - (\(x\) - 1)2
(\(x\) - 1) ≥ 0 ⇒ - (\(x\) - 1)2 ≤ 0
Emax = 0 ⇔ \(x\) = 1
Để tìm các điểm tới hạn của hàm E, chúng ta cần tìm các giá trị của x tại đó đạo hàm của E bằng 0.
Lấy đạo hàm của E theo x, ta được:
E' = -2x + 2
Đặt E' bằng 0 và tìm x:
-2x + 2 = 0
-2x = -2
x = 1
Vậy điểm tới hạn của E là x=1.
Để tìm các điểm tới hạn của hàm C, chúng ta cần tìm các giá trị của x tại đó đạo hàm của C bằng 0.
Lấy đạo hàm của C theo x, ta được:
C' = (2x)(3x-10)(3x-16) + (x^2-1)(3)(3x-10) + (x^2-1)(3)(3x-16)
Đặt C' bằng 0 và giải tìm x:
(2x)(3x-10)(3x-16) + (x^2-1)(3)(3x-10) + (x^2-1)(3)(3x-16) = 0
Phương trình này khá phức tạp và không có nghiệm đơn giản. Nó sẽ yêu cầu thao tác đại số hơn nữa hoặc các phương pháp số để tìm các điểm tới hạn của C.

Sửa đề là \(a+b=5\) nhé.
Có 2 cách để giải dạng bài này. Cách 1 là từ điều kiện đề cho, giải hệ phương trình tìm được \(a,b\) rồi thay số vào tính. Nhưng trong nhiều trường hợp cách này khá dài dòng nên mình sẽ làm theo cách thứ 2 như sau:
\(A=a^2+b^2=\left(a+b\right)^2-2ab=5^2-2.3=19\)
\(B=a^3+b^3=\left(a+b\right)^3-3ab\left(a+b\right)=5^3-3.3.5=80\)
\(AB^2=AH^2+BH^2\Rightarrow AH^2=AB^2-BH^2\left(1\right)\left(Pitago\right)\)
\(AC^2=AH^2+CH^2\Rightarrow AH^2=AC^2-CH^2\left(2\right)\left(Pitago\right)\)
\(\left(1\right),\left(2\right)\Rightarrow AC^2-CH^2=AB^2-BH^2\)
\(\Rightarrow AB^2+CH^2=AC^2+BH^2\)
\(\Rightarrow dpcm\)
Ta có \(AB^2-AC^2=\left(BH^2+AH^2\right)-\left(CH^2+AH^2\right)\) \(=BH^2-CH^2\) \(\Rightarrow AB^2+CH^2=AC^2+BH^2\), đpcm.
(Bài này kết quả vẫn đúng nếu không có điều kiện tam giác ABC vuông tại A.)