Cho |x|=|y| và x>0; y<0. Tính giá trị biểu thức 2x+y
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\dfrac{6^{13}-3\cdot6^{12}+3^{13}}{9^5\left(4^6+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2^{13}\cdot3^{13}-2^{12}\cdot3^{13}+3^{13}}{3^{10}\left(2^{12}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3^{12}\left(2^{13}-2^{12}+1\right)}{3^{10}\left(2^{12}+1\right)}=\dfrac{3^2\cdot\left[2^{12}\left(2-1\right)+1\right]}{2^{12}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{9\left(2^{12}+1\right)}{2^{12}+1}\)
=9

Bn viết sai hoặc là viết thiếu câu hỏi r.
Chớ mik đọc hổng hỉu j hớt á

\(\dfrac{x+5}{97}+\dfrac{x+5}{98}+\dfrac{x+5}{99}=0\\
\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right).\left(\dfrac{1}{97}+\dfrac{1}{98}+\dfrac{1}{99}\right)=0\)
Vì \(\dfrac{1}{97}+\dfrac{1}{98}+\dfrac{1}{99}\ne0\) nên:
\(x+5=0\\
\Rightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy...
\(\dfrac{x+5}{97}+\dfrac{x+5}{98}+\dfrac{x+5}{99}=0\)
=>\(\left(x+5\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{97}+\dfrac{1}{98}+\dfrac{1}{99}\right)=0\)
=>x+5=0
=>x=-5

(3x-5)(2y+7)=100
=>(3x-5;2y+7)\(\in\){(1;100);(100;1);(-1;-100);(-100;-1);(2;50);(50;2);(-2;-50);(-50;-2);(4;25);(25;4);(-4;-25);(-25;-4);(5;20);(20;5);(-5;-20);(-20;-5);(10;10);(-10;-10)}
=>(3x;2y)\(\in\){(6;93);(105;-6);(4;-107);(-95;-8);(7;43);(55;-5);(3;-57);(-45;-9);(9;18);(30;-3);(1;-32);(-20;-11);(10;13);(25;-2);(0;-27);(-15;-12);(15;3);(-5;-17)}
=>(x;y)\(\in\){(2;93/2);(35;-3);(4/3;-107/2);(-95/3;-4);(7/3;43/2);(55/3;-5/2);(1;-57/2);(-15;-9/2);(3;9);(10;-3/2);(1/3;-16);(-20/3;-11/2);(10/3;13/2);(25/3;-1);(0;-27/2);(-5;-6);(5;3/2);(-5/3;-17/2)}
(3x - 5)(2y + 7) = 100
Ta có: 100 = 1 x 100 = 2 x 50 = 4 x 25
Do 2y + 7 là số lẻ nên 2y + 7 chỉ có thể = 1 hoặc 25
Trường hợp 1: 2y + 7 = 1
⇒ 2y = 1 - 7
⇒ 2y = -6
⇒ y = (-6) : 2
⇒ y = -3
Vậy 3x - 5 = 100
⇒ 3x = 100 + 5
⇒ 3x = 105
⇒ x = 105 : 3
⇒ x = 35
Trường hợp 2: 2y + 7 = 25
⇒ 2y = 25 - 7
⇒ 2y = 18
⇒ y = 18 : 2
⇒ y = 9
Vậy 3x - 5 = 4
⇒ 3x = 4 + 5
⇒ 3x = 9
⇒ x = 9 : 3
⇒ x = 3
Vậy (x; y) ϵ {(35; -3); (3; 9)}


|x-1|+|2x-2|+|3x-3|=12
=>\(\left|x-1\right|+2\left|x-1\right|+3\left|x-1\right|=12\)
=>\(6\left|x-1\right|=12\)
=>|x-1|=2
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=2\\x-1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: \(\widehat{MON}+\widehat{O_1}+45^0=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{O_1}=180^0-90^0-45^0=45^0\)
Ta có: \(\widehat{O_1}=\widehat{MNO}\left(=45^0\right)\)
mà hai góc này là hai góc ở vị trí so le trong
nên OB//AM
b: Ta có: OB//AM
MA\(\perp\)AB
Do đó: OB\(\perp\)BA

a: m\(\perp\)a
n\(\perp\)a
Do đó: m//n
b: m//n
=>\(\widehat{A_1}=\widehat{ABC}\)(hai góc so le trong)
=>\(\widehat{A_1}=72^0\)
c: Xét ΔABC có \(\widehat{BAC}+\widehat{ACB}+\widehat{ABC}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{C_1}=180^0-64^0-72^0=44^0\)
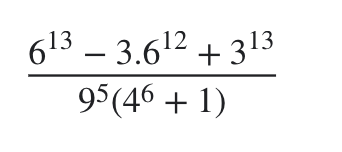

|x|=|y|
mà x>0; y<0
nên x=-y
2x+y=-2y+y=-y
\(\left|x\right|=\left|y\right|\) và \(x>0;y< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow y=-x\)
\(\Rightarrow2x\pm x=x\)
Vậy \(2x+y=x\)