
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(A=\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x^3-1}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)\left(\dfrac{x+2}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x}\right)\left(x\ne1;0\right)\\ =\left[\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x^2+x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\right]\left[\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right]\\ =\dfrac{x+1-x^2-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x^2+2x-x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{-x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x^2+x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{-x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\\ =\dfrac{-x}{x^2-2x+1}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;0\right\}\)
\(A=\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x^3-1}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)\left(\dfrac{x+2}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)-x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1-x^2-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x^2+x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\cdot x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{-x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)

a: Xét (O) có
CM,CA là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: CM=CA và OC là phân giác của góc MOA
Xét (O) có
DM,DB là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: DM=DB và OD là phân giác của góc MOB
AC+BD
=CM+MD
=CD
b: \(\widehat{COD}=\widehat{COM}+\widehat{DOM}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\widehat{MOA}+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\widehat{MOB}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\widehat{MOA}+\widehat{MOB}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\widehat{AOB}=90^0\)
=>ΔCOD vuông tại O
c: Xét ΔCOD vuông tại O có OM là đường cao
nên \(OM^2=MC\cdot MD\)

Bài 4:
d:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+4}{x-1}+\dfrac{x-4}{x+1}=\dfrac{x+8}{x-2}+\dfrac{x-8}{x+2}+6\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)+\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+8\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-8\right)\left(x-2\right)+6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2+8}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+32+6x^2-24}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2+8}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{8x^2+8}{x^2-4}\)
=>\(\left(2x^2+8\right)\left(x^2-4\right)=\left(8x^2+8\right)\left(x^2-1\right)\)
=>\(2x^4-32=8x^4-8\)
=>\(-6x^4=24\)
=>\(x^4=-4\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy: Phương trình vô nghiệm
c:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;-3;-8;-10\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2+4x+3}+\dfrac{5}{x^2+11x+24}+\dfrac{2}{x^2+18x+80}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+8\right)}+\dfrac{2}{\left(x+8\right)\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+8}+\dfrac{1}{x+8}-\dfrac{1}{x+10}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+10}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{9}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>(x+1)(x+10)=52
=>\(x^2+11x-42=0\)
=>(x+14)(x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-14\left(nhận\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
b:
ĐXKĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-2;-3;-4;-5;-6\right\}\)\(\dfrac{1}{x^2+5x+6}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+7x+12}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+9x+20}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+11x+30}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+\dfrac{1}{x+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+5}+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>(x+2)(x+6)=32
=>\(x^2+8x-20=0\)
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\left(nhận\right)\\x=2\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: \(\dfrac{x^2}{x^2+2x+2}+\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-2x+2}-\dfrac{4x^2-20}{x^4+4}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^2\left(x^2-2x+2\right)+x^2\left(x^2+2x+2\right)-4x^2+20}{\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+2\right)}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^4-2x^3+2x^2+x^4+2x^3+2x^2-4x^2+20}{x^4+4}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^4+20}{x^4+4}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(322\left(x^4+4\right)=65\left(2x^4+20\right)\)
=>\(322x^4+1288-130x^4-1300=0\)
=>\(192x^4=12\)
=>\(x^4=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a)\sqrt{2+\sqrt{3}}-\sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{4+2\sqrt{3}}}{\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{1^2+2\cdot1\cdot\sqrt{3}+\left(\sqrt{3}\right)^2}-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}\right)^2-2\cdot\sqrt{3}\cdot1+1^2}}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)^2}-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1-\sqrt{3}+1}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =\sqrt{2}\)
b)
\(\sqrt{3+\sqrt{5}}-\sqrt{3-\sqrt{5}}-\sqrt{2}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{6+2\sqrt{5}}}{\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}}{\sqrt{2}}-\sqrt{2}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^2+2\cdot\sqrt{5}\cdot1+1^2}}{\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^2-2\cdot\sqrt{5}\cdot1+1^2}}{\sqrt{2}}-\sqrt{2}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)^2}}{\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}}{\sqrt{2}}-\sqrt{2}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1-\sqrt{5}+1-2}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =\dfrac{0}{\sqrt{2}}\\ =0\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{45}\\\dfrac{y}{2}-\dfrac{x}{2}=28\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{45}\\\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{x}{2}+28\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x+56}=\dfrac{1}{45}\\y=x+56\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}45\left(x+56\right)+45x=x\left(x+56\right)\\y=x+56\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}90x+2520=x^2+56x\\y=x+56\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-34x-2520=0\\y=x+56\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=70\\x=-36\end{matrix}\right.\\y=x+56\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x = 70 => y = 70 + 56 = 126
Khi x = -36 => y = (-36) + 56 = 20

a.
Gọi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}n_{CaCO_3}=x\left(mol\right)\\n_{MgCO_3}=y\left(mol\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề có hệ phương trình: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}100x+84y=4,68\\x+y=\dfrac{1,2395}{24,79}=0,05\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0,03\\y=0,02\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(m_{CaCO_3}=0,03.100=3\left(g\right),m_{MgCO_3}=0,02.84=1,68\left(g\right)\)
b.
\(CM_{HCl}=\dfrac{2\left(x+y\right)}{0,25}=0,4\left(M\right)\)
\(n_{CO_2}=\dfrac{1,2395}{24,79}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH:
\(CaCO_3+2HCl\rightarrow CaCl_2+H_2O+CO_2\)
x 2x x x x
\(MgCO_3+2HCl\rightarrow MgCl_2+H_2O+CO_2\)
y 2y y y y
Có hệ PT:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}100x+84y=4,68\\x+y=0,05\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0,03;y=0,02\)
\(a,m_{CaCO_3}=0,03.100=3\left(g\right)\)
\(m_{MgCO_3}=4,68-3=1,68\left(g\right)\)
b, \(C_{M\left(HCl\right)}=\dfrac{0,1}{0,25}=\dfrac{2}{5}\left(M\right)\)
\(C_{M\left(CaCl_2\right)}=\dfrac{0,03}{0,25}=\dfrac{3}{25}\left(M\right)\)
\(C_{M\left(MgCl_2\right)}=\dfrac{0,02}{0,25}=\dfrac{2}{25}\left(M\right)\)

Sửa đề: B là giao điểm có hoành độ dương của (P) và (d)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (P) và (d):
−x² = x − 2
x² + x − 2 = 0
x² − x + 2x − 2 = 0
(x² − x) + (2x − 2) = 0
x(x − 1) + 2(x− 1) = 0
(x − 1)(x + 2) = 0
x − 1 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0
*) x − 1 = 0
x = 1
y = −1² = −1
B(1; −1)
*) x + 2 = 0
x = −2
y = −(−2)² = −4
A(−2; −4)
* Phương trình đường thẳng OB:
Gọi (d'): y = ax + b là phương trình đường thẳng OB
Do (d') đi qua O nên b = 0
=> (d'): y = ax
Do (d') đi qua B(1; −1) nên:
a = −1
=> (d'): y = −x
Gọi (d''): y = a'x + b' là đường thẳng đi qua A(−2; −4)
Do (d'') // (d') nên a' = −1
=> (d''): y = −x + b
Do (d'') đi qua A(−2; −4) nên:
−(−2) + b = −4
b = −4 − 2
b = −6
=> (d''): y = −x − 6

Kẻ đường cao BD của tam giác ABC \(\left(D\in AC\right)\)
Khi đó \(AD=AB.cosA=c.cosA\)
\(BD=AB.sinA=c\sqrt{1-cos^2A}\)
\(CD=AC-AD=b-c.cosA\)
Tam giác BCD vuông tại D
\(\Rightarrow BC^2=CD^2+BD^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2=\left(b-c.cosA\right)^2+\left(c\sqrt{1-cos^2A}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2=b^2-2bc.cosA+c^2.cos^2A+c^2\left(1-cos^2A\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc.cosA\)
Ta có đpcm.

5)
a) \(3x+8y=26\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{26-3x}{8}\)
Vì \(y\inℤ\) nên \(\dfrac{26-3x}{8}\inℤ\)
\(\Rightarrow26-3x⋮8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\equiv2\left(mod8\right)\)
Vì \(ƯCLN\left(3,8\right)=1\) nên đặt \(x=8q+r\left(0\le r< 8\right)\) thì:
\(3\left(8q+r\right)\equiv2\left(mod8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow24q+3r\equiv2\left(mod8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3r\equiv2\left(mod8\right)\)
Thử từng trường hợp, ta thấy ngay \(r=6\).
Vậy \(x=8q+6\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{26-3x}{8}=\dfrac{26-3\left(8q+6\right)}{8}=\dfrac{8-24q}{8}=1-3q\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm nguyên là \(\left(8q+6,1-3q\right)\) với \(q\inℤ\) bất kì.
b) Cho \(1-3q>0\Leftrightarrow q< \dfrac{1}{3}\)
Cho \(8q+6>0\Leftrightarrow q>-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Do đó \(-\dfrac{3}{4}< q< \dfrac{1}{3}\). Mà \(q\inℤ\Rightarrow q=0\)
Thế vào \(x,y\), pt sẽ có nghiệm nguyên dương là \(\left(6;1\right)\)
Câu 6 làm tương tự nhé bạn.

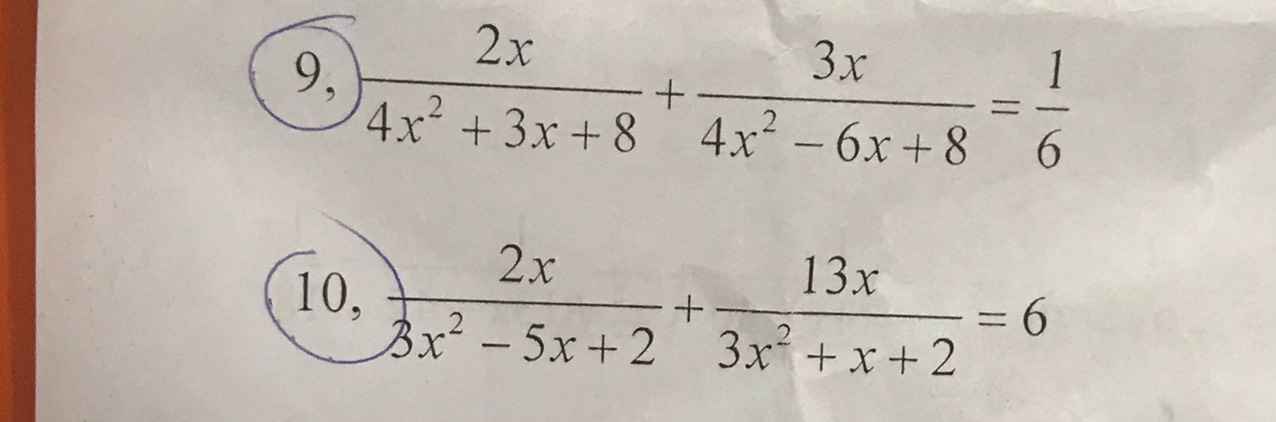


Bài 2:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}+\dfrac{5\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
=>6x+1+5x-25=3x-6
=>11x-24=3x-6
=>8x=18
=>x=9/4(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x-4}{x\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
=>2x-(x-1)(x+2)+(x-4)(x-2)=0
=>\(2x-\left(x^2+x-2\right)+x^2-6x+8=0\)
=>\(x^2-4x+8-x^2-x+2=0\)
=>-5x+10=0
=>x=2(loại)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-1}{x-3}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{x}{x-3}+\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(-1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)-x+3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>-(x+1)^2-x+3+(x-1)2=0
=>\(-x^2-2x-1-x+3+x^2-2x+1=0\)
=>-5x+3=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{3}{5}\left(nhận\right)\)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-3\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{6}{x+3}=\dfrac{5}{6-x^2-x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+3-6\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{-5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>x+3-6(x-2)=-5
=>x+3-6x+12+5=0
=>-5x+20=0
=>x=4(nhận)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>-2
\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{x^3+8}=\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-2x^2-16-5x-10}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=0\)
=>\(2x^2-4x+8-2x^2-5x-26=0\)
=>-9x-18=0
=>x=-2(loại)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x^2+x+1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-x+1}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^6-1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
=>2(x^2-1)=2(x+2)^2
=>\(x^2-1=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+4x+4-x^2+1=0\)
=>4x+5=0
=>\(x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\left(nhận\right)\)
Bài 3:
c:
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-1}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{3x-12}{x-6}\)
=>
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;2;\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt{7}}{2}\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{4}{x^2-3x+2}-\dfrac{3}{2x^2-6x+1}+1=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{4\left(2x^2-6x+1\right)-3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)}{\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(2x^2-6x+1\right)}=-1\)
=>\(8x^2-24x+4-3x^2+9x-6=-\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left[2\cdot\left(x^2-3x\right)+1\right]\)
=>\(5x^2-15x-2=-\left[2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+2\right]\)
=>\(5\left(x^2-3x\right)-2+2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+2=0\)
=>\(2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+10\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-3x\right)\left(x^2-3x+5\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-3x+5=\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{11}{4}>=\dfrac{11}{4}>0\forall x\)
nên x(x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
a:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{8;9;10;11\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{8}{x-8}+\dfrac{11}{x-11}=\dfrac{9}{x-9}+\dfrac{10}{x-10}\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{8}{x-8}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{11}{x-11}+1\right)=\left(\dfrac{9}{x-9}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{10}{x-10}+1\right)\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-8}+\dfrac{x}{x-11}-\dfrac{x}{x-9}-\dfrac{x}{x-10}=0\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{1}{x-8}+\dfrac{1}{x-11}-\dfrac{1}{x-9}-\dfrac{1}{x-10}\right)=0\)
=>x=0(nhận)
b:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;4;5;6\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{x}{x-5}=\dfrac{x}{x-4}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x-6\right)-x\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-2x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{-2x}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}-\dfrac{1}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\right)=0\)
=>\(x\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}=0\)
=>\(x\left(x^2-10x+24-x^2+8x-15\right)=0\)
=>x(-2x+9)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{9}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)