Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi A,B lần lượt là trung điểm của MP,MN. Gọi O là giao điểm của NA và PB
Ta có: \(MB=BN=\dfrac{MN}{2}\)
\(MA=AP=\dfrac{MP}{2}\)
mà MN=MP
nên MB=BN=MA=AP
Xét ΔBNP và ΔAPN có
BN=AP
\(\widehat{BNP}=\widehat{APN}\)
PN chung
Do đó: ΔBNP=ΔAPN
=>\(\widehat{BPN}=\widehat{ANP}\)
=>\(\widehat{ONP}=\widehat{OPN}\)
=>ON=OP
ΔMNP đều
mà PB là đường trung tuyến
nên PB\(\perp\)MN tại B
=>OB\(\perp\)MN tại B
Xét ΔOMN có
OB là đường cao
OB là đường trung tuyến
Do đó: ΔOMN cân tại O
=>OM=ON
mà ON=OP
nên OM=ON=OP
=>O là tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔMNP
Xét ΔMNP đều có PB là đường trung tuyến
nên \(PB=MN\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=5\sqrt{3}\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔMNP có
PB,NA là các đường trung tuyến
PB cắt NA tại O
Do đó: O là trọng tâm của ΔMNP
=>\(OP=\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot PB=\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot5\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{10\sqrt{3}}{3}\left(cm\right)\)
=>Bán kính là \(\dfrac{10\sqrt{3}}{3}\left(cm\right)\)

Câu 1:
x2−4x+3=0x^2 - 4x + 3 = 0x2−4x+3=0
Phương trình này là phương trình bậc hai có dạng chuẩn ax2+bx+c=0ax^2 + bx + c = 0ax2+bx+c=0 với:
- a=1a = 1a=1, b=−4b = -4b=−4, c=3c = 3c=3.
Tính biệt số Δ\DeltaΔ:
Δ=b2−4ac=(−4)2−4(1)(3)=16−12=4.\Delta = b^2 - 4ac = (-4)^2 - 4(1)(3) = 16 - 12 = 4.Δ=b2−4ac=(−4)2−4(1)(3)=16−12=4.
Vì Δ>0\Delta > 0Δ>0, phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
x=−b±Δ2a=4±22.x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{\Delta}}{2a} = \frac{4 \pm 2}{2}.x=2a−b±Δ=24±2.
Suy ra hai nghiệm:
x1=4−22=1,x2=4+22=3.x_1 = \frac{4 - 2}{2} = 1, \quad x_2 = \frac{4 + 2}{2} = 3.x1=24−2=1,x2=24+2=3.
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là x=1x = 1x=1 hoặc x=3x = 3x=3.
Câu 2
Phương trình:
x2−2(m−1)x+m2−m−4=0x^2 - 2(m-1)x + m^2 - m - 4 = 0x2−2(m−1)x+m2−m−4=0
Có hai nghiệm phân biệt khi:
Δ′=(m−1)2−(m2−m−4)>0.\Delta' = (m-1)^2 - (m^2 - m - 4) > 0.Δ′=(m−1)2−(m2−m−4)>0.
Tính toán:
m2−2m+1−m2+m+4>0.m^2 - 2m + 1 - m^2 + m + 4 > 0.m2−2m+1−m2+m+4>0. −m+5>0.- m + 5 > 0.−m+5>0. m<5.m < 5.m<5.
Ta có điều kiện:
x12−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.x_1^2 - 2x_2(x_2 - 2) + m^2 - 5m = 0.x12−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.
Sử dụng định lý Vi-ét
x1+x2=2(m−1),x_1 + x_2 = 2(m-1),x1+x2=2(m−1), x1x2=m2−m−4.x_1 x_2 = m^2 - m - 4.x1x2=m2−m−4.
Dùng đẳng thức:
x12=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2.x_1^2 = (x_1 + x_2)^2 - 2x_1 x_2.x12=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2.
Thay vào:
(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.(2(m-1))^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4) - 2x_2(x_2 - 2) + m^2 - 5m = 0.(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.
Biến đổi:
4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2x22+4x2+m2−5m=0.4(m-1)^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4) - 2x_2^2 + 4x_2 + m^2 - 5m = 0.4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2x22+4x2+m2−5m=0.
Dùng x22=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2x_2^2 = (x_1 + x_2)^2 - 2x_1x_2x22=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2, thay vào:
4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2[(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)]+4x2+m2−5m=0.4(m-1)^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4) - 2[(2(m-1))^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4)] + 4x_2 + m^2 - 5m = 0.4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2[(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)]+4x2+m2−5m=0.
Rút gọn:
4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8−2[4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8]+4x2+m2−5m=0.4(m^2 - 2m + 1) - 2m^2 + 2m + 8 - 2[4(m^2 - 2m + 1) - 2m^2 + 2m + 8] + 4x_2 + m^2 - 5m = 0.4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8−2[4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8]+4x2+m2−5m=0.
Sau khi tiếp tục biến đổi và rút gọn, ta giải phương trình để tìm các giá trị mmm thỏa mãn.
Kết quả cuối cùng là m=3m = 3m=3 (thỏa mãn cả hai điều kiện trên).

a: Xét (\(O_1\)) có
ΔAEH nội tiếp
AH là đường kính
Do đó: ΔAEH vuông tại E
=>HE\(\perp\)AC tại E
Xét \(\left(O_2\right)\) có
ΔHFB nội tiếp
HB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔHFB vuông tại F
=>HF\(\perp\)CB tại F
Xét ΔCHA vuông tại H có HE là đường cao
nên \(CE\cdot CA=CH^2\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔCHB vuông tại H có HF là đường cao
nên \(CF\cdot CB=CH^2\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra \(CE\cdot CA=CF\cdot CB\)
=>\(\dfrac{CE}{CB}=\dfrac{CF}{CA}\)
Xét ΔCEF và ΔCBA có
\(\dfrac{CE}{CB}=\dfrac{CF}{CA}\)
\(\widehat{ECF}\) chung
Do đó: ΔCEF~ΔCBA
=>\(\widehat{CEF}=\widehat{CBA}\)
mà \(\widehat{CEF}+\widehat{FEA}=180^0\)(hai góc kề bù)
nên \(\widehat{FEA}+\widehat{FBA}=180^0\)
=>AEFB là tứ giác nội tiếp

a: Các kết quả có thể xảy ra nằm trong tập hợp sau:
\(\Omega=\left\{\left(1;1\right);\left(1;2\right);...;\left(6;5\right);\left(6;6\right)\right\}\)
=>Có 36 kết quả có thể xảy ra
b: Gọi A là biến cố "Tổng số chấm ở hai con xúc sắc là 7"
=>A={(1;6);(2;5);(3;4);(4;3);(5;2);(6;1)}
=>n(A)=6
=>\(P_A=\dfrac{6}{36}=\dfrac{1}{6}\)
a) Xúc xắc 1 có 6 kết quả (6 mặt)
Xúc xắc 2 có 6 kết quả
Số kết quả xảy ra khi tung 2 xúc xắc là:
`6 xx 6 = 36` (kết quả)

Bài 17:
a:
Xét tứ giác OBAC có \(\widehat{OBA}+\widehat{OCA}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên OBAC là tứ giác nội tiếp
=>O,B,A,C cùng thuộc một đường tròn
Xét (O) có
AB,AC là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: AB=AC
=>A nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(1)
Ta có: OB=OC
=>O nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra OA là đường trung trực của BC
=>OA\(\perp\)BC tại H và H là trung điểm của BC
Xét (O) có
ΔBCD nội tiếp
BD là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBCD vuông tại C
=>BC\(\perp\)CD
mà OA\(\perp\)BC
nên OA//CD
b: Xét (O) có
ΔBED nội tiếp
BD là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBED vuông tại E
=>BE\(\perp\)AD tại E
Xét ΔABD vuông tại B có BE là đường cao
nên \(AE\cdot AD=AB^2\left(3\right)\)
Xét ΔABO vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(AH\cdot AO=AB^2\left(4\right)\)
Từ (3),(4) suy ra \(AE\cdot AD=AH\cdot AO\)
=>\(\dfrac{AE}{AO}=\dfrac{AH}{AD}\)
Xét ΔAEH và ΔAOD có
\(\dfrac{AE}{AO}=\dfrac{AH}{AD}\)
\(\widehat{EAH}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAEH~ΔAOD
=>\(\widehat{AHE}=\widehat{ADO}\)
Bài 15:
a:
Xét (O) có
ΔBEC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBEC vuông tại E
=>BE\(\perp\)AC tại E
b:
Xét (O) có
ΔBFC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBFC vuông tại F
=>CF\(\perp\)AB tại F
Xét ΔABC có
BE,CF là các đường cao
BE cắt CF tại H
Do đó: H là trực tâm của ΔABC
=>AH\(\perp\)BC tại D
Xét tứ giác BFHD có \(\widehat{BFH}+\widehat{BDH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên BFHD là tứ giác nội tiếp
Xét tứ giác CEHD có \(\widehat{CEH}+\widehat{CDH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên CEHD là tứ giác nội tiếp
Ta có: \(\widehat{FDH}=\widehat{FBH}\)(BFHD nội tiếp)
\(\widehat{EDH}=\widehat{ECH}\)(CEHD nội tiếp)
mà \(\widehat{FBH}=\widehat{ECH}\left(=90^0-\widehat{BAC}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{FDH}=\widehat{EDH}\)
=>DA là phân giác của góc FDE

`3x^2 + 4x - 4 = 0`
`<=> 3x^2 - 2x + 6x - 4 = 0`
`<=> (3x^2 - 2x) + (6x - 4) = 0`
`<=> x (3x - 2) + 2(3x - 2) = 0`
`<=> (x + 2)(3x - 2) = 0`
`<=> x = -2` hoặc `x = 2/3`
Vậy ...

`69^2022`
`= (...9)^2022`
Có cùng chữ số tận cùng với `9^2022`
Ta có: `9^2022 = 9^(1011.2) = (9^2)^1011 = 81^1011` có tận cùng chữ số 1
Vậy ....
\(15^{15^{15^{15}}}\) có tận cùng là chữ số 5 do các chữ số tận cùng là 5 mũ bao nhiêu cũng tận cùng là 5 ngoại từ mũ 0

Để 4 n + 3 3 n + 1 3n+1 4n+3 thuộc Z thì 4n + 3 chia hết cho 3n + 1
⇒ 3 ( 4 n + 3 ) ⋮ 3 n + 1 ⇒3(4n+3)⋮3n+1 ⇒ 12 n + 9 ⋮ 3 n + 1
⇒12n+9⋮3n+1 ⇒ ( 12 n + 4 ) + 5 ⋮ 3 n + 1
⇒(12n+4)+5⋮3n+1
⇒ 4 ( 3 n + 1 ) + 5 ⋮ 3 n + 1
⇒4(3n+1)+5⋮3n+1
⇒ 5 ⋮ 3 n + 1 ⇒5⋮3n+1
⇒ 3 n + 1 ∈ { ± 1 ; ± 5 }
⇒3n+1∈{±1;±5} +) 3n + 1 = 1
⇒ n = 0
⇒n=0 ( chọn ) +) 3 n + 1 = − 1
⇒ n = − 2 3 3n+1=−1
⇒n= 3 −2 ( loại ) +) 3 n + 1 = 5
⇒ n = 4 3 3n+1=5
⇒n= 3 4 ( loại ) +) 3 n + 1 = − 5
⇒ n = − 2 3n+1=−5
⇒n=−2 Vậy n = 0 hoặc n = -2
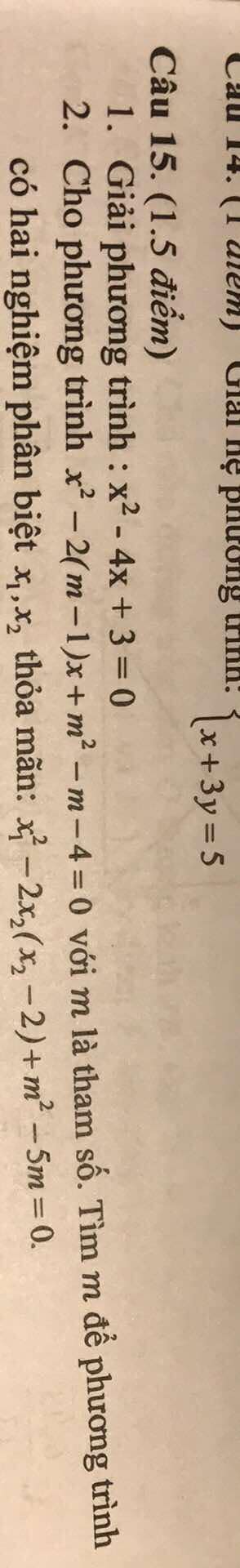
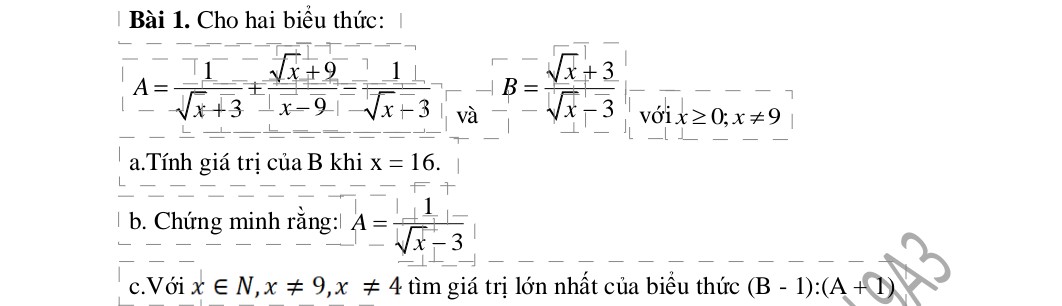
a: Khi x=16 thì \(B=\dfrac{4+3}{4-3}=\dfrac{7}{1}=7\)
b: \(A=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+3}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+9}{x-9}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3+\sqrt{x}+9-\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+6-\sqrt{x}-3}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+3}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)