Làm tròn 2826 đến hàng trăm.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có:
`3` giờ `36` phút `= 216` phút
Mà `216 : 4 =54` phút
Suy ra: `3` giờ `36` phút `: 4 = 54` phút

Nửa chu vi mảnh vườn là:
80:2=40(m)
Chiều dài mảnh vườn là:
40-15=25(m)
Đáp số:25 m
Nửa chu vi mảnh vườn hình chữ nhật là:
`80 : 2 = 40 (m)`
Chiều dài mảnh vườn hình chữ nhật là:
`40 - 15 = 25 (m)`
Đáp số: `25 m`

`P=3x^2-3x^4+1/2x^5+0,75`
`=1/2x^5-3x^4+3x^2+0,75`
Bậc của B chính là bậc của hạng tử có bậc cao nhất là `1/2x^5` có bậc 5
`=>P` có bậc 5`

Xác suất của sự kiện lấy được quả bóng màu đỏ là:
15 : 50 = \(\frac{3}{10}\)

Giải:
Theo bài ra ta có:
\(\overline{ba}\) = 2 x \(\overline{ab}\) + 18
10b + a = 20a + 2b + 18
10b - 2b = 20a - a + 18
8b = 19a + 8
8b + 19b = 19b + 19a + 8
27b = 19.(a + b) + 18 (1)
Thay a + b = 9 vào (1)
27b = 19.9 + 18
27b = 171 + 18
27b = 189
b = 189 : 27
b = 7
a = 9 - b
a = 9 - 7
a = 2
Vậy \(\overline{ab}\) = 27

Bài này kết quả -11 đúng không cả nhà ơi
= 2(-1) - 5.1 + 4.-1 -3 = -11
Khi x=-1 thì \(P\left(-1\right)=2\cdot\left(-1\right)^3-5\cdot\left(-1\right)^2+4\cdot\left(-1\right)-3\)
\(=2\cdot\left(-1\right)-5\cdot1-4-3\)
=-2-5-4-3
=-7-3-4
=-14

9,15 : 0,5 + 9,15 x 9 - 9,15
= 9,15 x 2 + 9,15 x 9 - 9,15 x 1
= 9,15 x (2 + 9 - 1)
= 9,15 x (11 - 1)
= 9,15 x 10
91,5

Giải:
Thời gian ô tô thứ nhất đi từ A đến B không kể thời gian nghỉ là:
10 giờ 30 phút - 30 phút - 6 giờ = 4 giờ
Cùng một quãng đường vận tốc tỉ lệ nghịch với thời gian nên tỉ số thời gian xe thứ nhất và thời gian xe thứ hai đi hết quãng đường AB là:
40 : 45 = \(\frac89\)
Thời gian xe thứ hai đi hết quãng đường AB không kể thời gian nghỉ là:
4 : \(\frac89\) = 4,5 (giờ)
Ô tô thứ hai đến B lúc:
6 giờ + 4,5 giờ + 30 phút = 11 giờ
Đáp số: 11 giờ

Ta có: \(\left(3x-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)^2>=0\forall x\)
\(\left|2y-6\right|>=0\forall y\)
Do đó: \(\left(3x-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)^2+\left|2y-6\right|>=0\forall x,y\)
mà \(\left(3x-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)^2+\left|2y-6\right|< =0\)
nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-\dfrac{1}{6}=0\\2y-6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=\dfrac{1}{6}\\2y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{18}\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
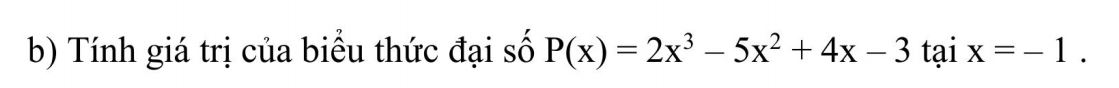
số 2826 làm tròn đến hàng trăm : 2800
2830