X(2x-1)+1/3-(2/3)x=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


x2 - 4x + 2 = ( x2 - 4x + 4 ) - 2 = ( x - 2 )2 - 2 ≥ -2 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> x = 2 . Vậy GTNN của bthuc = -2
x^2 - 4x + 2
= x^2 - 4x + 4 - 2
= ( x - 2 ) ^2 - 2
\(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2-2\ge-2\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi và chỉ khi
x - 2 = 0
x = 0 + 2
x = 2
vậy min = -2 khi và chỉ khi x = 2

\(A=x\left(y^2-z^2\right)+y\left(z^2-x^2\right)+z\left(x^2-y^2\right)\)
\(=x\left(y-z\right)\left(y+z\right)+yz^2-yx^2+zx^2-zy^2\)
\(=\left(y-z\right)\left[x.\left(y+z\right)\right]-x^2\left(y-z\right)-yz\left(y-z\right)\)
\(=\left(y-z\right)\left(xy+xz\right)-x^2\left(y-z\right)-yz\left(y-z\right)\)
\(=\left(y-z\right)\left(xy+xz-x^2-yz\right)\)
\(=\left(y-z\right)\left[\left(xy-x^2\right)+\left(xz-yz\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(y-z\right)\left[x\left(y-x\right)-z\left(y-x\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(y-z\right)\left(y-x\right)\left(x-z\right)\)

x2 - 4xy + 4y2 - x + 2y
= ( x - 2y )2 - ( x - 2y )
= ( x - 2y )( x - 2y - 1 )

x^2 - 4x + 4 = 5 ( x - 2 )
x^2 - 4x + 4 - 5 ( x - 2 ) = 0
( x - 2 ) ^2 - 5 ( x - 2 ) = 0
( x - 2 ) ( x - 2 - 5 ) = 0
( x - 2 ) ( x - 7 ) = 0
x - 2 = 0 hoặc x - 7 = 0
x = 2 hoặc x = 7
c) (x-2)^2=5(x-2)
=> x-2=5 hoặc x-2 =0
=> x=7 hoặc x=2
d) (2x-3)^2=(5-x)^2
=> 2x-3=5-x
=> x=8/3

144a2 - 81 = 9( 16a2 - 9 ) = 9( 4a - 3 )( 4a + 3 )
36a2 - 49b2 = ( 6a - 7b )( 6a + 7b )
a2 - 4b2 = ( a - 2b )( a + 2b )
1/4a2 - b2 = ( 1/2a - b )( 1/2a + b )
4/9a4 - 25/4 = ( 2/3a2 - 5/2 )( 2/3a2 + 5/2 )
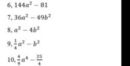
2x2-x+1/3-2/3x=0
6x2-5x+1=0
6x2-3x-2x+1=0
(x-1)(2x-1)=0
x-1=0 và 2x=1
x=1 và x=1/2
\(x\left(2x-1\right)+\frac{1}{3}-\left(\frac{2}{3}\right)x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x+\frac{1}{3}-\frac{2x}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-\frac{5}{3}x+\frac{1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{6x^2-5x+1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-2x-3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(3x-1\right)-\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\2x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=1\\2x=1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\frac{1}{3};\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)