
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left(2,5x-\dfrac{4}{7}\right):\dfrac{8}{21}=-1,5\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{5}{2}x-\dfrac{4}{7}\right):\dfrac{8}{21}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{5}{2}x-\dfrac{4}{7}=\dfrac{-3}{2}\cdot\dfrac{8}{21}=\dfrac{-24}{42}=\dfrac{-4}{7}\)
=>\(\dfrac{5}{2}x=-\dfrac{4}{7}+\dfrac{4}{7}=0\)
=>x=0

\(-\dfrac{13}{38}=\dfrac{-13\cdot88}{38\cdot88}=\dfrac{-1144}{3344};\dfrac{29}{-88}=\dfrac{29\cdot\left(-38\right)}{\left(-88\right)\left(-38\right)}=\dfrac{-1102}{3344}\)
mà -1144<-1102
nên \(-\dfrac{13}{38}< \dfrac{29}{-88}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{13}{38}>\dfrac{13}{39}=>\dfrac{-13}{38}< \dfrac{-13}{39}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\\dfrac{29}{88} < \dfrac{29}{87}=>\dfrac{-29}{88}>-\dfrac{28}{87}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(=>\dfrac{-13}{38}< -\dfrac{1}{3}< \dfrac{-29}{88}\)

b: \(\dfrac{-8}{-20}=\dfrac{18}{45};\dfrac{-8}{18}=\dfrac{-20}{45};\dfrac{-20}{-8}=\dfrac{45}{18};\dfrac{18}{-8}=\dfrac{45}{-20}\)
c: \(\dfrac{4}{8}=\dfrac{16}{32};\dfrac{4}{16}=\dfrac{8}{32};\dfrac{8}{4}=\dfrac{32}{16};\dfrac{16}{5}=\dfrac{32}{8}\)
\(\dfrac{4}{32}=\dfrac{8}{64};\dfrac{4}{8}=\dfrac{32}{64};\dfrac{8}{4}=\dfrac{64}{32};\dfrac{32}{4}=\dfrac{64}{8}\)

TH1: x<-2
Phương trình sẽ trở thành: \(3x\left(-x-1\right)-2x\left(-x-2\right)=12\)
=>\(-3x^2-3x+2x^2+4x-12=0\)
=>\(-x^2+x-12=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=1^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot\left(-12\right)=1-4\cdot12=1-48=-47< 0\)
=>Phương trình vô nghiệm
TH2: -2<=x<-1
Phương trình sẽ trở thành:
\(3x\left(-x-1\right)-2x\left(x+2\right)=12\)
=>\(-3x^2-3x-2x^2-4x-12=0\)
=>\(5x^2+7x+12=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=7^2-4\cdot5\cdot12=49-20\cdot12=49-240=-191< 0\)
=>Phương trình vô nghiệm
TH3: x>=-1
Phương trình sẽ trở thành:
\(3x\left(x+1\right)-2x\left(x+2\right)=12\)
=>\(3x^2+3x-2x^2-4x-12=0\)
=>\(x^2-x-12=0\)
=>(x-4)(x+3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(nhận\right)\\x=-3\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(-\dfrac{2}{5}+\dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{-1}{6}+\dfrac{-2}{5}\\ =\left(\dfrac{-2}{5}+\dfrac{-2}{5}\right)+\left(\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{6}\right)\\ =\dfrac{-4}{5}+\left(\dfrac{9}{12}+\dfrac{2}{12}\right)\\ =\dfrac{-4}{5}+\dfrac{11}{12}\\ =\dfrac{-48}{60}+\dfrac{55}{60}\\ =\dfrac{55-48}{60}\\ =\dfrac{7}{60}\)

Bài 6: Kẻ Dm//Ax
Vì Dm//Ax
nên \(\widehat{mDA}+\widehat{xAD}=180^0\)(hai góc trong cùng phía)
=>\(\widehat{mDA}=180^0-150^0=30^0\)
Ta có: \(\widehat{mDA}+\widehat{mDE}=\widehat{ADE}\)
=>\(\widehat{mDE}=80^0-30^0=50^0\)
Vì \(\widehat{mDE}+\widehat{yED}=180^0\)
mà hai góc này là hai góc trong cùng phía
nên Dm//Ey
=>Ax//Ey
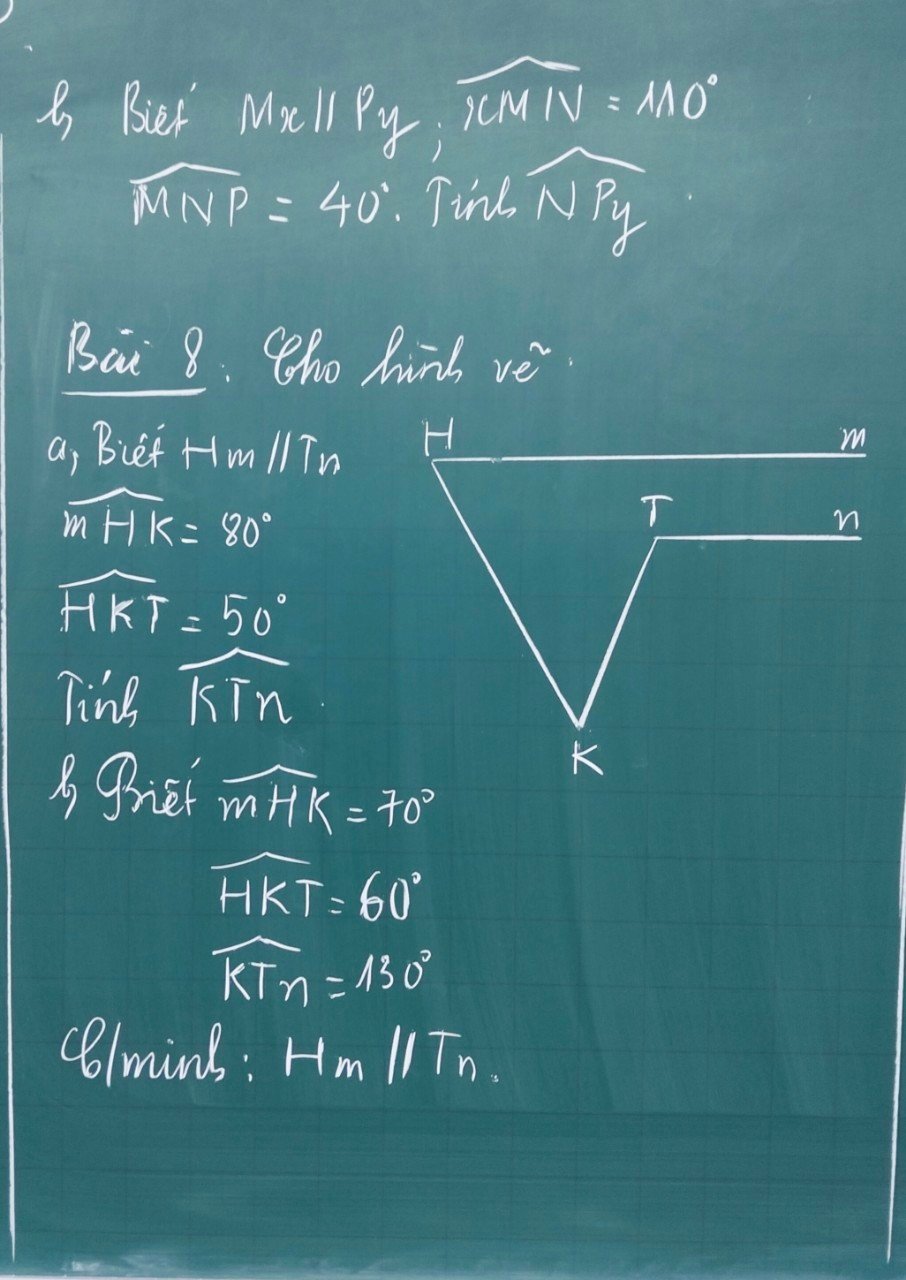
Bài 8:
a: Gọi A là giao điểm của KT với Hm
Xét ΔKAH có \(\widehat{KAH}+\widehat{KHA}+\widehat{AKH}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{KAH}=180^0-80^0-50^0=50^0\)
Vì Hm//Tn nên \(\widehat{nTA}=\widehat{TAH}=50^0\)
\(\widehat{nTA}+\widehat{nTK}=180^0\)(hai góc kề bù)
=>\(\widehat{nTK}=180^0-50^0=130^0\)
b: Gọi A là giao điểm của KT với Hm
Xét ΔKAH có \(\widehat{KAH}+\widehat{KHA}+\widehat{HKA}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{KAH}+70^0+60^0=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{KAH}=50^0\)
Ta có: \(\widehat{nTK}+\widehat{nTA}=180^0\)(hai góc kề bù)
=>\(\widehat{nTA}=180^0-130^0=50^0\)
Ta có: \(\widehat{nTA}=\widehat{HAK}\left(=50^0\right)\)
mà hai góc này là hai góc so le trong
nên Hm//Tn

\(\widehat{mOn};\widehat{mOt}\) là hai góc kề bù
=> \(\widehat{mOn}+\widehat{mOt}=180^o\)
Mà: \(\widehat{mOn}=50^o\)
\(=>50^o+\widehat{mOt}=180^o\\ =>\widehat{mOt}=180^o-50^o\\ =>\widehat{mOt}=130^o\)

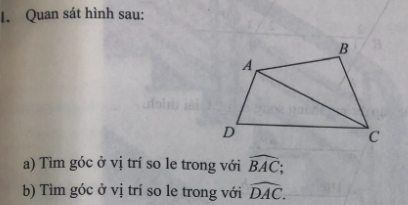
a: Góc so le trong với \(\widehat{BAC}\) là góc ACD
b: Góc so le trong với \(\widehat{DAC}\) là góc BCA


 Giúp mik !❤
Giúp mik !❤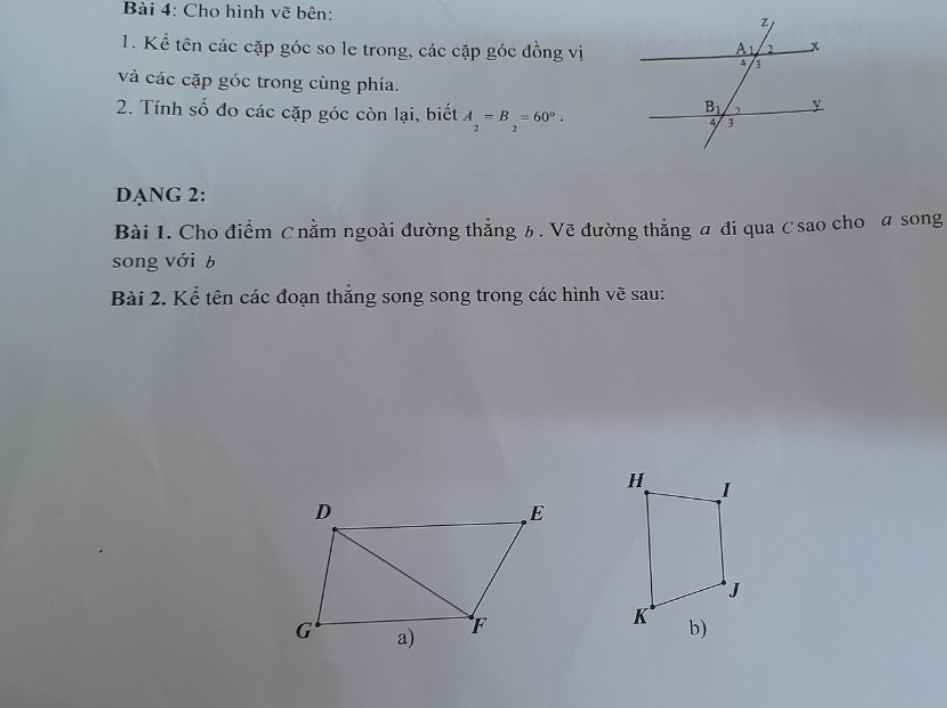
a: Oy nằm giữa Ox và Ot
=>\(\widehat{xOy}+\widehat{yOt}=\widehat{xOt}\)
=>\(\widehat{yOt}+30^0=50^0\)
=>\(\widehat{yOt}=20^0\)
b: Vì Ox là tia đối của tia Oz nên \(\widehat{xOz}=180^0\)