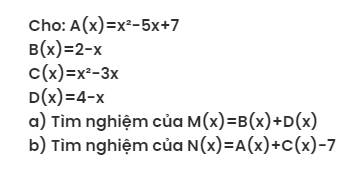Consider 2002 intergers ai,i=1,2,3,...,2002 such that a1-3 + a2-3 +... + a2002-3=1/2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Each term of S is n!(n2 + n + 1) = n![n(n + 1) + 1] = n(n + 1)n! + n!
By definition, n(n + 1)n! + n! = n! + n(n + 1)!
Therefore, S can be simplified as
1! + 1.2! + 2! + 2.3! + ... + 100! + 100.101!
So \(\dfrac{S+1}{101!}=\dfrac{1+1!+1\cdot2!+2!+2\cdot3!+...+100!+100\cdot101!}{101!}\)
\(=\dfrac{2!+1\cdot2!+2!+2\cdot3!+3!+...+100!+100\cdot101!}{101!}\)
\(=\dfrac{3!+2\cdot3!+3!+...+100!+100\cdot101!}{101!}\)
\(=\dfrac{4!+3\cdot4!+4!+...+100!+100\cdot101!}{101!}\)
\(=...\)
\(=\dfrac{100!+99\cdot100!+100!+100\cdot101!}{101!}\)
\(=\dfrac{101!+100\cdot101!}{101!}\)
\(=1+100=101\)
Hence, \(\dfrac{S+1}{101!}=101\)

\(2^{30}< 24^{30}\)
\(3^{30}< 24^{30}\)
\(4^{30}< 24^{30}\)
\(\Rightarrow2^{30}+3^{30}+4^{30}< 24^{30}+24^{30}+24^{30}\)
\(\Rightarrow2^{30}+3^{30}+4^{30}< 3.24^{30}\)

- \(\dfrac{13}{49}\) + \(\dfrac{12}{48}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{3}{18}\)
= - \(\dfrac{13}{49}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6}\)
= - \(\dfrac{13}{49}\) + ( \(\dfrac{3}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{2}{12}\))
= - \(\dfrac{13}{49}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
= - \(\dfrac{26}{98}\) + \(\dfrac{49}{98}\)
= \(\dfrac{23}{98}\)

Bài 1:
a, \(\dfrac{7}{-13}\) và \(\dfrac{8}{-13}\)
\(\dfrac{7}{13}\) < \(\dfrac{8}{13}\)
- \(\dfrac{7}{13}\) > - \(\dfrac{8}{13}\) (Khi nhân cả hai vế của bất đẳng thức với một số âm thì dấu của bất đẳng thức đổi chiều)
b, \(\dfrac{-9}{-31}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{31}\) > 0 > \(\dfrac{10}{-31}\)
c, \(\dfrac{17}{50}\) < \(\dfrac{18}{50}\) ⇒ - \(\dfrac{17}{50}\) > - \(\dfrac{18}{50}\)
Bài 2:
a, \(\dfrac{1111}{3131}\) = \(\dfrac{1111:101}{3131:101}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{31}\)
b, \(\dfrac{1313}{8181}\) = \(\dfrac{1313:101}{8181:101}\) = \(\dfrac{13}{81}\)
\(\dfrac{131313}{818181}\) = \(\dfrac{131313:10101}{818181:10101}\) = \(\dfrac{13}{81}\)
\(\dfrac{1313}{8181}\) = \(\dfrac{131313}{818181}\)
c, \(\dfrac{101010}{212121}\) = \(\dfrac{101010:10101}{212121:10101}\) = \(\dfrac{10}{21}\)
\(\dfrac{1010}{2121}\) = \(\dfrac{1010:101}{2121:101}\) = \(\dfrac{10}{21}\)
\(\dfrac{101010}{212121}\) = \(\dfrac{1010}{2121}\)
Bài 3:
a, \(\dfrac{5}{6}\) = \(\dfrac{25}{30}\); \(\dfrac{3}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{18}{30}\) vì \(\dfrac{25}{30}\) > \(\dfrac{18}{30}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) > \(\dfrac{3}{5}\)
b, \(\dfrac{-5}{6}\) = \(\dfrac{-35}{42}\); \(\dfrac{6}{-7}\) = \(\dfrac{-36}{42}\)
Vì \(\dfrac{35}{42}\) < \(\dfrac{36}{42}\) nên - \(\dfrac{35}{42}\) > - \(\dfrac{36}{42}\)
Vậy \(\dfrac{-5}{6}\) > \(\dfrac{6}{-7}\)
c, \(\dfrac{-3}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-9}{15}\); \(\dfrac{2}{-3}\) = \(\dfrac{-10}{15}\) vì \(\dfrac{9}{15}\) < \(\dfrac{10}{15}\) nên - \(\dfrac{9}{15}\) > - \(\dfrac{10}{15}\)
Vậy \(-\dfrac{3}{5}>\dfrac{2}{-3}\)

Bài 1:
a.
$7< 8\Rightarrow \frac{7}{13}< \frac{8}{13}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{7}{-13}> \frac{8}{-13}$
b.
$\frac{-9}{-31}=\frac{9}{31}> 0> \frac{10}{-31}$
c.
$17< 18\Rightarrow \frac{17}{50}< \frac{18}{50}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{-17}{50}> \frac{-18}{50}$ hay $\frac{-17}{50}> \frac{18}{-50}$
Bài 2:
a.
$\frac{1111}{3131}=\frac{1111:101}{3131:101}=\frac{11}{31}$
b.
$\frac{1313}{1818}=\frac{1313:101}{1818:101}=\frac{13}{18}=\frac{13.10101}{18.10101}=\frac{131313}{181818}$
c.
$\frac{101010}{212121}=\frac{101010:10101}{212121:10101}$
$=\frac{10}{21}$
$\frac{1010}{2121}=\frac{1010:101}{2121:101}=\frac{10}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{101010}{212121}=\frac{1010}{2121}$

\(\dfrac{-9}{-31}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{31}\) > 0
\(\dfrac{10}{-31}\) < 0
Vậy \(\dfrac{-9}{-31}\) > \(\dfrac{10}{-31}\)
\(\dfrac{-9}{-31}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{31}\) > 0
\(\dfrac{10}{-31}\) = \(\dfrac{-10}{31}\) < 0
Vì \(\dfrac{9}{31}\) > 0 > \(\dfrac{-10}{31}\) ⇒ \(\dfrac{-9}{-31}\) > \(\dfrac{10}{-31}\)

`#040911`
`a)`
`M(x) = B(x) + D(x)`
`\Rightarrow M(x) = 2 - x + 4 - x =0`
`\Rightarrow (2 + 4) - (x + x) = 0`
`\Rightarrow 6 - 2x = 0`
`\Rightarrow 2x = 6`
`\Rightarrow x = 6 \div 2`
`\Rightarrow x = 3`
Vậy, nghiệm của `M(x)` là `x = 3`
`b)`
`N(x) = A(x) + C(x) - 7`
`\Rightarrow N(x) = x^2 - 5x + 7 + x^2 - 3x - 7 = 0`
`\Rightarrow (x^2 + x^2) - (5x + 3x) + (7 - 7) = 0`
`\Rightarrow 2x^2 - 8x = 0`
`\Rightarrow 2x(x - 4) = 0`
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy, nghiệm của đa thức `N(x)` là `x \in {0; 4}.`

Do 2009 > 0 \(\Rightarrow f\left(2009\right)=2009+1=2010\)
DO -1004 < 0 \(\Rightarrow f\left(-1004\right)=1-2\cdot\left(-1004\right)=2009\)

\(A=\dfrac{3+2\left|x+2\right|}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\)
\(=\dfrac{2+2\left|x+2\right|+1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(1+\left|x+2\right|\right)+1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(1+\left|x+2\right|\right)}{1+\left|x+2\right|}+\dfrac{1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\)
\(=2+\dfrac{1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\)
Ta có \(\left|x+2\right|\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+\left|x+2\right|\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1+\left|x+2\right|}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\ge\dfrac{1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2+\dfrac{1}{1+\left|x+2\right|}\le1+2=3\)
\(\Rightarrow A\le3\)
Dấu \("="\) xảy ra khi \(x+2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
Vậy giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức \(A\) là \(3\)