Quy đồng các phân thức sau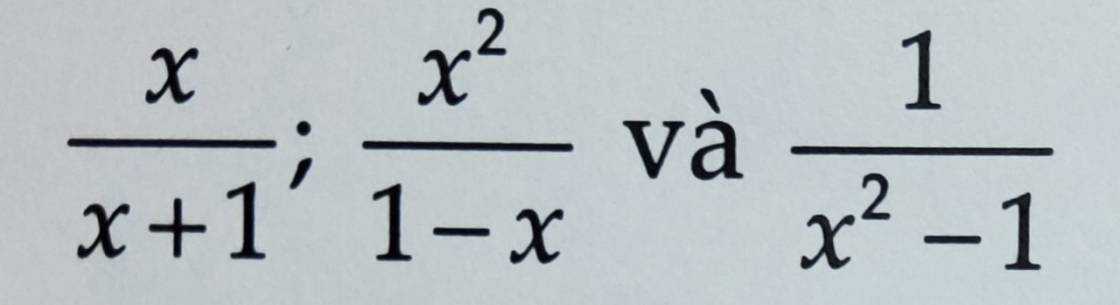
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi số có 4 chữ số thỏa mãn là \(\overline{abcd}\). Khi đó a có 4 cách chọn (từ 1 đến 4). Còn các chữ số b, c, d đều có 5 cách chọn (từ 0 đến 4). Do đó có tất cả \(4.5.5.5=500\) số thỏa mãn ycbt.

1. Smartphones can be expensive because they come with many features.
=> Smartphones come with many features, so they can be expensive
2. Smartwatches can track your heart rate. They can also receive messages.
=> Smartwatches not only can track your heart rate, but also can receive messages
3. I enjoy taking photos with my phone, but the storage gets full quickly.
=> Although I enjoy taking photos with my phone, the storage gets full quickly.
4. Tablets are lightweight, so they are easy to carry in a bag.
=> Because tablets are lightweight, they are easy to carry in a bag.
5. I use noise-canceling headphones so that I can focus better in a noisy environment.
=> Because of using noise-canceling headphones, I can focus better in a noisy environment.

Bài 10
a; Giao của d1 với trục ox là điểm có hoành độ thỏa mãn
\(x\) - 3 = 0 ⇒ \(x\) = 3
Giao của d1 với trục oy là điểm có tung độ thỏa mãn y = 0 - 3 = -3
Giao của d2 với trục ox là điểm có hoành độ thỏa mãn
3 - \(x\) = 0 ⇒ \(x\) = 3
Giao của d2 với trục oy là điểm có tung độ thỏa mãn y = 3 - 0 = 3
Ta có đồ thị d1 và d2 như hình dưới
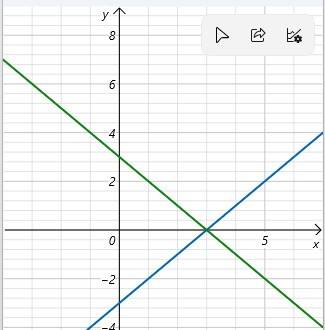
b; Giao của d1 và d2 là điểm có phương trình hoành độ thỏa mãn
\(x\) - 3 = 3 - \(x\)
2\(x\) = 6
\(x\) = 6 : 2
\(x\) = 3; ⇒ y = 3- 3 =0
Vậy giao của d1 và d2 là A(3;0)
Bài 9:
Giao của d1 với trục ox là điểm có hoành độ thỏa mãn
2\(x\) - 3 = 0 ⇒ \(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Giao của d1 với trục oy là điểm có tung độ thỏa mãn
y = 2.0 - 3 = - 3
Giao của d2 với trục ox là điểm có hoành độ thỏa mãn
-3 - \(x\) = 0 ⇒ \(x\) = 0
Giao của d2 với trục oy là điểm có tung độ thỏa mãn
y = -3 - 0 = -3
Ta có đồ thị như hình dưới đây
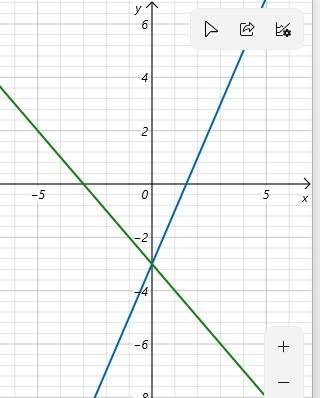
Giao của d1 và d2 là điểm có hoành độ thỏa mãn phương trình
2\(x\) - 3 = -3 - \(x\)
2\(x\) + \(x\) = 0
3\(x\) =0
\(x\) = 0
⇒ y = -3 - 0
y = - 3
Vậy giao của d1 và d2 là điểm B(0; -3)

\(\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{x^2-5x+6}-\dfrac{2x-4}{x-2}\left(ĐK:x\ne3;x\ne2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x-4}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2x-4}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{3x^2-8x+10}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{\left(2x-4\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2+3x^2-8x+10-\left(2x^2-6x-4x+12\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^2-7x+8-2x^2+10x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3x-4}{x^2-5x+6}\)

\(n_{BaCl_2}=\dfrac{200.20,8\%}{208}=0,2\left(mol\right)\\ PTHH:BaCl_2+H_2SO_4\rightarrow BaSO_4+2HCl\\ n_{BaSO_4}=n_{H_2SO_4}=n_{BaCl_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\\ a,m_{kt}=m_{BaSO_4}=233.0,2=46,6\left(g\right)\\ b,C\%_{ddH_2SO_4}=\dfrac{0,2.98}{200}.100\%=9,8\%\)

\(\dfrac{x}{x+1}=\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-x}{x^2-1}\)
\(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}=\dfrac{-x^2}{x-1}=\dfrac{-x^2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-x^3-x^2}{x^2-1}\)