xếp 81 hình vuông nhỏ thành 1 hình vuông lớn hỏi có tất cả bao nhiêu hình vuông trong hình
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Do f(2) = 6
⇒ 2² - 2b + 4 = 6
8 - 2b = 6
2b = 8 - 6
2b = 2
b = 2 : 2
b = 1
Vậy khi f(2) = 6 thì b = 1
Do f(2) = 6
⇒ 2² - 2b + 4 = 6
8 - 2b = 6
2b = 8 - 6
2b = 2
b = 2 : 2
b = 1
Vậy khi f(2) = 6 thì b = 1

\(E=\left(2-x\right)\left(1+2x\right)+\left(1+x\right)-\left(x^4+x^3-5x^2-5\right)\)
\(=2+4x-x-2x^2+1+x-x^4-x^3+5x^2+5\)
\(=-x^4-x^3+\left(-2x^2+5x^2\right)+\left(4x-x+x\right)+\left(2+1+5\right)\)
\(=-x^4-x^3+3x+4x+8\)
--------
\(G=\left(x^2-7\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-14\right)+x\left(x^2-2x-22\right)+35\)
\(=x^3+2x^2-7x-14-2x^2+28x+x-14+x^2-2x^2-22x+35\)
\(=x^3+\left(2x^2-2x^2+x^2-2x^2\right)+\left(-7x+28x+x-22x\right)+\left(-14-14+35\right)\)
\(=x^3-x^2+7\)
--------
\(D=\left(3x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(x+5\right)-6\left(3x-2\right)\)
\(=6x^2+21x-2x-7-x^2-5x-x-5-18x+12\)
\(=\left(6x^2-x^2\right)+\left(21x-2x-5x-x-18x\right)+\left(-7-5+12\right)\)
\(=5x^2-5x\)
\(E=\left(2-x\right)\left(1+2x\right)+\left(1+x\right)-\left(x^4+x^3-5x^2-5\right)\)
\(=2+4x-x-2x^2+1+x-x^4-x^3+5x^2+5\)
\(=-x^4-x^3+3x^2+4x+8\)
\(G=\left(x^2-7\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-14\right)+x\left(x^2-2x-22\right)+35\)
\(=x^3+2x^2-7x-14-\left(2x^2-28x-x+14\right)+x^3-2x^2-22x+35\)
\(=2x^3-29x+21-2x^2+29x-14\)
\(=2x^3-2x^2+7\)
\(D=\left(3x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(x+5\right)-6\left(3x-2\right)\)
\(=6x^2+21x-2x-7-\left(x^2+6x+5\right)-18x+12\)
\(=6x^2+x+12-x^2-6x-5=5x^2-5x+7\)

Gọi số lần xuất hiện mặt 4 chấm;5 chấm;6 chấm lần lượt là a(lần),b(lần),c(lần)
(Điều kiện: \(a,b,c\in Z^+\))
Số lần xuất hiện mặt 4 chấm bằng 2/3 lần số lần xuất hiện mặt 5 chấm
=>\(\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{b}{3}\)
Số lần xuất hiện mặt 5 chấm bằng 60% số lần xuất hiện mặt 6 chấm
=>\(\dfrac{b}{3}=\dfrac{c}{5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{b}{3}=\dfrac{c}{5}\)
Tổng số lần xuất hiện mặt 4 chấm;5 chấm; 6 chấm là:
a+b+c=100-15-17-18=50
Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{b}{3}=\dfrac{c}{5}=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2+3+5}=\dfrac{50}{10}=5\)
=>\(a=2\cdot5=10;b=3\cdot5=15;c=5\cdot5=25\)
Do đó: số lần xuất hiện mặt 4 chấm;5 chấm;6 chấm lần lượt là 10 lần; 15 lần; 25 lần
Số lần số chấm xuất hiện là số lẻ là:
15+15+18=48(lần)
=>Xác suất thực nghiệm là \(\dfrac{48}{100}=\dfrac{12}{25}\)

Ta có:
Q(x) = x² + 4x + 9
= x² + 2x + 2x + 4 + 5
= (x² + 2x) + (2x + 4) + 5
= x(x + 2) + 2(x + 2) + 5
= (x + 2)(x + 2) + 5
= (x + 2)² + 5
Do (x + 2)² ≥ 0 với mọi x ∈ R
⇒ (x + 2)² + 5 > 0 với mọi x ∈ R
Vậy Q(x) vô nghiệm

Do 1 > 0
\(\left|x\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow1+\left|x\right|>0\)
Do đó \(1+\left|x\right|=-2\) là điều vô lý
\(\Rightarrow\) Không tìm được \(x\) trong trường hợp này
Vậy bài của em là sai

a. M(x) = x² + 2x – 3 + x² - 9x + 5
= 2x2 - 7x + 2
N(x) = x² + 2x – 3 - x² + 9x - 5
= 11x - 8

Đặt \(\dfrac{a}{b}=\dfrac{b}{c}=\dfrac{c}{d}=\dfrac{d}{a}=k\)(k<>0)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}d=a\cdot k\\c=d\cdot k=a\cdot k\cdot k=ak^2\\b=ck=ak^3\\a=bk=ak^4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a=ak^4\)
=>\(ak^4-a=0\)
=>\(a\left(k^4-1\right)=0\)
=>\(k^4-1=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}k=1\\k=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(M=\dfrac{3a+b}{5b-d}+\dfrac{2b+3c}{2d-b}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\cdot ak^4+ak^3}{5\cdot ak^3-ak}+\dfrac{2\cdot ak^3+3\cdot ak^2}{2\cdot ak-ak^3}\)
\(=\dfrac{ak^3\left(3k+1\right)}{ak\left(5k^2-1\right)}+\dfrac{ak^2\left(2k+3\right)}{ak\left(2-k^2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{k^2\left(3k+1\right)}{5k^2-1}+\dfrac{k\left(2k+3\right)}{2-k^2}\)
TH1: k=1
=>\(M=\dfrac{1^2\left(3\cdot1+1\right)}{5\cdot1^2-1}+\dfrac{1\left(2\cdot1+3\right)}{2-1^2}=\dfrac{4}{4}+\dfrac{5}{1}=6\)
TH2: k=-1
=>\(M=\dfrac{\left(-1\right)^2\cdot\left(-3+1\right)}{5\cdot\left(-1\right)^2-1}+\dfrac{\left(-1\right)\left(2\cdot\left(-1\right)+3\right)}{2-\left(-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2}{4}+\dfrac{1}{1}=-\dfrac{1}{2}+1=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
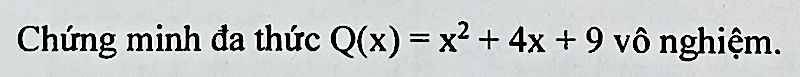
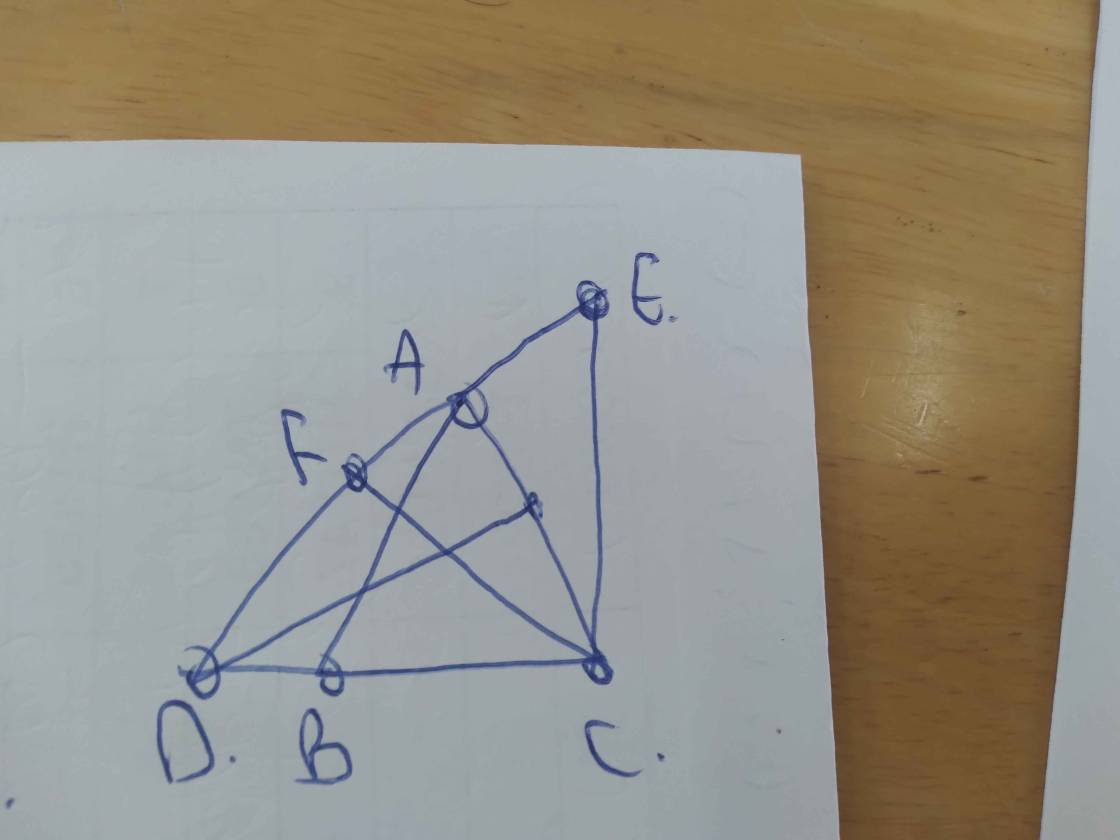
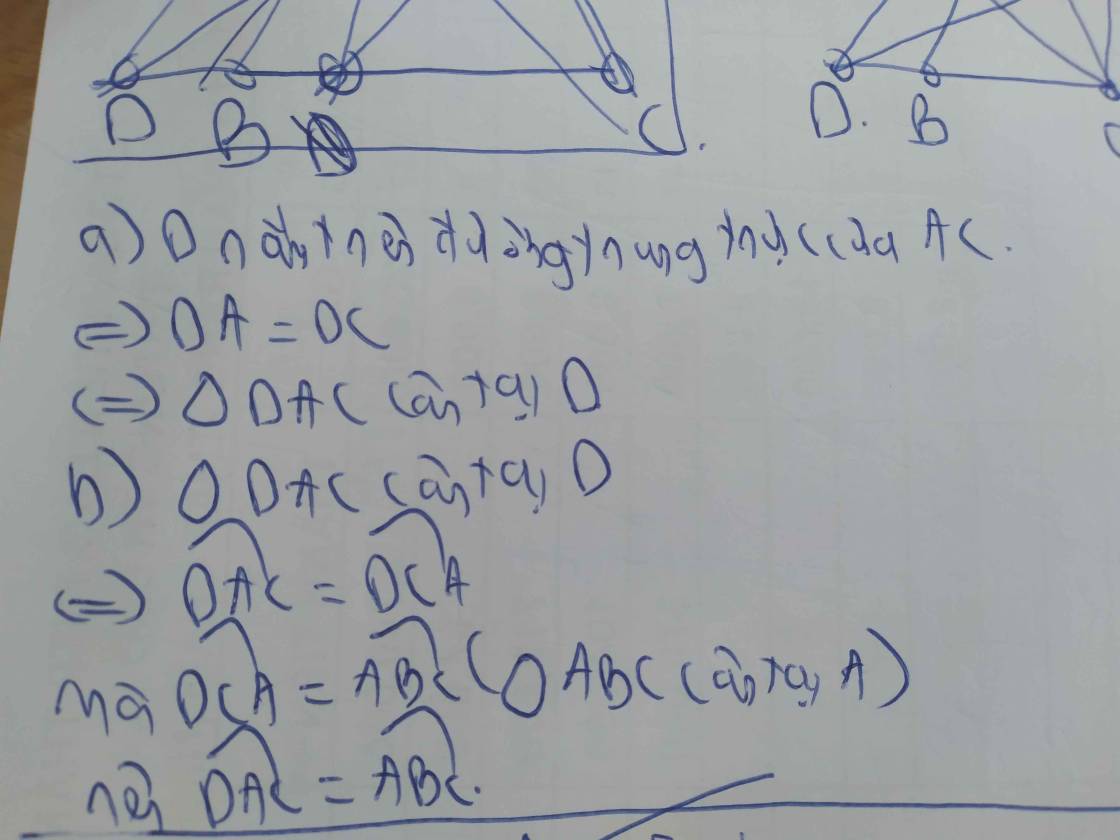


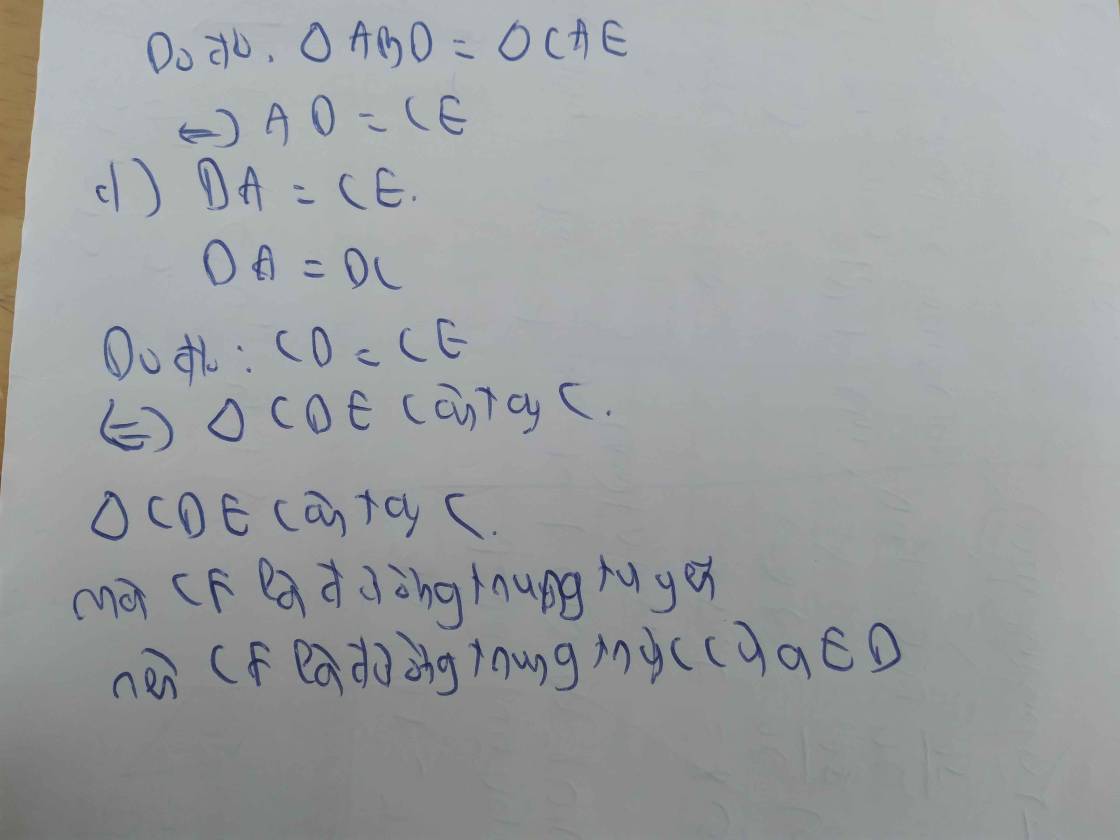
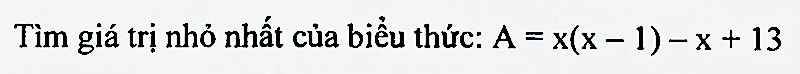
Hình đâu vậy bạn?