Câu 13. (1 điểm) Cho $x, \, y, \, z\ne 0$ thoả mãn $x+y+z=0$. Tính giá trị của biểu thức $A=\dfrac{xy}{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-{{z}^{2}}}+\dfrac{yz}{{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{zx}{{{z}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}$.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
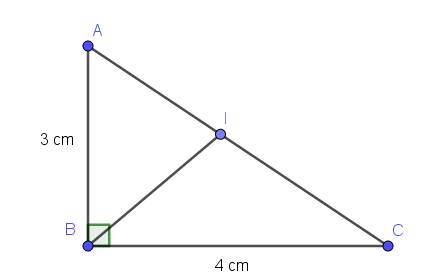
Áp dụng định lý Pitago: $AC=\sqrt{AB^2+BC^2}=\sqrt{3^2+4^2}=5$ (cm)
Áp dụng tính chất tia phân giác:
$\frac{IA}{IC}=\frac{AB}{BC}=\frac{3}{4}$
Mà $IA+IC=AC=5$
$\Rightarrow IA=5:(3+4).3=\frac{15}{7}; IC=5:(3+4).4=\frac{20}{7}$ (cm)

(2x+3)2-(2x+5)2
= 4x2+12x+32-4x2+20x+52
=12x+9-12x-8x-25
=9-8x-25
=(-16)-8x

Lời giải:
$(2x+3)^2+(2x+5)^2=4x^2+12x+9+4x^2+20x+25$
$=8x^2+32x+34$



câu a, \(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\); \(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}\); \(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\) (đk \(x\)≠ -1; 1)
\(x^2\) - 1 = ( \(x\) - 1).(\(x\) + 1)
\(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right).\left(x-1\right)}\);
\(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}\) = \(\dfrac{-x^2}{x-1}\)= \(\dfrac{-x^2.\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
b, \(\dfrac{10}{x+2}\); \(\dfrac{5}{2x-4}\); \(\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\) (đk \(x\) ≠ -2; 2)
2\(x-4\) = 2.(\(x\) - 2); 6 - 3\(x\) = - 3.(\(x\) - 2)
\(\dfrac{10}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{10.2.3\left(x-2\right)}{2.3\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{60\left(x-2\right)}{6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{2x-4}\) = \(\dfrac{5.3\left(x+2\right)}{2.3\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{15.\left(x+2\right)}{6.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{3.\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-1.\left(x+2\right)}{3.2.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-2.\left(x+2\right)}{6.\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\)
c, \(\dfrac{x}{2x-4}\); \(\dfrac{1}{2x+4}\) và \(\dfrac{3}{4-x^2}\) đk \(x\) ≠ 2; -2
\(\dfrac{x}{2x-4}\) = \(\dfrac{x}{2.\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x+2\right)}{2.\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2x+4}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2.\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{2.\left(x+2\right).\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4-x^2}\) = \(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-6}{2.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)

Lời giải:
a. ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{\begin{matrix}
3x\neq 0\\
x+1\neq 0\\
2-4x\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
x\neq 0\\
x\neq -1\\
x\neq \frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
\(P=\left[\frac{(x+2)(x+1)+3x.2}{3x(x+1)}-3\right].\frac{x+1}{2(1-2x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{x^2+3x+2+6x-9x(x+1)}{3x(x+1)}.\frac{x+1}{2(1-2x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{-8x^2+2}{3x(x+1)}.\frac{x+1}{2(1-2x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{-2(2x-1)(2x+1)(x+1)}{6x(x+1)(1-2x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{1+2x}{3x}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{x^2-x}{3x}=\frac{x-1}{3}\)
Tại $x=2023$ thì:
$P=\frac{2023-1}{3}=\frac{2022}{3}=674$
c.
Để $P$ nguyên thì $x-1\vdots 3$
$\Rightarrow x=3k+1$ với $k$ nguyên bất kỳ.
Kết hợp với ĐKXĐ thì $x=3k+1$ với $k\in\mathbb{Z}$

\(B=\dfrac{2x+y}{2x^2-xy}+\dfrac{8y}{y^2-4x^2}+\dfrac{2x-y}{2x^2+xy}\left(x\ne0;y\ne\pm2x\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+y}{x\left(2x-y\right)}-\dfrac{8y}{4x^2-y^2}+\dfrac{2x-y}{x\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2x+y\right)^2}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}-\dfrac{8xy}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2x-y\right)^2}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2+4xy+y^2-8xy+4x^2-4xy+y^2}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{8x^2-8xy+2y^2}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(4x^2-4xy+y^2\right)}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(2x-y\right)^2}{x\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(2x-y\right)}{x\left(2x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x-2y}{2x^2+xy}\)
Với \(x\ne0;y\ne\pm2x\), xét: \(x=\dfrac{1}{2};y=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(tmdk\right)\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2};y=-\dfrac{3}{2}\) vào \(B\), ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{4\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}-2\cdot\dfrac{-3}{2}}{2\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{-3}{2}}=\dfrac{5}{-\dfrac{1}{4}}=-20\)
\(Toru\)
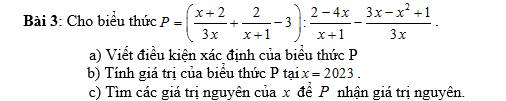
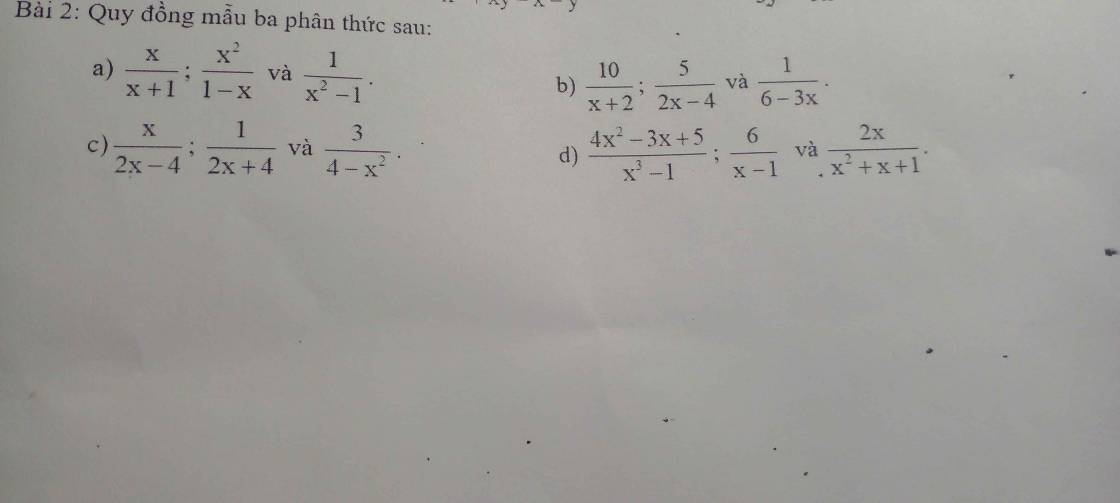
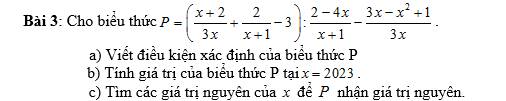
 help!
help!