Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(2MCl_n\rightarrow2M+nCl_2\)
Ta có :
\(n_{Cl2}=\frac{1,68}{22,4}=0,075\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_M=\frac{0,075.2}{n}=\frac{0,15}{n}\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow M_M=\frac{5,85}{\frac{0,15}{n}}=39n\left(\frac{g}{mol}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n=1\Rightarrow M_M=39\left(\frac{g}{mol}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow M:Kali\left(K\right)\)
Vậy CTHH của muối là KCl
\(2MCl-->2M+Cl2\)
\(n_{C_{ }l2}=\frac{1,68}{22,4}=0,075\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_M=2n_{Cl2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_M=\frac{5,85}{0,15}=39\left(K\right)\)
Vậy M là Kali

Đáp án B
nkhí = 0,02 (mol)
2MCln → 2M + nCl2
0,04/n ← 0,02 (mol)
Mmuối = ![]() = 55,5n
= 55,5n
Với n = 2 => M = 40 (Ca)

Đáp án C
nkhí = 0,25 (mol)
2MCln → 2M + nCl2
0,5/n ← 0,25 (mol)
MM = ![]() = 32n
= 32n
Với n = 2 => M = 64 (Cu)

1)
CTHH MXn
\(n_{X_2}=\dfrac{0,896}{22,4}=0,04\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(n_{MX_n}=\dfrac{0,08}{n}\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(n_{AgX}=0,08\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(M_{AgX}=\dfrac{11,48}{0,08}=143,5\left(g/mol\right)\) => MX = 35,5 (g/mol)
=> X là Cl
2)
\(n_{MCl_n}=\dfrac{0,08}{n}\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_M=\dfrac{0,96}{M_M}\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(\dfrac{0,08}{n}=\dfrac{0,96}{M_M}\)
=> MM = 12n (g/mol)
Xét n = 1 => Loại
Xét n = 2 => MM = 24 (g/mol) => M là Mg
Xét n = 3 => Loại
Vậy M là Mg
M' có hóa trị II
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{4,162-0,96-2,242}{32}=0,03\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: 2Mg + O2 --to--> 2MgO
0,04-->0,02------>0,04
2M' + O2 --to--> 2M'O
0,02<-0,01------>0,02
=> MM' = \(\dfrac{2,242}{0,02}=112\left(g/mol\right)\)
a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\%n_M=\dfrac{0,04}{0,04+0,02}.100\%=66,67\%\\\%n_{M^{\cdot}}=100\%-66,67\%=33,33\%\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\dfrac{M_M}{M_{M^{\cdot}}}=\dfrac{24}{112}=\dfrac{3}{14}\)
c) \(n_O=0,06\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(n_{H_2O}=0,06\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(n_{H_2SO_4}=0,06\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(C_{M\left(H_2SO_4\right)}=\dfrac{0,06}{0,5}=0,12M\)


mik đã giải chi tiết lắm rồi nếu ko hiểu bn hỏi lại nhé !
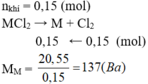
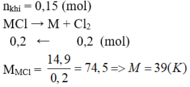
Để xác định công thức phân tử của muối clorua kim loại hoá trị 1, ta cần làm các bước sau:
1. Tính số mol kim loại thu được ở catot
\(n_{\text{kim}\&\text{nbsp};\text{lo}ạ\text{i}} = \frac{\text{kh} \overset{ˊ}{\hat{\text{o}}} \text{i}\&\text{nbsp};\text{l}ượ\text{ng}\&\text{nbsp};\text{kim}\&\text{nbsp};\text{lo}ạ\text{i}}{\text{kh} \overset{ˊ}{\hat{\text{o}}} \text{i}\&\text{nbsp};\text{l}ượ\text{ng}\&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\&\text{nbsp};\text{c}ủ\text{a}\&\text{nbsp};\text{kim}\&\text{nbsp};\text{lo}ạ\text{i}} = \frac{6 , 24}{M}\)
2. Tính số mol khí clor (Cl₂) thu được ở anot
Vậy số mol khí Cl₂ là:
\(n_{\text{Cl}_{2}} = \frac{1 , 9832}{22 , 4} = 0 , 0885 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)
Mỗi phân tử Cl₂ tương ứng với 2 electron, do đó số mol electron tham gia quá trình điện phân là:
\(n_{\text{electron}} = 2 \times n_{\text{Cl}_{2}} = 2 \times 0 , 0885 = 0 , 177 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)
3. Liên hệ giữa số mol electron và số mol kim loại
\(n_{\text{kim}\&\text{nbsp};\text{lo}ạ\text{i}} = n_{\text{electron}} = 0 , 177 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)
Do đó, khối lượng mol của kim loại là:
\(M = \frac{6 , 24}{0 , 177} \approx 35 , 3 \&\text{nbsp};\text{g}/\text{mol}\)
4. Xác định kim loại
Như vậy, kim loại này là Na.
5. Xác định công thức muối
Kết luận:
Công thức phân tử của muối clorua kim loại là NaCl.