
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




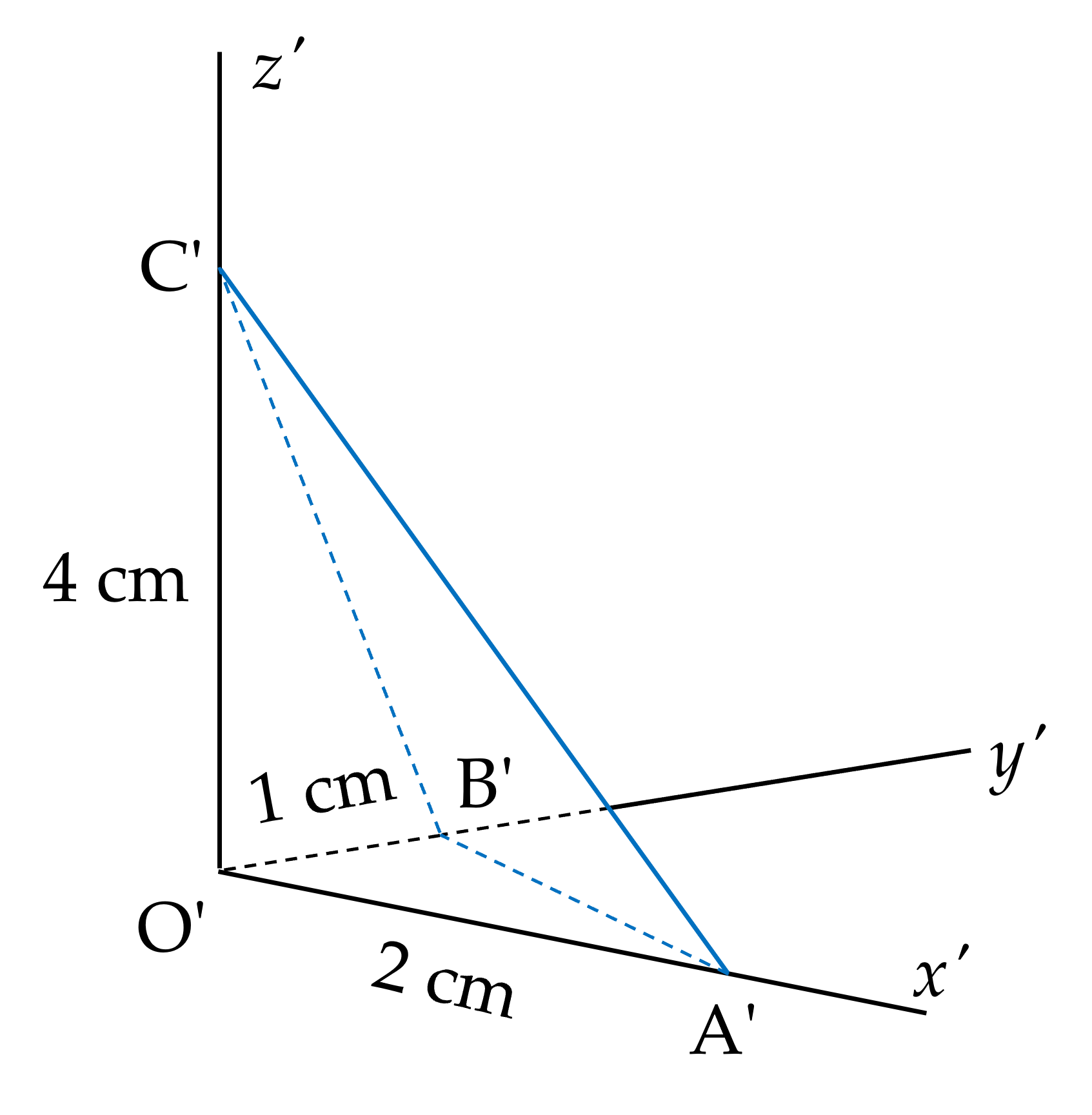
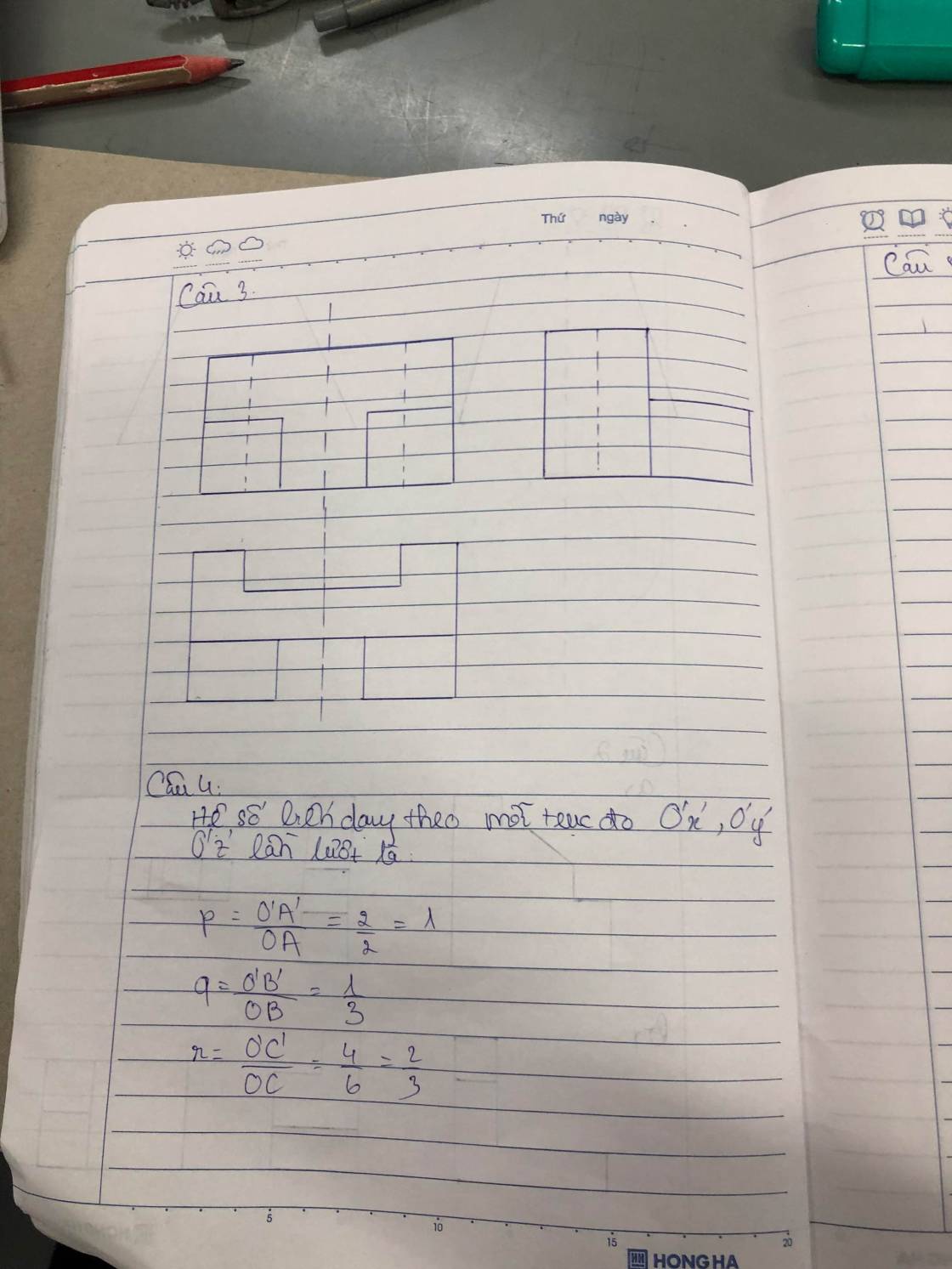
Hệ số biến dạng theo mỗi trục đo O'x', O'y', O'z' lần lượt là:
p=O'A'OA=22=1�=�'�'��=22=1;
q=O'B'OB=13�=�'�'��=13;
r=O'C'OC=46=23�=�'�'��=46=23.

a)

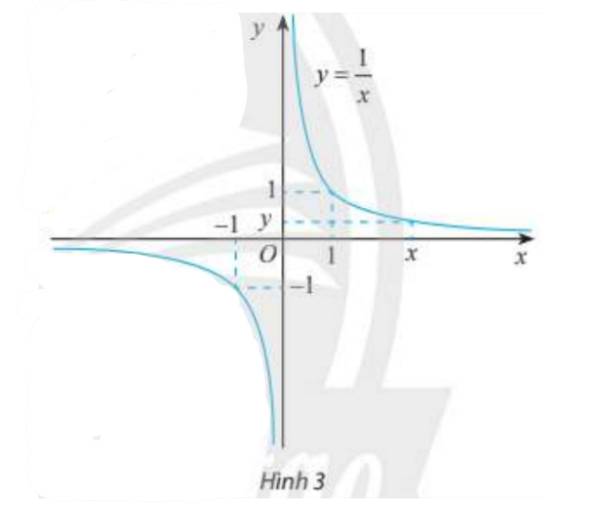
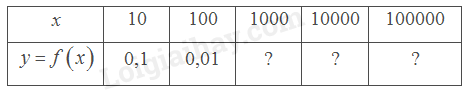
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng lớn (dần tới \( + \infty \)).
b)
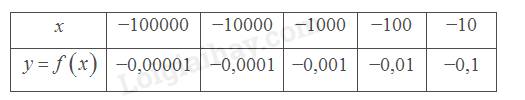
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng bé (dần tới \( - \infty \)).


1.
\(u_{n+1}=4u_n+3.4^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_{n+1}-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(n+1\right).4^{n+1}=4\left[u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n\right]\)
Đặt \(u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n=v_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}v_1=2-\dfrac{3}{4}.4=-1\\v_{n+1}=4v_n\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow v_n=-1.4^{n-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow u_n=\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n-4^{n-1}=\left(3n-1\right)4^{n-1}\)
2.
\(a_n=\dfrac{a_{n-1}}{2n.a_{n-1}+1}\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=2n+\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}-\left(n-1\right)^2-\left(n-1\right)\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=b_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b_1=2-1-1=0\\b_n=b_{n-1}=...=b_1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=n^2+n\Rightarrow a_n=\dfrac{1}{n^2+n}\)

ĐKXĐ: \(-2\le x\le3\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x+2}+2\sqrt{3-x}=a\Rightarrow4\sqrt{6+x-x^2}-3x=a^2-14\)
Mặt khác \(a^2=\left(\sqrt{x+2}+2\sqrt{3-x}\right)^2\le5\left(x+2+3-x\right)=25\)
\(\Rightarrow a\le5\)
Và \(\sqrt{x+2}+\sqrt{3-x}+\sqrt{3-x}\ge\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{3-x}\ge\sqrt{5}\) \(\Rightarrow a\ge\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{5}\le a\le5\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(a^2-14=ma\Leftrightarrow\frac{a^2-14}{a}=m\) với \(a\in\left[\sqrt{5};5\right]\)
\(f\left(a\right)=\frac{a^2-14}{a}\Rightarrow f'\left(a\right)=\frac{2a^2-a^2+14}{a^2}=\frac{a^2+14}{a^2}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)\) đồng biến \(\Rightarrow f\left(\sqrt{5}\right)\le f\left(a\right)\le5\)
\(\Rightarrow-\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}\le f\left(a\right)\le\frac{11}{5}\Rightarrow-\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}\le m\le\frac{11}{5}\)

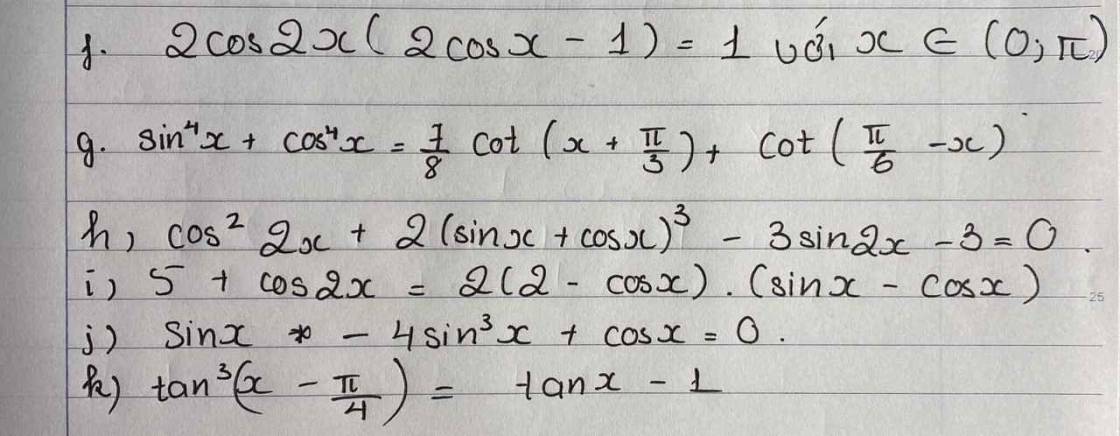
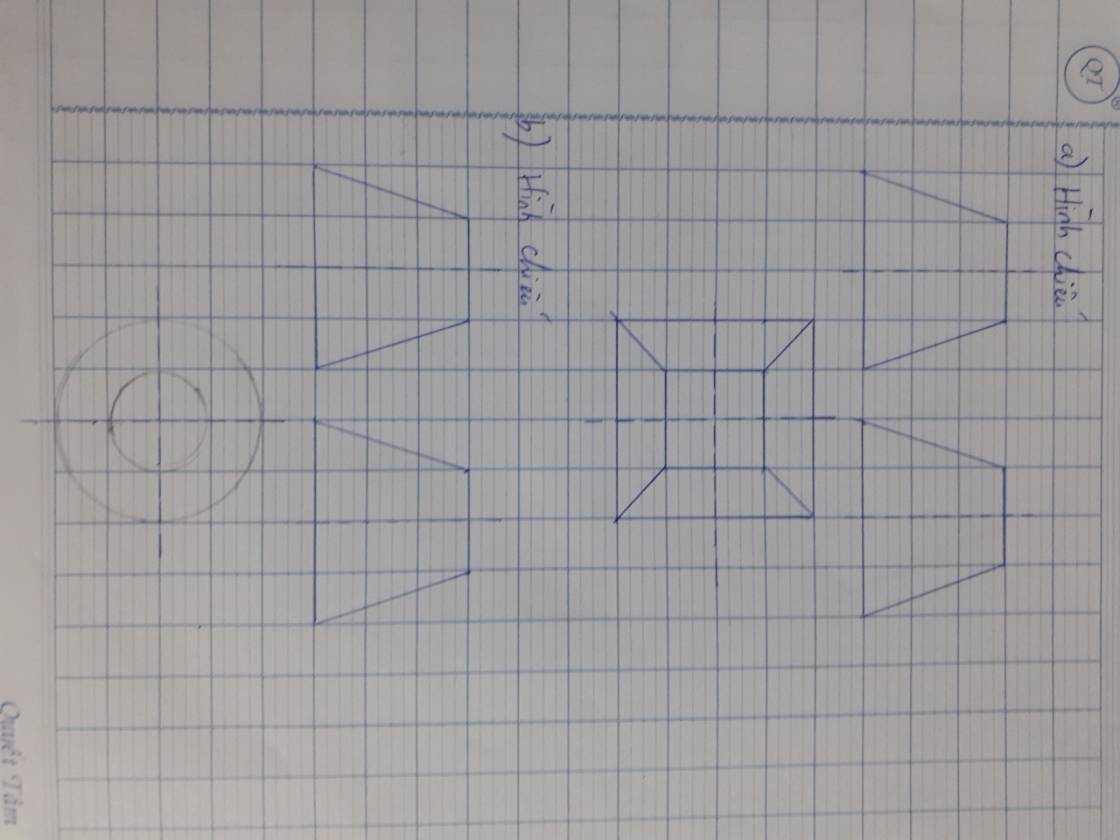
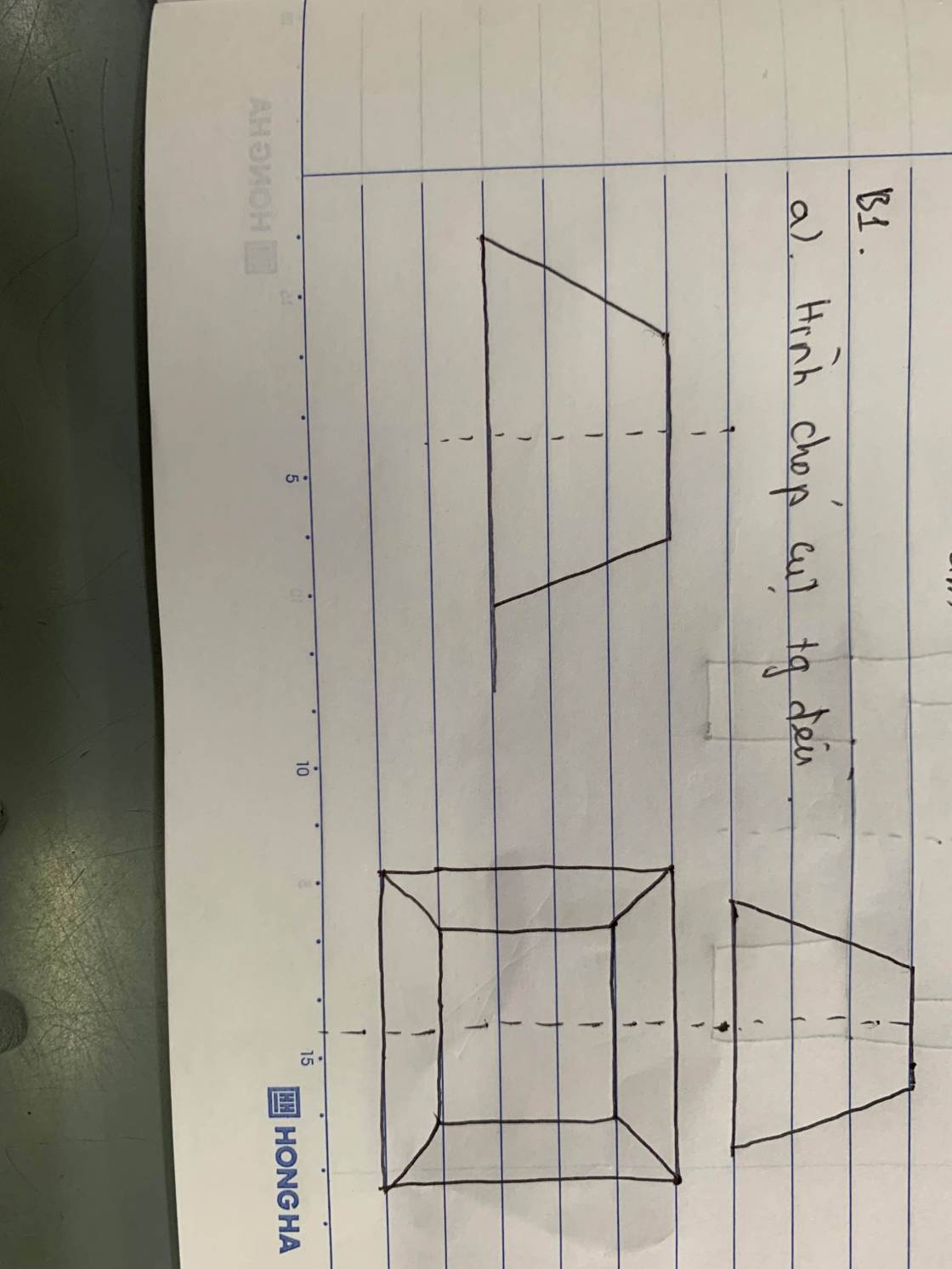
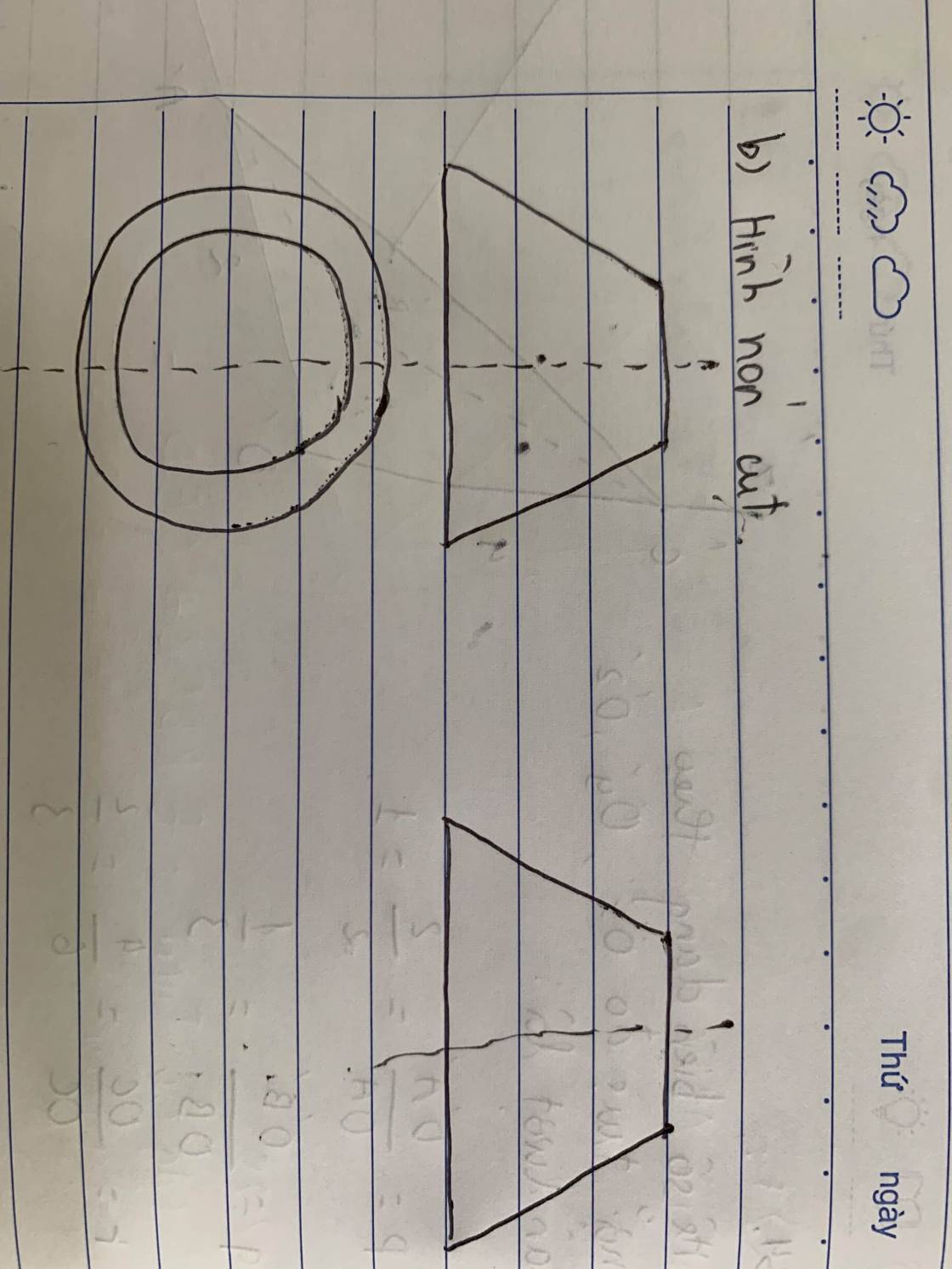
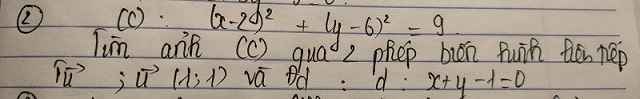



Đặt \(\left(\dfrac{x}{4};\dfrac{y}{2};z\right)=\left(a;b;c\right)\Rightarrow a;b;c\ge0\)
Từ giả thiết \(\Rightarrow16^a+16^b+16^c=34\)
Do \(a;b;c\ge0\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}16^a\ge1\\16^b\ge1\\16^c\ge1\\16^{a+b}\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(16^a-1\right)\left(16^b-1\right)+\left(16^{a+b}-1\right)\left(16^c-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16^{a+b}-16^a-16^b+1+16^{a+b+c}-16^{a+b}-16^c+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16^{a+b+c}\ge16^a+16^b+16^c-2=32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a+b+c\ge log_{16}32=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(P_{min}=\dfrac{5}{4}\) khi \(\left(a;b;c\right)=\left(0;0;\dfrac{5}{4}\right)\) và hoán vị
Đặt (𝑥4;𝑦2;𝑧)=(𝑎;𝑏;𝑐)⇒𝑎;𝑏;𝑐≥0(4x;2y;z)=(a;b;c)⇒a;b;c≥0
Từ giả thiết ⇒16𝑎+16𝑏+16𝑐=34⇒16a+16b+16c=34
Do 𝑎;𝑏;𝑐≥0⇒{16𝑎≥116𝑏≥116𝑐≥116𝑎+𝑏≥1a;b;c≥0⇒⎩⎨⎧16a≥116b≥116c≥116a+b≥1
⇒(16𝑎−1)(16𝑏−1)+(16𝑎+𝑏−1)(16𝑐−1)≥0⇒(16a−1)(16b−1)+(16a+b−1)(16c−1)≥0
⇔16𝑎+𝑏−16𝑎−16𝑏+1+16𝑎+𝑏+𝑐−16𝑎+𝑏−16𝑐+1≥0⇔16a+b−16a−16b+1+16a+b+c−16a+b−16c+1≥0
⇔16𝑎+𝑏+𝑐≥16𝑎+16𝑏+16𝑐−2=32⇔16a+b+c≥16a+16b+16c−2=32
⇔𝑎+𝑏+𝑐≥𝑙𝑜𝑔1632=54⇔a+b+c≥log1632=45
𝑃𝑚𝑖𝑛=54Pmin=45 khi (𝑎;𝑏;𝑐)=(0;0;54)(a;b;c)=(0;0;45) và hoán vị